Category: Enterprise Mobility
Mobility is booming. The number of mobile users worldwide touched 4.43 billion in 2015, and the figure is expected to reach 5.07 billion by 2019.
The rise of mobility has corresponded with a surge in demand and acceptance of mobile apps. However, expecting a free ride by conjuring up a namesake app is asking for trouble.
Enterprises have no option these days but to roll out mobile apps for the convenience of their internal users and employees, but success demands such apps be of high quality and have a high degree of user adoption. Here are some tips in the direction.
1. Get the Basics Right
When it comes to mobile apps, the first degree of association is with a responsive design, where the format adjusts automatically, to suit the highly fragmented screen size of mobile devices. However, responsive design is now the basic requirement, as is effective planning on the scope of the app, and creating a prototype.
It requires much more effort that such basics to build a successful mobile app.
2. Never Compromise on the UX
The best apps are well designed, both in terms of visuals and the user experience (UX).
Never underestimate the power of simplicity. A simple, neat and clean interface best suits most mobile devices, with its small form factors. Simplicity is not just in the design, but also in the feature list. Make sure to eliminate any unnecessary feature, and make everything clearly visible. Even subtle changes in design make a big difference in usability.
The best UX design is also relative to the platform. Each platform has a native way of screen layouts, displaying information, and navigation. For instance, iOS tabs have a built-in NavigationController, facilitating multiple levels of navigation inside each tab. Android tabs, on the other hand, are shallow, and have no in-tab navigation. Trying to implement iOS-like functionality in Android, such as in-tab navigation leads to confusion, and is counterintuitive.
3. Focus on a Specific Function
The biggest mistake related to mobile apps is considering the app as a micro version of the website. The most successful apps cater to a specific function or niche. It solves a specific problem or does a limited number of things, but enables doing it well. For instance, a field service app makes the life of a field service technician easier, by allowing her to download the relevant inspection forms, access information related to the plant she is visiting, and connect with external help for real-time troubleshooting. Saddling the app with unnecessary features such as customer care, sales reports and more would only serve to make the app bloated, harder to use, and counter-intuitive.
At the same time, make sure every single enterprise app is part of a wider mobile strategy, and as an opportunity to engage with customers, be it external customers or internal customers, in a better way. Spend time on the purpose of the app, making sure it serves a specific purpose that is needed in the first place. Also, make sure each app is a vital spoke, and all apps added together to complete the comprehensive whole in organizational functionality.
4. Leverage the Features of the Mobile
Unlike websites, a mobile app has the capability to push information to users, leveraging geolocation services to offer improved services, adjust to slow data speeds and overall offer a dynamic and proactive experience for users. Such options unlock new possibilities and go a long way in ensuring the success of the mobile app. Effective Planning is critical in adding such rich functionality to make apps more useful.
5. Get the Development Right
Many a time, apps are rushed into the market, without adequate testing, since the app would be needed desperately. An imperfect or half-baked app is more likely to do more harm than good, by impeding productivity. Follow agile development procedures to develop the app well first time round.
Make sure to test often. Discovering the font positions are off, or the app simply crashing on loading, after spending weeks on development, is a recipe for disaster. Very often the solution at such an advanced stage of development would be ineffective quick-fixes which will lead to the failure of the app. Frequent testing enables identifying the problem and affecting a fix immediately before discovery or fix becomes too difficult.
The coder, the tester, and all other stakeholders connected with the app development process would do well to consider themselves as end users, and see how the apps pan out when using it. It is also a good idea to involve the actual end user in the development process.
6. Enable Platform-Agnostic Development
Android is now the dominant platform with over 50% market share in most markets. The iPhone is popular for enterprise users as well. BYOD, which is prevalent in many enterprises make the mobile screen hopelessly fragmented though, with varying screen size and OS variants. In such a state of affairs, trying to optimize for specific platforms is asking for trouble. The best practice in cross-platform development is to build the code completely abstracted, as if it is a local web service. Make programming modules platform-agnostic by making programming logic independent from the screens and platform in which it will run. Such an approach will also enable code reuse, accelerating the code development process. With the logic decoupled from the platform, only the user interface code need to be built separately for each platform.
The best practice in cross-platform development is to build the code completely abstracted, as if it is a local web service. Make programming modules platform-agnostic by making programming logic independent from the screens and platform in which it will run. Such an approach will also enable code reuse, accelerating the code development process. With the logic decoupled from the platform, only the user interface code need to be built separately for each platform.
7. Track the App Effectively
An app development project is not one-off but a continuous process of evolution. Use tools to track whatever is happening inside the apps, such as what users click and use, traffic sources, and other parameters, to fine tune the app during the next release. Use the first batch of users to test metrics and understand the real value of each user, before continuing with more systematic campaigns.
The mobile space is highly fragmented, and it requires a high degree of expertise to roll out successful apps. A successful app invariably involves a great deal of experimentation and trial-and-error. Partnering with us would allow you to gain from our experience and expertise in developing hundreds of highly successful enterprise apps, cutting across industries. We have done the hard grind, understanding what works and what does not work. When you partner with us, you get things done easily without having to go through the painful trial and error yourself.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
More and more enterprises seek to ride the mobility wave towards improving their efficiency and becoming more competitive. Gartner estimates enterprise app demand to grow about five times faster compared to the internal capacity of IT organizations, by 2017. Today’s digital employee use an average of three different devices in their daily routine, and with the spread of IoT and wearable devices, this number is set to increase to five or six devices a day. Mobile phone sales are expected to touch 2.1 billion units by 2019, fueling demand for enterprise apps.
Enterprises find it a challenge to develop, deploy and maintain mobile apps to match the ever increasing demand, leave alone being proactive to preempt competition.
An earlier Gartner survey on mobile app development, conducted in 2014, reveals a majority of organizations have developed fewer than 10 apps, with a good majority of them not having released any mobile apps at all.
Many enterprises grossly underestimate the time and resources required for developing mobile apps, especially the time taken for integration. They find the coding part especially vexatious and arduous. Moreover, hiring developers with good mobile skills is becoming progressively difficult and costly.
Rapid Mobile Application Development Approaches

Enterprises need to develop mobile apps, and develop it fast, to keep pace with the enterprise app demand. They need to use development tools capable of producing apps rapidly, to reduce the gap between demand and supply.
Solutions are in sight though. Significant innovation, mostly through powerful Rapid Mobile Application Development (RMAD) tools is fast replacing native development tools and traditional coding approaches.
RMAD is generally implemented through an effective two-pronged bimodal approach. The first mode involves the creation of stable infrastructure and APIs that enable apps to retrieve and deliver data to back-end systems seamlessly, without disrupting enterprise applications. The second prong involves the deployment of agile approaches to quickly deliver front-end app features required by the business.
The RMAD approach generally starts with requirement gathering through workshops or focus groups, prototyping an early iterative model using no-code or low-code platform, end users testing the design, and reusing software components to the extent possible during the main development phase. Visual development tools like MDD further facilitate iterative, rapid, and collaborative design, with developers able to share prototypes, gather feedback, and refine the requirements.
Several Rapid Mobile Application Development (RMAD) approaches, such as drag-and-drop code-less tools, automated code generation, model-driven development, virtualization, construction of forms, and other methods allow people with little or no coding skills, especially business managers and those with business facing roles to develop applications on-the-fly, and iterate on these designs.
Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
 Several low code app development platforms enable rolling out apps in double-quick time. Some of the most popular ones are Appian Quick Apps, Xamarin, Zoho Creator, Microsoft Power Apps, Salesforce Lightning, and others, each offering various levels of low code options, and each having varied levels of effectiveness and popularity.
Several low code app development platforms enable rolling out apps in double-quick time. Some of the most popular ones are Appian Quick Apps, Xamarin, Zoho Creator, Microsoft Power Apps, Salesforce Lightning, and others, each offering various levels of low code options, and each having varied levels of effectiveness and popularity.
Such low-code and no-code platforms do away with the need to code by offering declarative development options such as drag-and-drop visual interfaces, point-and-click tools, object mapping, process modeling, form builders, WYSIWYG editors, and other options. Even the few lines of code involve standard languages commonly in use, such as JavaScript, SQL, CSS, and more. These languages are familiar to anyone who has a decent level of education in IT.
Most of these platforms enable creating an app quickly and then layering customization and added features on top of it. Using these options, enterprise users may develop their own apps without writing a line of code, or keeping code to a minimum, for any optional customization.
Such declarative development options are popular in several areas of application development, such as
- Logic, criteria, and filtering
- User interface
- Reports and Data Visualizations
- App roles and authentication
- Data import and export rules
- Integration with other apps and systems
The best low-code platform offers step-by-step workflows for most application authoring processes. Point-and-click tools, for instance, guide the user through each step of the process, enabling keeping things in context. Other tools may enable connecting the application with an internal corporate directory such as Microsoft Active Directory, to facilitate single sign-on integration.
Low code platforms also come with much integration in-built as well. A common and very popular integration is online data storage services such as Dropbox, Microsoft OneDrive, Google Drive, and more.
Low code platforms offer various approaches, with the space rife for innovations. A model-driven development (MDD) approach, for instance, uses visual models for defining data models, application and process logic, user interfaces, and other elements.
Limitations of DIY App Development Platforms
Codeless development brings IT the business together, facilitating more rapid, iterative, flexible, and collaborative development. However, it still pays to enlist the services of a professional enterprise app development company. Low-code platforms, for all the ease and automation it offers, do not eliminate the need for programming completely, and no-code platforms still have several inherent limitations for enterprise use. For instance, these options are specifically weak on integration and user interface, especially mobile UI.
DIY app development platforms are definitely worth a try if these are your baby steps towards the app development world, and your app does not handle critical tasks. However, if you are remaking an app, and wants it to handle mission critical functions, or is customer facing, it may not be worth the risk to go for DIY. Due to limited options available, you will have to either adjust the app according to what is available or seek a real developer’s help to add the extra functions that are not available within the platform.
If you don’t want to take a chance in your enterprise application development, partner with established custom software development companies such as ours, to be assured of a complete web application, with custom layout, ability to access servers on the device, pixel-perfect displays, and much more. You gain from our experience and expertise spanning across several projects, cutting across industries and sectors.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Mobiles have become all pervasive. Today’s customers and enterprise users alike prefer these devices as the medium of choice. Businesses are increasingly realizing the need to deliver mobile apps and solutions to power their business. However, certain mobile app myths inhibit businesses from leveraging the full potential of mobility to drive growth.
Myth 1: Developing enterprise apps is a long drawn out process
Conventional methods of development are indeed time-consuming. As a rule of thumb, it would take about six months before a new app hits the app store. Multiply the figure by the number of apps required for the business, and an app strategy becomes a non-starter even before it is conceptualized.
However, newer and innovative methods facilitate rapid development and deployment, dispelling the common app development myth of long drawn out process. In fact, using ready-made solutions that require no coding, it is even possible to roll out highly intuitive apps within a few hours or even less! Code-reuse, backend services that speed up integration and other developments also contribute to accelerated development.
The latest cross-platform development approach further reduces development time. Forrester estimates app developers using as much as ten different coding languages, such as JavaScript, HTML5, Objective C, C#, Node.js and more, making the task a complex and resource-intensive one. Newer app platforms, with a “bring your own toolkit” approach allow the use of any coding languages as the developer fancies, reducing the learning curve greatly. Platforms such as Xamarin greatly speed up development by requiring coding of key parts of the application just once and reusing the code across different platforms.
Ready to use cloud-based solutions, for hosting, testing, and other key functions make life still easier for the developer.
Myth 2. Mobile App Development is a One-off Project
One of the biggest app development myth is the development process being a one-off project. Launching an app is akin to starting a business. There is no end in sight, and one can never let their guard down. Just like cutting the ribbon is just the beginning, rolling out the app for users is just the start. Apps need to grow in response to changes in business requirements and changes in technology. If nothing else, the invariable bugs that crop out need to be addressed. A stagnant app will soon become obsolete.
A good approach to adopt is the minimum viable product (MVP) concept, by developing the core functionality, and adopting an iterative product development approach. It offers unbridled flexibility and makes it easier to make changes, as required.
Myth 3: More the function, better the app
A common mobile app myth is considering an app as a miniature version of the enterprise website, and packing in features into it, when the very concept of an app is to offer a specific and focused functionality to a targeted set of users. Apps trying to kill many birds with one stone are almost to a rule slow, difficult to control, bloated, and memory hogs.
High-quality graphics help, but enterprise users seek functionality and ease of getting their job done, over bells and whistles. A clearly defined success, usability (UX), simplicity and above all a clearly defined purpose are the crucial ingredients of success.
A related myth is business apps being data heavy, placing high loads on the device and backend systems. However, the reality is different. An average 4G smartphone is expected to use 5,114 MB per month in cellular data by 2017. The best mobile platforms take large amounts of data from the backend but transmit only a fraction of it to the handset, after filtering it as required. Intuitive developers limit the size of data transfer per app, to say 1 MB or less.
Myth 4: Mobile Applications Come Cheap
For some reason, many people equate mobile solutions with low costs and grossly underestimate the budget for delivering mobility solutions. While simple apps may be developed on the fly with minimal investment, development of highly functional apps requires a lot of effort. A simple UX and powerful features require a complicated backend. As a rule of thumb, more advanced the feature list, higher the cost.
Preparation of the concept, design of the architecture solution, the user interface design and graphics, testing, distribution of the app, user support, and training for end users, all require a sizable investment, more so for using the latest technologies that facilitate accelerated development.
Myth 5: Mobile Applications = Smartphones
Perhaps the biggest myth associated with mobile apps is equating apps with smartphones. While smartphone users are indeed the highest consumers of mobile apps, enterprise apps are equally useful for a host of other devices, including the quintessential tablets, handheld consoles, smart watches, smart glasses, sensor powered things, cars, appliances, and other post-modern devices, suiting a host of business purposes.
In all, mobile apps will be downloaded an estimated more than 248 billion times, and generate a revenue of more than $77 billion, by 2017.
Myth 6: Data Related Myths
Many enterprises, especially those having made large investments in enterprise resource planning (ERP) and other systems are hesitant to develop mobile apps that cannot plug in seamlessly into these existing technologies. Backend systems and APIs such as Sharepoint, MySQL, Oracle, and SAP may not necessarily be accessible through mobile. However, the emergence of enterprise-grade MBaaS (mobile backend as a service) solution with an API infrastructure solves most of these issues and enables mobiles devices to easily access legacy systems.
Myth 7. Mobile App Development Is About Writing Code
Developing a successful mobile app requires much more that coding. Knowledge of Android and iOS technologies is the basic requirement. The comprehensive application design, starting with the initial idea, and covering functionality design, user interface design, graphics requires good expertise, and preferably experience. There is also a need to keep abreast with the latest technology, react to new trends in double-quick time, adapt to latest hardware, and also cater to newer devices such as smart watches.
Each use case varies, resulting in the need for different development languages and toolkits, and requiring connectivity solution for different backend systems and data sources. In the mobile space, support across multiple versions of device operating systems also becomes critical. Cloud-based mobile application platforms make the developer’s life easy, though.
The average development project involves an average of 20 different stakeholders, such as business managers, project managers, developers, in-house IT representatives, employee or end user stakeholders, top management representative, and others. It requires a high level of collaboration to bring these stakeholders together, and ensure the development process takes place seamlessly.
Mobility is much more than developing apps. It requires a wider mobility strategy, and a concentrated effort to deliver cutting edge mobility solution. With our extensive experience cutting over several industries, and a rich talent pool, we are best poised to partner with you in rolling out high-quality mobile apps to further your business, leveraging the full potential of the mobile devices, while at the same time keeping expectations real, separating myth from reality.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Less than one in every four small business has a mobile app, now, but this figure is set to rise to 50% of all small businesses, by 2017. The simple explanation for the app boom is customers wanting to engage through mobile devices. While less than 10% of all internet traffic came from mobile devices three years ago, this figure is close to 70% at the end of 2016.
Customer preferences apart, there are several reasons why it makes sense to roll out business apps.
Improved Visibility and Enhanced Sales
As the adage goes, “Out of sight, out of mind.” This is truer than ever before today, as customers, faced with information glut from hyper-competitive marketers of all hues, have short attention spans. Inducing a customer to download an app is the sure-fire way of ensuring the business remains visible.
An average American spends more than two hours a day fiddling with smartphones. If nothing else, being “in the way” when such users unlock, scrolls, and search for the apps they want creates an unconscious bond with the brand.
The presence of an app on the customer’s smartphone also makes it that much easier for marketers to send in push notifications to the mobile. A mobile app is the digital equivalent of a blank billboard sign, with the customer a virtual captive audience. The marketer can make the app hip, stylish, functional, informative, or anything else, depending on what appeals to target customers more, and what drives engagement most.
The rule of “effective frequency” in advertising holds that hearing or seeing a brand about 20 times is what it takes to get truly noticed. The more often customers involved with the app, or simply recall the brand, the more they would be inclined to buy at the earliest opportunity.
Such improved visibility works. A case in point is 35.4% of last year’s Black Friday sales being completed on mobile devices, almost double the proportion of previous years.
Better Communication
Mobile apps facilitate a direct communication channel between stakeholders, be it between customers and marketers, between team members, between managers and staff, between channel partners and senior management, or anyone else. All relevant information passes directly to the app user’s customer’s fingertips, without having to wonder whether the message went through to the intended recipient.
With more and more customers now preferring self-service, mobile apps offers an effective medium to initiate the transaction. For instance, a customer may use the mobile app to reserve the table, or even place the order, before coming in. An employee may use the in-house HR app to apply for leave, or report being late to work due to an emergency, with the app doing all the follow up processing automatically.
A survey by Clutch survey found the following elements as most valuable to include in small business apps:
- Customer loyalty features, such as rewards and loyalty points
- Social networking updates
- Push notifications on latest news and offers
- Personalized interactions
Streamlined Internal Processes
A good mobile app improves sales and improves communications. However, the benefit of enterprise apps goes far beyond boosting engagement and increasing sales. Businesses are slowly but surely realizing the power of mobile apps in transforming internal processes.
Mobile apps streamline businesses processes, reducing paperwork, giving specific direction and framework to convoluted or vague processes, and accelerating the execution of tasks. For instance, a field service app offers a wealth of real time practical information to field service executives and quality inspectors, enabling them to schedule field visits dynamically and interactively, connect with the main office to get help on troubleshooting field equipment, get inspection forms auto-generated for the location, and also auto-populated. Likewise, employees could use an expense claim app to capture bills and submit it automatically, eliminating manual paperwork and avoiding time on non-productive activity.
Mobile apps have the potential to transform operations and logistics as well. Intuitive apps to scan bar codes and track inventory make the system accurate and quicken up the process. Connecting the app to a cloud-based CMS improves transparency greatly, making explicit the status of a product or package to all stakeholders. Improved prediction, better planning, and improved customer satisfaction are just some of the benefits resulting from such transparency.
Effective Workforce
Internal apps make life easy for workforce, cutting across hierarchies and functions. Managers could use apps to track their employees in real time, allocate work, see work queues, and track the status of pending work, or the work done by the team. The rank and file may use apps to collaborate with other team members effectively, refer technical manuals and instruction books, follow the recommended workflow and work queue, upload documents, and do more. Regardless of the nature of work, there is faster turnaround times with an enterprise app.
With mobility in an unprecedented boom phase, there is no better time than today to roll out apps for your business. However, the stakes are high, and it is important to get the process right. Your best bet in business app development is to partner with a professional app development company like us. We have vast experience and a highly talented pool of developers. Enterprises come to us, convinced by our ability to understand your requirements and roll out the latest and innovate mobile apps.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
A mobile app offers tremendous potential for efficiency, growth, increased revenue, but only if executed right. The development stage is most critical, for faulty execution can render the effort waste, and result in a dysfunctional app that impedes rather than facilitates the business.
Success in developing mobile apps requires clarity of purpose and focus, and to attain it, developers and other stakeholders need to ask some crucial questions.
1. What is the Purpose of the App?
Many times, enterprises are too caught up in the mobility hype, and develop apps just for the sake of it. Such apps may not have a specific purpose, and may actually be another version of the corporate website.
Successful apps are highly focused, catering to a specific function, purpose, or niche. Zero in on the specific purpose, or the precise problem for which the app is being developed. Consider why an app is required for the purpose, how customers may benefit out of it, and how an app can be a better option than a responsive website.
2. Who are the Key Stakeholders?
It is imperative to identify the stakeholders associated with the app upfront. Understand who owns the app, who is funding it, who will be using it, who will benefit from it, who will be responsible for the data that would keep the app functional, who would be responsible for day to day maintenance of the app, and so on. Questions such as who are the decision makers, who all are empowered for the business side of the app, and more, are also pertinent.
The success of any app depends on successful communication with the stakeholders, to understand their requirements, gain clarity on their role, and take feedback. Understanding end users enable app designers to tweak their profile, improving the power of the app considerably.
3.What is the Deadline?
The deadline to release the app is often a function of the purpose. For instance, if the app is meant for a specific sporting event or concert, the entire work becomes waste if the app is not up and running in time for the event. Even otherwise, things change in today’s fast-paced world, and tight deadlines are more the norm than the exception. Even a few days delay can make a big difference in the patronage of the app, or the app serving its intended purpose.
Related to the deadline is the release schedule. It is common enough practice to have multiple release dates for an app, with each release adding new functionality on an incremental basis. Many apps launch different versions, such as for iPhone and Android, on different dates.
4.What is the Programming Methodology?
A basic upfront requirement when it comes to creating a mobile app is creating a wire-frame, which makes explicit how the user will experience and interact with the app. The visual designs and UX is also critical and requires addressing at the very onset.
Another essential requirement is to create product backlog that enables defining and prioritizing the functional and nonfunctional requirements of the app.
Any app requires application programming interfaces, outside services and systems, and integration with third-party vendors. Research on these aspects, arrange for the necessary integration, and factor in the time taken for achieving such validations.
5.How is the App going to be Hosted?
Consider whether the app would be plugged into an existing infrastructure, or whether new infrastructure, such as hosting space, need to be provisioned.
Apps also require post-launch support for bug fixes and tweaks based on user feedback.
6. From where will the App be Downloaded?
The delivery channels of the app can impact the design of the app. For B2B and B2C apps, getting listed on Google Play and iTunes store are critical, and the requirements for listing needs to be addressed at the design and development stage.
Read this blog to get few quick tips for faster approval of iOS apps.
7. What is the Security Blueprint?
Security is an important consideration in today’s high-stakes business environment. Provision adequate security protocols and ensure the code is secure, to pre-empt hackers attacking the corporate network through code vulnerability. A related task to be complete is drafting the privacy policy of the app.
8. Are there Corporate Guidelines or other Considerations to Adhere to?
Enterprise apps may have to adhere to corporate guidelines, such as branding conventions, consistent screen design, the design of the icons, and more. The impact is mostly felt in design considerations.
9. What are the Risks Associated with the Project?
Any app development will face risks and uncertainties that could impede or even subvert the project, or at the very least let timelines go awry. A best practice is to build a risk register at the onset, and document the actions and the stakeholders responsible for the action, for each risk factor.
10. What is the Budget?
The budget is often overlooked when it comes to developing mobile apps, and a major reason is the difficulty in estimating one. With the fragmented mobile marketplace, there are too many variables at play, including multiple operating systems, different testing environments, and more.
Also, an app project goes much beyond the coding and compilation. It involves several critical components such as researching for the app, undertaking competitor analysis, designing an intuitive UX, and more, and all these tasks can influence the budget in a big way. There are also hosting costs, on-going optimization of the app when in use, costs for push notification services, costs for scaling the back end as the user base grows, and more.
The possibilities are endless, but the budget brings in a reality check. The trick is to optimize the possibilities within the constraints of the available budget.
There is no one-size-fits-all method in developing a mobile app. The best approach is customising the process to suit the client. It requires the services of a seasoned and experienced partner who knows to ask the right questions, and guide the client to get the right answers as well. We are competent in this front, having successfully developed a diverse range of mobile apps for many clients, cutting across industries. Contact us now and kick-start your enterprise app development process.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Mobility is the midst of an unprecedented boom phase, as more and more enterprises seek to leverage the advantages it offers in terms of remaining connected anytime and anywhere, unmatched convenience, improved efficiency, and more. Most enterprises now regard investments in mobility as a key cutting-edge initiative, and this holds true for both B2C and B2B enterprises.
However, amidst the mobility boom, many enterprises falter on the implementation front. About two out of every three IT leaders list mobility as their top priority in 2016, and there is no dearth of mobile apps in enterprises. However, only 48% of enterprises have a formal mobile strategy in place. Enterprises lose out on the full benefits of mobility without a coherent strategy. Many organizations are still in early stages of their mobile strategy development, and remain overwhelmed with technology standards, data governance, and security challenges, leave alone application development and user experience.
The Elements of a Mobility Strategy
Mobility driven solutions speeds up processes, makes systems more efficient and transparent, and enhances employee engagement. Above all, mobility has the potential to power long-term growth, and transform businesses. However, it requires a coherent mobile strategy to effect a successful digital transformation.
The first wave of mobility boosted efficiency in a big way. Mobility is now on the cusp of a new wave, where enterprises are increasingly leveraging mobile devices to innovate, to unlock business value, and power disruptive change.
-
Mobility 1.0: Migrating Existing Digital Assets to Mobile
The first wave of the mobility revolution involves migrating or extending existing functions and apps to mobility. This includes mobile-optimizing websites, and launching micro apps for specific purposes, such as approvals, expense reporting, and time tracking.
-
Mobility 2.0: Transform Existing Processes
The second wave of mobility revolution involves enhancing capabilities of existing apps, by infusing it with new functionality that fully leverages the possibilities offered by mobility. An app could, for instance, offer functionality based on smartphone features such as bar-code scanning, image scanning, and location data. Retailers could improve in-store customer service by offering real-time information and discounts to customers, based on GPS or location data. Temperature and vibration data, derived from sensors, could minimize downtime in processing plants.
Mobile enabled processes are on the whole simpler, faster, convenient, and accurate. For instance, a mobile expense submitting process, which auto-populate forms and allow capturing receipts digitally using the smartphone camera, is much quicker and easier than the cumbersome paperwork and productivity killing tasks otherwise required for the process.
-
Mobility 3.0: New Business Models
The biggest benefits of mobility realize by combining technology with process transformation.
New design paradigms based on touch and voice navigation, combined with the portability mobility infuses dynamism into business processes, and unlocks many possibilities not viable before.
Integrating mobility and analytics enable a shift from standardized to personalized, which improves engagement and customer satisfaction, and also allows enterprises to conserve resources, without using it for prospects and customers who do not need it, or are unlikely to be impressed by it. Companies could also offer new contextual services, integrating location, device type, transaction history, social media sentiment, and other relevant information.
The success of any business in today’s highly competitive world requires a proactive approach, rather than dealing with events reactively. Proactiveness requires being driven by insights, and the ability to remain connected with the stakeholders and the ecosystem, in real time. Mobile devices facilitate the collaboration and cooperation required to apply proactive measures.
Examples of how mobility can transform business models are aplenty:
- Tech player Square allows consumers and businesses to accept credit card payments, by integrating a tiny device on the headphone jack of a mobile device, eliminating the need for a swiping machine or a financial intermediary
- Commuters in Spain and Germany pay for their travel tickets through contactless smart cards and payment systems, powered by NFC-enabled smartphones. Widespread adoption of the concept can eliminate cash tills and ticket counters in a big way.
- Mobility inspired augmented reality solutions revolutionize the way their field forces access parts and repair documentation. What took several individuals with specialized training days to complete now requires just a few hours, and just a single ordinary repair technician with general training, and who knows how to use a smartphone app. A three-dimensional augmented reality (AR) app guides the technician step-by-step through the repair, identifying all the parts and seeing exactly what actions to take via animated video clips.
The Wider Ecosystem
A successful mobile strategy cannot be executed in isolation. It is rather part of a wider digital strategy that includes social, analytics, and cloud, among other things. The social-mobility-analytics-cloud (SMAC) stack enables organizations to embark on a digital revolution, offering ubiquitous connectivity and new ways of interacting with their ecosystem. The cloud especially complements the mobile strategy perfectly. Apart from cloud-resident SaaS (Software as a Service) applications that deliver mobile applications, the cloud offers storage solutions, testing environments for cloud-based enterprise app development, mobile application middle-ware and development tools, and also Analytics as a Service (AaaS) capabilities.
Using mobility as part of a toolkit, to reinvent internal processes and transform business models works wonders as long as the harbingers of change know what they are doing. The best approach is to partner with an experienced and established solutions provider. We bring to the table not just skills and talent, but also the ability to gain from our experience of having executed several successful mobility projects, cutting across sectors. We not only lend our expertise on designing highly efficient systems, but also help you guide decisions around the essential architecture, standards, security, and governance decisions.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
The only constant thing in today’s world is change. Enterprise software is likewise going through a major churn, to reflect changes in the wider ecosystem.
Until not too long ago, enterprise software development took a rigid and predictable model of requisitioning-requirements gathering-code writing-testing-delivery. The end product, which often took months or even years to develop, was delivered through desktops and laptops. Many enterprises, risk-averse as they are, stuck on to such time-tested formulas. However, the times they are a-changing and enterprises soon began to find out the hard way that who do not change inevitably find themselves “drenched to the bone,” if they aren’t already.
1. Enterprise Software is Becoming Lean, Mean, and Fast
Competitive pressures force today’s businesses to become lean and mean. The fast-paced business environment also raises the need for speed. Businesses are now hard-pressed to take decisions, to take advantage of an opportunity during the short window while it lasts. Likewise, businesses have no option but to be flexible and agile, to seize opportunities in the way it comes, and to please highly demanding customers. Unless the enterprise software, on which business processes and workflows run, are itself is not agile and seamless, businesses cannot position itself to be agile.
Today’s enterprise software seeks to leverage the power of simplicity. However, the need to deliver a simple front end, while ensuring the software is power-packed, often results in a complex backend. The wide range of emerging technologies both in the development and delivery process facilitates the reconciliation. A case in point is the emerging Docker technology that enables developers to create code that can run in their own containers, making the apps nimble.
Today’s enterprise software users are also far less tolerant of bugs and inefficiencies in software applications, and expect developers to implement fixes, and roll out updates rapidly.
2. Functional Programming is Gaining Centrestage
The high velocity of change forces IT leaders to innovate. One innovation that has caught on and now become the norm is functional programming. Many enterprises now build several small software components using functional components, and then architecture systems out of many such small software components
With the focus on speed and ease, enterprise apps are now becoming highly focused, including only what is really required, doing away with the frivolous. Instead of a single bloated one-size-fits-all enterprise app or software, enterprises are developing specific apps for specific functions. Tying the different front end apps together is a cloud-based backend and database, to which the apps sync seamlessly.
There is a new approach to the nature and structure of coding enterprise software as well. Developers are also abandoning the lengthy process of collecting specs and rather going ahead with a project through a new Minimum Viable Product (MVP) approach. The MVP may be regarded as a “lite” version of a feature concept, requiring just a fraction of the time that it takes to build the full feature. After releasing the MVP product and gathering feedback, developers upgrade it to a full blown version.
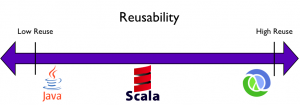
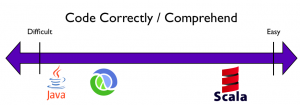
Time tested procedural programming languages such as C and Java still retain their dominance, but new functional programming languages such as Scala, Erlang and Clojure,noted for the power, are fast gaining ground.
3. The Rise of Collaboration
Enterprise software is increasingly becoming business driven by business users, rather than tech-heavy. While hitherto businesses adjusted their processes according to what the tech team dished out, today business managers are key stakeholders in the development process.
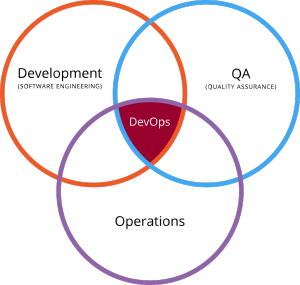
A trend fast gaining ground is DevOps, a spin-off from the time-tested agile and lean methods of software delivery. DevOps basically entails bringing together a cross-disciplinary community, who build and evolve highly flexible and resilient systems. The different stakeholders associated with enterprise software, including coders, operations engineers, managers, and others come together and involve in all stages of application development, right from design to testing.
4. Enterprise Software is Becoming Analytic Heavy
Today’s businesses are increasingly becoming data driven, and facilitating the trend is big developments in deep learning and analytical capabilities.
Most enterprise software today come with built-in analytic capabilities that allow users to scour available data and generate customized reports, on-the-fly. Technologies such as Apache Spark enable businesses to develop machine learning capabilities more easily than before.
However, the successful application of analytics to crunch data requires contextual analytics. In other words, enterprise software developers need to ensure the application of analytics to data is based on a deep contextual understanding of what is relevant. Human judgment may work in some ad-hoc cases, but has its limitations, and in any case, impedes seamless operations. There is no workaround to develop a working contextual awareness model for data analytics.
5. The Cloud, Mobility, and Security
The two big changes in recent times, the cloud and mobility have its impact on enterprise software as well. While some enterprises still run enterprise software applications on in-house servers, more and more enterprises are migrating to the cloud, and opting for the SaaS model. SaaS ensures greater flexibility, anytime, anywhere availability, and lesser total cost of operations (TCO.) SaaS also facilitates mobility, or delivery of enterprise apps through mobile apps, which is now indispensable considering the prevalence of a highly mobile workforce and the need to remain connected at all times.
However, the cloud, the mobility, and the Bring your own device (BYOD) programs raise the stakes of security. Enterprise software developers are smartly but slowly realizing the need to develop robust code and plug vulnerabilities that prevent debilitating attacks from malicious intruders, both internal and external, out to steal confidential data, intellectual property, and trade secrets.
Enterprise software development is now evolving into a continuous process, a distinct shift from a one-off project approach. In this constant battle to stay relevant and stay secure, your in-house IT teams, who has more pressing priorities, is sure to be swamped. Partner with us if you want to leverage the skill sets of our highly talented and resourceful team of developers, backed up by our experience in delivering hundreds of powerful and customized enterprise apps.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Enterprise mobility has come a long way in improving organizational efficiency and helping companies empower their workforce digitally. It has been estimated that by 2020 the global revenue generated by enterprise mobility software market would surpass $140 billion annually. With a compound annual growth rate of 15%, it is also expected to be spearheading nearly 15 to 20 percent of annual IT spending by global organizations. The driving forces behind the growing market for enterprise mobility products are the increased productivity factor for mobile workforce and the availability of low-cost smart devices. 2016 is running to a close and so we decided to have a glance of what’s going to be the state of Enterprise Mobility in 2017.
Let us see the direction in which enterprise mobility will head into in 2017:
Market Focus
As usual, 2017 has a very robust growth outlook in existing markets especially North America, which will be the primary leader globally in terms of enterprise mobility adoption. However there will be a new name on the top of the list for fastest growing markets – Asia Pacific (APAC). With a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 21 percent, APAC markets are expected to be an area of huge focus for enterprise mobility product vendors.
Flexible Device Management
Very recently, Forrester claimed that mobility is of prime importance for 71% of organizations. This means they will promote almost all kinds of mobile devices amongst its workforce. Bring Your Own Device or BYOD as it is affectionately known globally, will create room for newer policies in device management and control. Integrating flexibility into the BYOD ecosystem will be a challenge as good majority of employees would utilize the same device for personal and office use.
Information on the Go
Taking a leaf out of the previous trend, the rapid rise in number of devices will pose another challenge for information access. Enterprise data or information would be scattered across multiple organizational departments, hierarchies, geographical locations, etc. But for the end user or mobile workforce, all they need is information on the go, at their fingertips. Cross channel and intra-organizational data communication policies would face increasing pressure to synchronize information across mediums so that more informed decisions can be taken by end users.
Cloud Synchronization
It is hard to call Cloud a buzzword now not because it is irrelevant but because it is a norm for the entire tech world. From music to high end computing, consumers and enterprises are exploiting the world of cloud computing to manage their data. Enterprise mobility is no exception as cloud computing offers room for workforce to retrieve mission critical data from the cloud on demand rather than having to pre-integrate it with their devices. Application development for enterprise mobility too will face increased smoothness with more and more dev teams focusing on creating simple front end applications for mobile devices, while heavy duty tasks get organized and executed on private cloud infrastructure of the organization.
computing, consumers and enterprises are exploiting the world of cloud computing to manage their data. Enterprise mobility is no exception as cloud computing offers room for workforce to retrieve mission critical data from the cloud on demand rather than having to pre-integrate it with their devices. Application development for enterprise mobility too will face increased smoothness with more and more dev teams focusing on creating simple front end applications for mobile devices, while heavy duty tasks get organized and executed on private cloud infrastructure of the organization.
Security
Perhaps for the last few years, when people speak about trends in tech, especially when it involved data communication across channels, security had been the number one point on the list. Today we pick security to occupy a lower position, not because it has become a guaranteed surety, but because of the huge improvements that have been witnessed in the world of data security. Thanks to cloud computing, it is easier for enterprises to have a focused area to spend on information security. Whether companies opt for established cloud service providers like, Amazon Web Services or Microsoft Azure, or whether they build their own private cloud infrastructure is not a relevant question in today’s cloud security context. Cyber-attacks are increasingly being reported globally and hence it is imperative for organizations to lay strict emphasis on security policies. The most challenging security scenario in the case of enterprise mobility would be the unmonitored usage of device on insecure public networks. Security applications would definitely find huge market scope in the coming years.
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT today is what cloud computing was 5 years ago – the rising area of focus for businesses. The ability of devices, or more specifically sensors, to communicate user dat a will be instrumental for future marketing campaigns to attract genuine customers. For enterprises, IoT will enable field service agents to better track their core operational data, which would then be utilized at higher levels to arrive at better decisions. Devices such as smartwatches and other wearable will begin to serve dual purposes such as personal convenience and official data collection mechanisms. The future looks bright for wearable and IoT tech.
a will be instrumental for future marketing campaigns to attract genuine customers. For enterprises, IoT will enable field service agents to better track their core operational data, which would then be utilized at higher levels to arrive at better decisions. Devices such as smartwatches and other wearable will begin to serve dual purposes such as personal convenience and official data collection mechanisms. The future looks bright for wearable and IoT tech.
Dedicated Mobile App Development Centers of Excellence
This is a culmination of all the above trends. With such a huge emphasis being directed towards enterprise mobility, organizations would require dedicated developer teams to build customizable solutions for enterprise mobility. These developers would be groomed as an agile workforce to support the massive amount of organizational activities being migrated to enterprise apps.
So there you have it folks, 7 trends we feel will shape the future of enterprise mobility in 2017 and beyond. Enterprise mobility is here to stay and is definitely moving in the direction of becoming a hotbed for tech innovations in the near future.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
The proliferation of smartphones of various hues has made the mobile ecosystem hopelessly fragmented. Cross platform mobile application development is the in-thing now, as developing a native app for each platform is both time-consuming and resource crunching. At the bare minimum, a new app has to be compatible with and available on Google Play, iTunes and Windows, the three major mobile platforms, and this basically entails reinventing the wheel three times over.
Building a cross platform mobile app, however, is not easy, owing to the differences in the programming language, event model, UI model, and resource models. HTML5 emerged as the bright new hope at the turn of the decade, but flattered to deceive, often creating data integrity, security, and syncing issues.
The following are ten popular cross-platform mobile application development tools that gained centre stage in 2016, not ranked in any particular order.
1. Xamarin
Microsoft’s Xamarin is the most powerful and robust among the several cross-platform application development tools in vogue. It enables developers to build applications for different operating systems, using a single programming language, code base, and class library.
With its C# codebase, Xamarin allows developers to roll out Android, iOS and Windows apps without duplicating the effort. Xamarin comes equipped with a rich set of features, such as Lambda Expressions, Dynamic programming, LINQ, and a wide range of new .NET APIs. It has added F# of late, as well. These features allow developers to share a lot of the app logic between platforms, drastically reducing time to market compared to building native UIs for each platform.
Xamarin supports both Model-View-Controller (MVC) and Model View ViewModel (MVVM) patterns. The MVC pattern allows developers to keep application logic and presentation separate, and modify, test, update, and maintain application code easily. The MVVM pattern allows programmers to reuse the code base to create other projects. Users need to chalk out platform specific code only for the UI, with the option to reuse all other code. The clients get a fluid performance of native apps without maintaining multiple code bases. Xamarin also offers a cloud service, facilitating the testing of any number of devices.
Custom plug-ins that may be compiled easily further promote reuse. Xamarin Forms allow developers to achieve 96% reusability on their projects.
2. Kinvey
Kinvey works on a cloud backed model, with HTML5 as the base. The suite Integration with Gizmox’s Visual WebGui HTML5 platform allow developers to roll out the apps developed under HTML5 using C# or VB.NET, and Visual Studio, thereby offering a solution to the security and other technical challenges that deploying cross-platform HTML5 poses. The app facilitates simple, fast-paced agile app development.
3. Xojo
Xojo positions itself on offering a simple way to create cross-platform apps, not just for mobile platforms such as Android and iOS, but also desktop apps for Windows, Linux, and OS X, and for Raspberry Pi as well.
The Xojo development tool allows developers to create a single code base and compiles the developed apps as native executables for the required platform. The powerful code editor and an intuitive drag and drop option make the task of developing apps very easy. The Xojo backend does all the work, and infuse the new apps with controls familiar to the platform, giving it the look and feel of an app developed on the native platform.
4. Appcelerator
 The Appcelerator app development platform facilitates coding in JavaScript, and offer several value-added features such as real-time mobile analytics, and Mobile backend as a service (MbaaS.) It offers a host of high-quality drag-and-drop palette, and achieves 60% to 90% of code reuse when publishing on different platforms.
The Appcelerator app development platform facilitates coding in JavaScript, and offer several value-added features such as real-time mobile analytics, and Mobile backend as a service (MbaaS.) It offers a host of high-quality drag-and-drop palette, and achieves 60% to 90% of code reuse when publishing on different platforms.
5. Mag+
The Mag+ app SDK is highly preferred in the print industry, for catalogs, magazines, and other marketing collateral. The app offers core components for each platform, and allow developers to build atop these components. It is even possible to roll out simple cross-platform apps in double quick time, without any coding.
6. Corona Labs
Corona is popular in the gaming industry, to develop cross-platform 2D graphics games app and educational apps. Corona adopts the powerful and flexible Lua programming language, which is written in C. Corona SDK generates instant results, as soon as the developers write the code. The SDK allows setting up prototypes in double quick time, with minimal code, accelerating time to market.
7. Cocos2D
Cocos2D is a set of frameworks that allow publishing to different mobile platforms, and even desktops from a single code base. Additionally, it offers the flexibility to code in C++, JavaScript, C#, objective C, and a few other languages.
Cocos2D is open source and mostly used to develop cross-platform games and animated content.
8. MobinCube
MobinCube offers a series of templates with drag-and-drop functionality, allowing users to roll out apps on the fly. The simple and easy non-code methodology allow even ordinary, non-technical users to develop apps that work across platforms.
9. Dropsource
Dropsource is a browser based app builder, offering automated solutions for creating Android and iOS apps. The editor offers easy drag and drop interface, connect apps with any RESTful API, and an integrated development environment to customise the source code.
10. BiznessApps
BiznessApps thrives on offering simple solutions to small businesses who want to get basic apps running without hassles. It facilitates developing cross platform apps and mobile websites, through drag-and-drop development and automated submission to the app store, without the need for coding. There are a host of value added features such as seamless integration with third-party systems, rich analytical insights, and more, on offer.
The many cross-platform application development tools on offer are all easily within reach, and the possibilities endless. However, you still have to develop the apps, and make sure to get the UX, the overriding concept and other crucial ingredients right. When you partner with us for your cross-platform mobile application development, you gain from our vast expertise and our highly skilled talent pool, who are seasoned in developing hundreds of cross-platform apps, for all purposes, and for all sectors.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Mobility is the in-thing now. The BYOD wave, coupled with a highly mobile workforce means most employees now access the enterprise network through their mobile devices. However, mobility poses security risks as well. Lurking cyber criminals can easily exploit a vulnerability or security loopholes in a mobile device to gain entry to the network, and wreak havoc. CIOs understand most employees regard mobile devices as the most critical tools for getting work done, but 83% of them are still reluctant to embrace the trend, owing to security concerns.
The following are some enterprise mobile security best practices to prevent such security nightmares from coming to pass.
Get the Approach Right
The basic aim of enterprise mobility security is similar to conventional network security, which is to limit exposure to unwanted or uninvited access, and to implement “in depth defense” to harden the system against attacks. Most security systems have multiple layers of protection in place, so that the system remains safe until help arrives, even if one or the first few layers are breached. However, beyond this basic approach, the needs of enterprise mobility security are markedly different.
Securing mobile devices requires a new approach, radically different from protecting conventional endpoints. Mobile devices are moving targets in use outside the organization’s perimeter, and as such traditional security layers such as the firewalls, spam and content filtering, and many other tools are ineffective.
Mobile operating systems such as Android and iOS are especially susceptible to malware attacks, in the same way Windows and Linux are vulnerable. Anti-malware software, updated on a regular basis, is the basic security tool for mobile devices. Any sound enterprise mobility security policy would recommend a sound anti-malware suite, with policies for keeping it updated.
Likewise, encryption is the name of the game for keeping corporate data and intellectual property safe in the Wild West that is cyberspace. Wireless communication is easy to intercept and snoop, making a strong case for encrypting all sensitive communication going in and out of mobile devices. There is also a good case for using VPNs that include encryption and strong authentication capabilities, to access cloud based systems or other remote services from mobile devices.
Remote wipe and lock, and ability to track the location of the mobile devices are also basic security features for enterprise mobility.
Have Strong Authentication in Place
Mobile devices are especially vulnerable to theft. Eight out of ten CIO’s believe smartphones increase organizational vulnerability through interception of data in transit or through device theft.
Any enterprise security best practice requires strong authentication mechanisms that go beyond conventional passwords.
Built-in biometrics, leveraging the smartphone’s facial recognition capabilities, fingerprint scanners, and voiceprint recognition offer a high level of security. Opt for multi-layered authentication, with add-on device passwords, so that the system does not give automatic access to sensitive information through any endpoint device.
Hypersensitive companies could program to wipe off data from the smartphone automatically, on encountering repeated failed login attempts.
Control Third-party Software
Third party software, which may come with latent vulnerabilities, such as black gateways, built-in back doors and drive-by download of rogue software, are loose ends in enterprise mobile security. In a perfect world, the enterprise could eliminate third-party software in favor on in-house enterprise mobility apps, but such an approach is a non-starter for most enterprises, owing to practical considerations and limitation of resources to develop custom apps. The next best thing for enterprises is to lay down policies that regulate the use of third-party apps. The policy could also white-list safe apps, or black-list apps dangerous for the network.
Many enterprises are now toying with developing their internal app stores that vets apps suitable for download by enterprise users.
Have Effective Control over the Network
There is no shortcut to having an effective control over the network. In the BYOD era, it is essential to have an up-to-date inventory of all devices authorized to access the network, and nip access of unauthorized devices in the bud.
Creating secured mobile gateways also enhances security in a big way. Securing the network is a team effort. The IT manager and the business manager needs to work together to list down the use-cases, systems and applications mobile users really need to access. Mobile traffic could then be directed through special gateways, complete with customized firewalls, content filtering, and other security controls enabled.
Another best practice is to make BYOD users log on to a remote virtual work environment, through VPN. In such sessions, only the screen output from work applications and systems transmits to the mobile device, and the data does not persist once the remote session ends.
It is also a good idea to conduct penetration testing on the network on a periodic basis, to identify and fix any loose ends.
Have Effective Control over the Device
The configuration of mobile devices is just as important as the choice of mobile devices. Best security practices dictate hiding Bluetooth from discovery, or disabling it altogether, and configuring the device to avoid unsecured wireless networks. A management client application, downloaded on the BYOD device, enable users to comply with such regulations.
Mobile hyper-visors and containers, especially useful for BYOD devices, enable enterprise system administrators to manage apps, data, policies and settings within a container on the employee’s personal device without such interventions intruding into personal content.
While there is a strong case for security, going overboard with security can impede usability. The trick is to strike a fine balance between effective security that is non-disruptive, and UX. It requires considerable experience and expertise to strike such a fine balance, and we have such expertise. Get in touch with us today, to leverage our talented team, who have several years of experience in securing even the most complex and diverse of all enterprise mobility networks.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new