Tag: microservices
Technology is getting better and better each day. Several technologies and architectural patterns have emerged and evolved during the past few years, and it only gets better with time. Microservices architecture or microservices is one of those patterns. It emerged from the world of domain-driven design and persistence.
In this article we will cover:
- What is microservices architecture?
- The difference between microservices, monolithic architecture, and service-oriented architecture (SOA)
- The benefits and examples of implementing Microservices Architecture.
What Is Microservices Architecture?
Microservices architecture is a specific method of designing software systems that can structure a single application as a collection of loosely coupled services.
Microservices architecture is made up of several components in their own individual compartments in the software. This makes them independently upgradeable or replaceable.
Microservices architecture simplifies the process of building and maintaining certain types of applications by breaking them down into many smaller pieces that work together. Though this increases the complexity, it offers greater advantages over the monolithic structure.
Now you may wonder: Isn’t Microservices just another name for monolithic architecture and service-oriented architecture (SOA)?
Let’s clarify that for you!
Read more: Progressive Web App Development: 10 Benefits
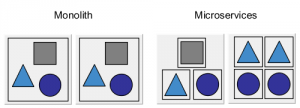
Microservices Architecture Vs. Monolithic Architecture
In the current age of Kubernetes, Monolithic architecture faces many limitations. Please note a few:
- Monolithic architecture is a single application. It is generally released once a year with the newest updates. Whereas, Microservices architecture is cloud-based and can be updated as required.
- Monolithic architecture is slow. Modifying a small section may require complete rebuilding and deployment of the software. Microservices on the other hand are faster to deploy and quick to isolate any defects.
- Monolithic architecture is harder to adapt to the specific or changing product lines while individual models of Microservices architecture enable scaling and development.
Microservices Architecture Vs. SOA (Service-oriented Architecture)
Microservices architecture is distinct from SOA. Here are a few differences:
- SOA model is dependent on ESBs and so it is slower. Whereas, microservices is faster as it leverages faster-messaging mechanisms.
- SOA focuses on imperative programming style, while microservices focuses on a responsive-actor programming style.
- SOA has an outsized relational database. But Microservices architecture tends to use NoSQL or micro-SQL databases.
Read more: Ways To Accelerate Business Growth and Success in 2021
Business Benefits Of Microservice Architecture
Microservices architecture can help your business grow quicker, increase productivity, and innovate better to deploy competitive products into the market. Here are some specific benefits of the Microservices architecture:
1. Better organization for efficiency
Microservices architecture organizes business applications. It can extend those applications to support plugins for new features, devices, etc. You can easily add more features to each of those popular applications to generate more revenue.
2. Increased scalability
Microservices architecture divides applications into smaller modules. Each of these modules can operate independently enabling businesses to scale applications up or down, as required. As these modules operate independently, a fault in the single module does not mean disruption of the entire system.
If one module fails due to outdated technology or the inability to further develop the code, developers can use another module. In other words, the applications continue to function even when one or more modules fail.
This capability allows developers the freedom to build and deploy services as needed without having to wait for the entire application to be corrected.
3. Easy to maintain
It is easier to maintain and test a single module as opposed to an entire system. Since each module has its own storage and database, organizations can build, test, and deploy all the modules with less complexity.
4. Faster development
Since all modules are loosely coupled, change in one module does not affect the performance of the other. This means you can update a single module at a time leading to faster development.
5. Enhanced performance
Microservices architecture can enhance the performance of the application. It reduces downtime while developers take their time to troubleshoot the issue and bring the system back to normalcy.
6. Dynamic yet consistent
The individual modular approach in Microservices architecture is easy to replicate. This allows for consistency in applications, which in turn makes managing these modules simple and easy.
Prominent Examples of Successful Microservices Implementation
Prominent examples of Microservices architecture are Amazon, Netflix, Uber, and Etsy. Over time these enterprises refactored their monolithic applications into Microservices-based architectures. This move has helped to quickly achieve scaling advantages, greater business agility, and unimaginable ROIs.
1. Amazon
In the early 2000s, untangling dependencies was a complicated process for Amazon developers. It faced development delays, coding challenges, and service interdependencies.
However, Amazon assigned ownership to each independent service team. This allowed the developers to identify the bottlenecks and resolve issues more efficiently. Also, it helped them create a very highly decoupled architecture.
2. Netflix
Within a year of starting its movie-streaming service, Netflix was suffering from service outages and scaling challenges. It experienced major database corruption and was on standstill for three days! That is when it decided to move towards more reliable, horizontally scalable systems in the cloud.
First, Netflix moved its movie-coding platform to cloud servers as an independent microservice. This allowed Netflix to overcome its scaling challenges and service outages.
3. Uber
Uber, the ride-sharing service faced growth hurdles. It struggled to launch new features, fix bugs, and integrate its global operations. Besides, it became increasingly difficult to make minor updates and changes to the system.
Uber then decided to move to cloud-based microservices. This allowed its developers to build individual functions like trip management or passenger management. This boosted the speed, quality, and manageability of their services. Among other things, they achieved more reliable fault tolerance.
4. Etsy
Etsy experienced poor server processing time. However, with the help of Microservices architecture, Etsy created a variety of developer-friendly tools and went live in 2016. From that point forward, Etsy benefits from a structure that supports continual innovation, faster upgrades, and more.
Read more: Enterprise Resource Planning Software: A Complete Guide!
How Fingent Can Help You Implement Microservices Architecture
Microservices architecture supersedes SOA and monolithic models. However, it has its challenges. This is where Fingent comes to your assistance.
Fingent can help you implement Microservices Architecture correctly to improve your productivity and ROI. Designing your architecture is not just a technological option. It is a necessity! It is a business decision that can directly affect your business growth. Fingent can help you take care of the technical aspect while you concentrate on your business goals. Give us a call and let’s get talking.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Big is not always beautiful, at least in the realm of enterprise software. Enterprises are increasingly finding the enterprise software behemoths they have painstakingly built up over the years a big liability in today’s business environment, which values nimbleness and flexibility.
The conventional top-down approach to developing enterprise software lumps together all functionality into a single process, and replicate it on multiple servers. More often than not such systems become bloated and unwieldy with every update. Apart from the bloat, even a small change to the system requires updating and re-deploying the server-side application, causing disruption that can wreak havoc in today’s fast-paced digital world.
Amazon took the lead to break down its large monolith system and deconstruct it into microservices. Netflix followed suit soon, rolling out an agile model that deconstructed its behemoth software stack, to keep up with two million daily API requests in a highly efficient manner. Soon the trickle became a deluge, with companies such as eBay, Google, Uber, and thousands of smaller companies adopting microservices in a big way.
What exactly is a Microservice?
Microservice is breaking down application development into compartments of small services. Each service comes with its own process, and use lightweight mechanisms such as an HTTP resource API for communication. The services are deployable, independently or tied together in a modular architecture. Each application comes with its own domain logic. It receives a request, and apply logic as appropriate, to generate a response. The process is usually choreographed using simple RESTish protocols.
Unlike libraries, which are components linked into a program and called using in-memory function calls, services are out-of-process components, which communicate with a mechanism such as a web service request, or remote procedure call. The use of services as components, instead of libraries, enables independent deployment.
Microservices are loosely coupled yet form a cohesive whole, creating a more robust and reliable system. The loose coupling improves cohesion as the more interdependent or coupled the system’s parts, the difficult it is to use, test, and maintain.
The atomic nature of micro services make it ideally suited to deploy to perform a single operation on a back-end system, such as retrieving a transaction history pertaining to a customer, verifying a person’s credit score, and more. Microservices may also coexist with the traditional monolith architecture. A good illustration is the Guardian website, originally designed as a monolith and now gradually evolving in a micro service direction. While the core of the website is still monolith, the addition of new features is by building micro services, using the API. Such an approach best suits temporary and fast changing requirements, such as sporting events, In such situations, rapid development languages may be deployed to put together a web page or component, on the fly.
Unlike earlier avatars of service based models such as Service Oriented Architecture (SOA), microservices are more granular, keeping protocols lightweight for fast and easy communication.
How do Microservers Make a Difference?
Microservices bring in nimbleness. Instead of single complex, unwieldy, and bloated behemoth system trying to do too many things at once, an array of small services seamlessly integrates multiple systems in a nimble and resilient manner. Such an approach perfectly gels into the world where immediacy and perfect functionality are considered basic requirements.
Since microservices breaks down functionality to a near atomic level and abstracts it, development teams can focus on maintaining or updating only the relevant services, doing away with the painful and time-consuming process of integration associated with monolithic applications. Since each service operates independently from all others, a failure of any service does not break the entire system. The problematic unit simply blows out while everything else functions as usual. The development process, which hitherto took weeks, can now be completed in just a few weeks. Also, businesses may add new features and functionality easily, without causing downtime to the system.
Microservices also allow retaining the focus on business processes. When building large processes, the focus generally tends to veer towards the technical layer, and in the process, the optimal business process takes a backseat. The flexibility of micro services also makes it very easy to make changes to the process, as required.
Yet another advantage of microservices is the incredible flexibility on offer. Microservices are free agents, not tied to any specific language or platform. Developers may choose whatever framework that catches their fancy, rather than stick to one-size-fits-all standards such as XML or SOAP. The developer has an option, for instance, to use Node.js to generate a simple reports page, and shift to C++ for a particularly gnarly near-real-time component.
Microservices are easy to build and deploy as well. It relies primarily on the popular JSON/REST interface, and offer straightforward authentication using HTTP, OAuth or other easy-to-use API keys. The optimal use of microservices results in highly efficient use of code, and reduction of the quantum of infrastructure required to run the application by as much as 50%.
The extreme nimbleness of micro services makes it the default model for building enterprise applications. However, enterprises still need to develop an efficient system out, and partnering with an established and experienced provider makes all the difference. We have at our disposal both a highly efficient and experienced team and the latest cutting edge tools to deliver highly nimble, flexible, and powerful enterprise software that provides your enterprise with the dynamism it deserves.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new