Category: Business
Mobility is growing at an exponential pace and mobility apps are the flavor of the season. However, it is still important to get the development right, to reap the benefits of mobility. A crucial consideration, to be taken upfront, is whether to opt for native apps or web apps.
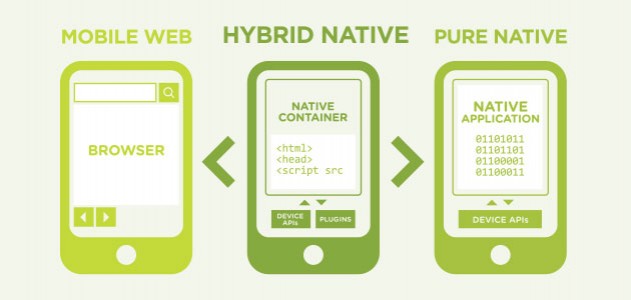
A Native App is developed specifically for a particular mobile device, customized for the operating system and other device configuration, and installed directly to the device, usually through app stores. At a basic level, there are separate native apps for Android devices and iPhones. A web app, on the other hand, is Internet-enabled app residing in the cloud, written in web code and accessible through the mobile device’s browser. Both native apps and web apps have its pros and cons. Web apps are similar to websites but more interactive.
Web Apps Surge in Popularity
Native mobile architecture is on its way out. Today, about 60% of the mobile architecture is mobile apps or hybrid, and just 26% of apps remain native.
The highly fragmented mobile space, coupled with the popularity of the BYOD environment where employees are free to use the device of their choice, make it commercially and practically unviable to develop native apps for each platform.
Native apps also lose out due to the need for velocity, so essential in today’s highly competitive environment. In most of the cases, the best time to roll out an app would be yesterday. Delays in rolling out the app may make the app obsolete, with competitors taking away the business. As such time to develop native apps for each platform is simply not available.
About 43% of companies now place movement as their top business capability, and they are still struggling to stay on par with the speed in which mobile technology advances.
Accessibility
Both web apps and native apps have its pros and cons, making trade-offs imperative.
On the face of it, web apps are accessible on any device, sparing the need for download onto the user’s mobile device. Such apps generally require internet connect to operate, though the latest web technologies such as IndexedDb, Web Storage, and AppCache deliver offline capabilities to web apps.
Functionality-Flexibility Trade-Off
Functionality wise, native apps, being optimized for the device, work faster and are more efficient, over web apps. A native app works as a standalone entity and remains totally compatible with the device’s hardware and native features, such as the accelerometer, camera and so on. Web apps, on the other hand, being generic, can usually access only a limited amount of a device’s native features. The biggest stumbling block is the difficulty of web apps to access the phone’s webcam, sensors, and some other hardware components. Web apps may also face difficulty in accessing the file system and local resources, but modern browsers adopt the File API, overcoming this big limitation. Generally, native apps are best suited for complex feature sets, whereas web apps are ideal when the requirement for native gestures is minimal.
While native apps, customized for the device, had a distinct superiority in the user interface, the gap has significantly narrowed in recent times, and there is very little difference in the user interface or usability between today’s web apps and native apps.
Moreover, where web apps compromise on functionality, it scores in flexibility. Web apps give developers unbridled freedom as the apps do not require approval from app stores, allowing release in any form and any type. Developers of native apps wanting to upload their app in app stores such as Google Play need to comply with the stipulations laid down by the respective app stores.
Robustness and Safety
Native apps, being leveraged to work seamlessly with the device’s built-in features, are efficient and faster. These apps also get the full support of the concerned app stores and marketplaces. Approval from the app marketplace denotes a high level of safety and security as well.
However, keeping native apps safe require the user to keep on updating the app at regular intervals, which is easier said than done. With web apps, the developer makes all the changes at the backend, without user intervention.
Development Approaches
The main difference between web apps and native apps is internal or in the development process.
Each mobile platform has unique features and unique set of platforms and requires compliance with its own unique development process. For instance, iOS uses Objective-C, Android uses Java, and Windows uses C++. Native apps have to comply with such requirements. Web apps, in contrast, are free of such customizations, with the developer free to use JavaScript, CSS3, HTML5, or any other Web application frameworks as per their desires.
However, there is a flip side to the story as well. Each mobile platform offers standardized SDK, development tools, and other user interface elements, using which developers may create native apps with considerable ease. Web apps do not get the convenience of such SDKs or tools, and the developer has to do the hard grind. This is changing of late, though, with the developer now having access to several tools and frameworks for creating web apps and deploying it to multiple mobile platforms and Web browsers.
Costs
Cost wise, developing a single web app that may be manipulated to suit any device is much more cost-effective that developing native apps for each device. Native apps also cost higher to maintain, considering the need to update many versions of the app.
There is no definite answer on whether native apps or web apps are better. What works best depends on the circumstances. Consider the target audience who are likely to use the app, the required features and functionality, the hardware features required in the app, the timeline, and the budget to decide on whether to opt for web apps or native apps. Either way, it requires expertise to understand the exact requirement and take the crucial decision on whether to go native or web. We have the expertise to help you in this regard, the talent to roll out cutting-edge solutions highly customized to suit your requirements, and the experience to get it right the first time round.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
In today’s tech-neutral age, talent is the key differentiator between companies, with employees a key source of competitive advantage. Top app developers are in high demand to ride the mobility wave, and enterprises scramble to retain developers from being poached.
Developers are by and large content with their current jobs, but three out of four developers are open to new opportunities, and would readily change to a job that offers them better working conditions. Even developers not actively seeking out jobs do spend around an hour per week checking on potential jobs. This is in addition to the time they spend with other developers and potential recruits on communities such as Stack Overflow. In such a state of affairs, employers need to remain on their toes always, to retain developers.
Here are some tips to retain top talent in your enterprise, without allowing competitors to lure them away.
Provide Opportunities to Grow
Most programmers are knowledge workers who value their skills and strive to keep themselves updated. One in every three programmers contribute to open source projects, and a whopping 81% of developers program as a hobby as well. These programmers are neither beholden to any organization, nor dependent on any corporate training program for their skill enhancement. They remain with their organization as long as it is worth their while, and simply move elsewhere if the organization get in the way of their development. Their loyalty is to themselves first and to any organization second. Organizations would do well to understand this fact and provide employees opportunities to grow and develop their skills.
A good salary and fringe benefits are now a basic requirement, rather than any special motivators to ensure employees stay. Rather, if an employee feels the enterprise offers them opportunities to enhance their skill-set, valuable exposure, time to spend in creative pursuits, and more, they are more likely to stay.
Get the Leadership Right
Very often how the employee is treated in an enterprise determines whether he or she sticks on or leaves. As a rule of thumb, an authoritative leadership style is a sure-fire way to doom for the enterprise, and a servant leadership style, where the focus is to serve the employee, by facilitating them to do their thing, works wonders.
Having said this, a charismatic leader, who can lead from the front and motivate employees by dint of authority can also work wonders, no matter the leadership style. A good case in point is Steve Jobs, who would yell and publicly shame his teammates when dissatisfied with their work, and yet made Macintosh engineers believe they could achieve the impossible.
Keep Employees Motivated
The most effective retention trick is to facilitate the employee harness their creativity in tasks that matter to them. Abraham Maslow’s time-tested need-hierarchy theory lists out five levels of needs or motivation that satisfied an employee, starting from the basic psychological and safety needs, a moving on progressively to need for affiliation, esteem, and self-actualization. Most developers, by dint of being “knowledge workers”, have already accomplished their basic needs, and look primarily at higher level needs such as esteem and self-actualisation.
The onus is on the enterprise, especially HR to craft retention strategies, keeping in mind what exactly motivates an employee, and would prompt them to stay. Challenging work assignments, rewarding projects that would enable them to gain the esteem of their co-workers and peers, a sense of satisfaction on having accomplished a project that is really useful, and more are some ways to retain the employee’s interest to stay.
Pamper the employee
Motivating the employee into staying is of no use unless the basic systems are in place. Developers being highly skilled “knowledge workers.” The onus is on the enterprise to facilitate a congenial working atmosphere to do their thing.
Facilitating the employee means pampering to their needs, and a flex-and-fun time, combined with work-from-home options lead the list of facilities sought after by most developers. About 64% of developers already work remotely at least one day each month, and 11% of developers work remotely on a full-time basis, as of now. Nevertheless, much more is required to keep developers happy, and facilitate their creativity. While 57% of developers valued the ability to work from home on vacation days most, 53% of employees valued vacation days, 47% of employees valued health benefits, 40% of employees valued work hours, and 40% of employees valued the equipment they use.
Autonomy and Career path
At times, retention of talent may have more to do with a dysfunctional enterprise than any other factor. A rigid and hierarchical enterprise, with a culture of deferring to authority, and where information is kept on a tight light is hardly congenial for developers, who value creativity and openness. Most talents seek to leave enterprises where talent and merit are not valued, where promotions are a matter of tenure and not merit, and where there are no mentors to guide them.
Programmers value autonomy and empowerment. Empowering them to take crucial decisions regarding their projects, entrusting them to engage with clients directly, drawing deadlines through a collaborative process rather than imposing one from the top, are all steps that make employees feel valued, appeal to their self-esteem, and go a long way in retaining them for the enterprise.
Also, enterprises that fail to chalk out a clear career path for their top talent risk them leaving. Not all developers make competent managers, and many of them do not even seek a managerial position. The onus is on enterprises to ensure progress in roles and responsibilities that suit them. A technical path, parallel to a managerial or supervisory role, may work best for technocrats who may not find managing people their cup of tea.
Top programmers seek continuous value. They seek out highly challenging projects and seek to leave when they perceive the projects they work on are futile or destined to failure.
Getting and retaining top app developers is not easy. However, we offer an effective alternative. We already have a team of highly talented, resourceful, and experienced app developers, with a track record of having delivered several intuitive mobility and other projects, for customers cutting across industries. When you hire us, you are free of all your human resources related worries. Retaining the top talent, pampering them, and preventing others from poaching the best talent becomes our headache, leaving you free to focus on your business.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Businesses, especially small businesses, these days are increasingly adopting cloud service technologies. Why?
It’s the flexibility, scalability and value features of the cloud that are apparently driving this growth in its adoption. The basic aim is to allow employees to work better and promote an efficient work environment, with their offices available everywhere, now that telecommuting is becoming more prevalent as a trend.
Here are some facts that prove how rapidly telecommuting is becoming mainstream:
- By 2020, cloud spending in terms of IT and services is likely to exceed half a trillion dollars.
- 70% of software revenues are based on cloud code – SaaS, PaaS or on-premise as ISV’s base on-premise on cloud platforms.
- Tweet: Almost 50% of large enterprises are looking to double up software and services development staff for cloud projects.

But, as a general fact,
do all businesses stand to gain from using cloud services?
Will all businesses reap equal and extensive benefits from using the cloud?
Is it beneficial for you to use the cloud?
The answer to all these questions depends on the size of the business as well as preferences in terms of data, storage, security and the like.
Before you jump on the bandwagon, you need to analyse your business scenario and your preferences to make an intelligent decision.
Is cloud migration the right way to go for you?
Cloud migration (or moving your apps and services to the cloud), is more of a long term trend. While it may have several benefits of its own, there are several factors that you need to consider before going for it.
When should you consider moving to the cloud?
- If your applications are experiencing an explosive increase in traffic and it is practically difficult for you to scale and arrange resources on the fly, in order to meet the rising demand.

- If you are a software solutions provider and your clients are increasingly demanding faster application development and deployment, and you want to facilitate that while cutting down on infrastructure overheads.
- If your clients are looking to expand their business and diversify geographically and you think it might be a challenge for you to accommodate a multi-region infrastructure system, including its due maintenance, time and human resources.
- If you are looking to reduce your operational costs and increase the effectiveness of your IT.

- If you are looking to set up a disaster recovery system for an entire data center, while still having adequate control over resources and keeping costs under check.
- If you are planning to expand your development team and make it widely distributed so as to allow even remotely located employees to work easily.
These are just some common situations where you could consider cloud migration. There may be more. If you can relate to at least some these, then you can probably start planning.
Small and medium businesses are more likely to be experiencing one or more of the above scenarios. They are the ones who are constantly undergoing rapid and drastic changes in terms of scale, profits and business size. Hence, the obvious features of the cloud like scalability and accessibility can come in very useful.
Large enterprises may have more sustained developments in their business, in which case, they may not necessarily need the cloud. There are other options for them which we’ll be getting into, in a while.
The flipside
Now let’s see some possible consequences that follow cloud migration. You might want to consider the flip side of things as well, before getting into it.
- If your application uses, stores and sends back a lot of sensitive data, then you might not be able to use the cloud. Even compliance regulations restrict you from maintaining such data, in sources like the cloud.
- If you are using proprietary software or technology, and you are looking to move to the cloud, then you have a problem. It might not be legally possible for you to move or deploy such software into the cloud.
- You might have to deal with transparency and control issues, as your hardware is being controlled by someone else.
- You might encounter latency or dormancy issues with certain operations when using the cloud.
- If you want to retain ownership of certain data in your application, then cloud might not be the thing for you. When you migrate your data to the cloud, you have no control of where your data gets stored.
- Shared resources can lead to occasional disturbances in terms of performance and efficiency.
- Your application’s design or architecture might not be suitable as such to fit the cloud architecture. Hence you might need to make certain modifications.

Again, these are only some limitations of cloud migration to get you started on the thinking process. The most common ones are listed above. You may have to deal with other minor issues as and when you migrate.
To make a judgment…
On a normal case, where you already have a setup, which is satisfactory to your employees as well as customers, and you don’t really need much scaling and maintenance at the moment, then you could very well continue as such. It would not be worth these limitations for you to disturb the existing smooth process.
If you are a startup company in the manufacturing industry, it might not be feasible to maintain in-house servers and applications for internal uses. You also might not encounter a lot of the above-mentioned issues as you don’t use the cloud to serve customers directly. In such cases, opting for cloud services might be the best way to go.
For those of you who own large business enterprises in the software industry, it might be better to go for a hybrid model – one which combines the best of cloud services as well as in-house servers or private servers. For applications that involve a lot of sensitive data, or for proprietary software, you could use your own servers, and for other applications, you could use cloud services. That way, you don’t have to compromise on security or data ownership issues while at the same time, attain the flexibility and scalability of the cloud.
You also have the option of private clouds. More on that soon.
The cloud computing model
From a broad perspective, you could go for one out of three cloud computing models – Iaas (Infrastructure as a Service), SaaS (Software as a Service) and PaaS (Platform as a Service).
In case of IaaS models, you don’t have to take care of storage, networking, CDN and virtualization. They can all be left to the IaaS provider.
In PaaS, the application platform, the development, and the database are all handled by the providers.
SaaS models take care of business management, CRM, security as well as tools.
It is important to choose the model once you have decided to for the cloud.

The cloud options
Large enterprises also have the option of choosing a private or a hybrid cloud model.
Private cloud is where you can create your own cloud using specific platforms like Openstack. That way you can access the benefits of the cloud, while still retaining data security and ownership. It is apt for businesses using secure and confidential information and core systems.
A public cloud is where all of your resources are hosted by a separate cloud service provider. It supports more number of customers and is better suited for companies having lesser confidential information, as all the resources are publicly shared and virtualized.
A hybrid cloud model is one in which your resources are spread over private and public clouds. Specific resources can be used in the private cloud, whereas those which do not need a high level of security can be hosted by the public servers. Large software enterprises can benefit from using this model as they can have the best of both worlds. It is a perfect blend of reliability, availability, security and reduced operations costs.
It is extremely important for business enterprises, whether large, medium or small to analyze their business and choose the appropriate cloud solution. If your business scenario demands cloud migration, then your next steps should be in choosing the right model. Once you know exactly what kind of cloud services you need, you can be sure you are doing the right thing.
Still confused? Talk to our experts and find the perfect solution.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Smartphone malware rose by 400% in 2016, and touched an all-time high, with an estimated 8.5 million malicious installation packages in existence!
With mobility in the middle of a golden boom, it is no secret smartphones are in the crosshairs of cyber criminals. By October 2016, 1.35% of all mobile devices across the world had already succumbed to malware attacks, up from 1.06% in April 2016. With restricting mobile devices now no longer an option, here are some tips to keep your business safe, amidst the rising malware threat.
1. Monitor Usage
An enterprising cyber-attacker could exploit latent vulnerabilities in an app to take control of the device, and use it as a bot. The ready example is the Mirai botnet and the associated DDoS attacks, the most devastating attacks in 2016. Mirai turned computer systems into remotely controlled “bots,” primarily targeting devices such as remote cameras and home routers, and in the process exposing the latent vulnerabilities of the emerging Internet of Things.
Trying to prevent such infiltration is likely a losing battle. Android platforms, being open source, are very distributed with different manufacturers, operating system vendors, app vendors, handset makers, carriers, and other stakeholders in the mix. Malware can be slipped in at any point. Monitoring network activity using any of the available network monitoring or anti-malware tools could detect abnormal traffic, and pinpoint it to a source, offering an effective solution to the menace.
2. Update the OS Regularly
The focus of any respectable cyber-security strategy is to prevent the smart device getting compromised in the first place, rather than making amends after it is flawed. Keeping the operating system up-to-date is the first step towards this effort. One of the reasons Android and other operating systems issue updates regularly is, to offer patches for vulnerabilities that may have surfaced recently, and which cyber attackers may exploit. The situation is graver in Android OS than any other OS, considering devices with Android OS accounted for 81% of malware infections in the second half of 2016.
3. Be Careful of Downloads
Download apps only from trusted sources, preferably only the Google Play Store, Apple’s store, or the official store of the respective OS or enterprise. They have an approval process for accepting apps on the iTunes. If the app has gone viral and is around for while, it is likely to be safe. The user ratings and comments offer a good indication of the reliability of the app. Google’s “Bouncer” for instance scans for problem apps in the PlayStore. However, all these methods are not foolproof.
As far as possible, stay away from such third-party app stores, or any source outside the official app store. However, at times, downloading from such sources may become inevitable. In such an eventuality, perform a background check on the app developer. Seek out reviews of the app wherever possible as well. Always err on the side of caution.
Also, consider the permissions sought at the time of installation. In modern smartphones, each app has its own work environment and is unable to access other apps’ data. The extent of activity the app can do depends on the permission it is granted, to access the phone’s features and data. If the app asks for a permission it is unlikely to need to perform its intended function, it raises a huge red flag.
4. Use a VPN
Determined hackers are always on the prowl, and logging on to public Wi-Fi make oneself especially vulnerable. Hackers on the same network have several tools to snoop on user activity. Encrypting the connection using a virtual private network (VPN) is a safe practice when using public connections.
5. Deploy an Antivirus Suite
An antivirus suite may seem obsolete in smartphone’s where each app works in isolation, depending on the privileges it receives. However, a good antivirus suite still has its uses but not just offering antivirus protection, but scanning app activity. With smartphones being used extensively for browsing, such anti-virus suites scan for malicious URL and shields the phone. Many antivirus suites offer value-added features, such as blacklisting problem numbers, ability to PIN protect private apps, Wi-Fi scanning options for improved security, and more.
6. Have Precautions in Place
At times, even with the precautions, malware inevitably strike. The hacker may not even have to slip in the malware. Merely following the smartphone owner and stealing the smartphone during one careless moment may do the trick in accessing sensitive corporate data.
Deploying a lock screen, having a remote wipe feature activated to use in case the smartphone is lost or compromised, activating the remote track facility, limiting remote access to internal apps or programs that involve sensitive corporate data, and more are some of the other features to protect the data even if the smartphone itself is compromised.
Very often, the weakest link in the security chain is not the technology, but the people. Often it is the failure in basic security practices or lack of common sense from employees that throw open the door for hackers to make their entry. Training and awareness, even on those things considered too obvious, can never be underestimated.
Have a solid and comprehensive mobile device management (MDM) strategy which encompasses and integrates all facets of security. Whether it is building state of the art cutting edge apps, with solid inbuilt security features, or instituting and deploying a company-wide security policy, we have the experience and expertise to do it and make an ideal partner for all your requirements.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
In today’s highly interconnected world, marked by the dominance of the social media, a poor app is a virtual death sentence for the brand. With several options readily available, users are more likely to abandon transactions and even delete the app altogether when they encounter glitches and obstacles, or if they encounter poor mobile app design. Getting quantifiable insights into the extent to which a user is satisfied or dissatisfied with the app, and identifying the pain points that cause dissatisfaction is of critical importance in the wider scheme of things.
A survey by HP in Europe and North America reveals 53% of mobile app users delete an app if it crashes, freezes or produces errors, 49% of users no longer use an app with response times longer than two seconds, and 36% of users shun apps that are battery hogs.
UX is the name of the game in developing highly intuitive mobile apps that delight the customer. Here are some tools that offer greater insights and empower the developers to deliver a great mobile app design, and by extension deliver superior UX.
1. New Relic APM
New Relic APM is the leading mobile app performance management (APM) software. APM software offers in-depth visibility into the data consumed by the app, detailed monitoring of vital parameters including network monitoring, and monitoring of how users interact with the app. It helps resolve issues affecting end-user experience and generates advanced trend analysis.
Using New Relic APM, app developers, could, for instance, generate crash reports on the fly, to identify the underlying reasons that caused the crash, identify the root cause of why the service is not as fast or reliable as expected, unearth and fix errors, and do more. Just a few clicks make explicit the bottlenecks that hinder performance.
New Relic APM especially scores high on transparency, making explicit what exactly takes place behind the scene, which code paths are running, and more. Using the tool enables developers to troubleshoot and improve the app on a proactive basis, rather than wait for errors or issues to flare up before fixing it reactively.
2. HPE AppPulse Mobile
HPE AppPulse Mobile is another popular APM tool, offering almost all the functionality and benefits available with NewRelic. It also offers some additional features, such as a tag list capturing the data end users generate through their interactions with the app. This tool scores very on its user-friendly nature, offering developers very powerful features without having to write a single line of code.
3. Dynatrace
Dynatrace is another tool that offers live performance monitoring, allowing developers to detect problems and nip issues in the bud before it grows and saps the vitality of the app. The app also makes explicit performance trends, facilitating diagnosis of performance and identifying degradation in performance over time.
4. Dell Foglight
Dell Foglight is yet another APM suite, making explicit the behind-the-scenes working of an app. This tool co-opts some valuable features, such as a central repository which saves time in analysis, and a high level of automation, which reduces manual works considerably. It is strong in history, enabling effective analysis over time, something not available with many other APM tools.
5. HP AppPulse Mobile
HP App Pulse Mobile documents user interactions with the app, logging their swipes, taps, and stretches the screen, to make explicit user behavior, and offering a blueprint for improvement. Tracking how users navigate an app reveals unintended obstacles, how users circumvent such obstacles, and at what point users simply abandon the transaction, resulting in lost sales and poor reviews.
HP App Pulse Mobile integrates with HP Haven big data analytics to analyze the performance and stability of the app, the resources the app consumes and identifies any issues plaguing the app. The tool generates a score that makes it easy to compare UX among apps, and also offers recommendations to fix the underlying root causes of issues connected with the apps.
6. AppSee
The AppSee tool makes explicit what exactly users are doing on the app. It offers a range of intuitive reports and materials, such as session recordings, analytics, and heat maps, which reveal rich insights into several areas of the apps, including the most popular areas of the apps, trouble spots, unwanted features, how users navigate the app, and much more.
7. Applause
The Applause tool taps into the power of crowdsourcing, to target groups of users who use the app and inviting them into a survey to test the app. Applause also offers in-house expert usability surveys, narrated captures, consultations, and more, all aimed at generating the right feedback for the app.
With mobility gaining widespread acceptance, and more and more functions being implemented through mobile apps, the stakes of a good UX has never been so important. Maintaining constantly high ratings and acceptance for the app is a challenge, and nothing beats professional help. When you partner with us for your app development works, you are guaranteed high-quality apps, customized to your requirements, and superior in all aspects. Our highly skilled, talented, and resourceful team makes it a point to pay finer attention to the detail and use their wealth of experience to deliver high-quality UX sure to gain widespread acceptance.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
The mantra of success in today’s hyper-competitive and tech-neutral age is offering unmatched value, topped up by incredible experience, to customers. With the focus on the end product, most enterprises overlook the fact that the software development team are often the front lines in delivering superior service. The software developing a glitch when an urgent work is pending, searching in vain for an essential feature overlooked by the development team, a convoluted process to achieve a simple thing are an all-too-common experience which frustrates a customer or the end user of the software.
Often such drawbacks are not because of any deep-rooted incompetency or incapability, but a result of lack of focus, or not paying attention to development process it deserves. The name of the game in keeping software developers happy, engaged and productive, all factors which have a proven correlation with end customer satisfaction.
Facilitate the Developer
The basic requirement to make developers happy is facilitating them. It is innate human nature that creativity and mentally intensive tasks such as writing quality code thrive only in an environment of freedom, where one can express their suggestions without fear of repercussions.
An open and transparent culture, with free flow of information, and without data silos is the basic and essential requirement.
Developers need to be empowered to take their own decisions, without having to run to their project manager for every small thing. Allowing developers to engage with the customer or end users directly, and freedom to make any changes that do not alter the scope of the project, goes a long way in empowering them and making them happy.
Side by side with creativity, human beings need very high levels of precision, focus and concentration to be able to write quality code. They require a comfortable atmosphere, with ready access to resources required to do their job well.
Another essential requirement, almost indispensable, is flex-time, and freedom to work from home. Creativity and inspiration never follow a 8 to 5 schedule.
Empowerment often creates a level playing field, allowing small startups to compete effectively with large behemoths, where the salary may be higher, but where organizational morass has set in, with an entrenched bureaucracy stifling creativity and freedom. There, developers may have to spend more time in paperwork, playing by the “rules of the game,” or worse, pampering egos, than do what they are meant to do – writing high-quality code.
Offer Perks
Lucrative salaries attract top talent, but perks ranging from on-site massages to unlimited coffee breaks, the ability to work from home, and more are the real motivating factors that attract top talent. The trick lies in understanding what developers want and design the perks likewise. HR plays a crucial role in this dimension, by talking to developers, and understanding what motivates them, especially during the recruitment stage. Flexibility, topped up by innovation in the delivery of perks and other benefits help the enterprise scale new heights in job satisfaction. Happy, engaged software developers produce high-quality results, which impacts everyone else involved in the development, delivery, marketing and sales of the product.
Forge a Shared Culture
The time-honored management concept of “hire for a fit” has never been more relevant than now. Competency aside, what matters above everything else is a cultural and emotional fit or shared values. Shared values, in essence, mean the company and the employee being on the same page with regards to striving to delight the customer, and seeking excellence in whatever work is done. On the software development front, this translates to the engaging the end user enthusiastically from the start to finish, resolving any questions and issues with calm professionalism. A solid project management system, complete with a collaborative platform, helps.
Create a Learning Organization
Peter Senge, the management guru advocates creates a “learning organization,” where the workforce continuously enhances their capabilities and keeps themselves relevant. From the individual, it requires inculcation of the attitude “Learning is a journey that has no end,” and the enterprise has to play the role of a facilitator, both by providing learning opportunities and forging a culture that encourages and value learning. Developers especially like playing with flashy new technologies. A competent developer, confident of his or her knowledge, is sure to add immense value to the end customer.
Forge a Clear Career Path
A brilliant artist or a top developer needn’t necessarily be a good manager / a leader. A well-deserved promotion up the corporate ladder may actually do more harm than good, both for the individual, who find his expression of creativity stifled and for the enterprise, who is stuck with a bad manager. The onus is on the enterprise to forge a career plan for their power-employees, with lateral promotions, or flexibility to continue the same job with a higher position if the situation so requires.
The stakes are high. The problem with an inferior product rarely ends with dissatisfied customers. In today’s hyper-connected age marked by the dominance of social media, customers can and do vent their feelings, resulted in a spiraling effect of bad image and lost potential customers.
The scramble for top talent has made developers, a pampered lot. A software developer who is even just a little bit better than the competition has the potential to generate a result that will bring exponential non-linear returns on the investment. Just as in professional sports, even a one percent advantage makes a big different in the end result. However, enterprises needn’t necessarily enter the talent rat-race. They can just as well enter into a partnership with us, who have a ready team of highly intuitive and professional app developers, ready to do your bidding. We have a track record of delivering several highly customized and dynamic mobility and other solutions to customers across the globe, cutting across industries and sectors.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Is e-Learning a Pull or Push technique?
e-Learning is a rage now, and for the right reasons. It allows the trainees to undertake the courses at their convenience, without the sessions being disruptive in nature. It also spares the hassles of organizing a physical training session. However, the effectiveness of e-Learning is still open to debate, especially since the crucial “face to face” interaction with the training is missing. The success of the learning intervention relies heavily on the approach adopted. The two major approaches are the “push” approach and the “pull” approach. One method cannot be said to be better than the other, with the right option depending on the situation.
The Push Approach
Many e-learning courses are heavy on information, but not interactive, meaning such courses merely “push” the information out to the learners. A typical “push” course makes explicit the objectives upfront, proceed to the course content, and at best may offer a quiz at the end or after a section. The success of the course depends on how well the content is designed and how well the content is visually engaging.
The push approach is relevant when all learners are on the same level and need to access all the available information equally. With the focus on information and not on the learning experience, it is quicker, cost effective and overall easier to construct e-Learning courses that push the information to the trainees.
The Pull Approach
The “pull” approach to e-Learning involves creating more interactive content, depending on what exactly the user requires. Changing the way the information is structured makes the course more engaging and interactive. Interactions, such as choosing one of the many options, “what do you want to learn next,” and more are embedded into the courses, making it more appealing.
For example, when explaining a concept, the push approach simply offers a page explaining the concept, complete with images and videos. The pull approach offers the same information, but only suggest ways to retrieve the information, leaving the user to retrieve the information in any proposed manner. It may also take the form of people exchanging information and discussing the concept, in a forum.
Another example of push technique in e-Learning is an interactive white paper or interactive infographic that asks questions and guides the trainee based on the answers given. The content mix would also include assessments, calculators, and videos, creating a highly personalized training material.
Instead of universal one-size fits all approach, the pull strategy focus on crafting the right types of reasons a person needs to pull the content. The information remains the same, but the way it is retrieved differs from user to user. E-courses allow the learner to “pull” what is required from the repository of available content offering autonomy in terms of accessibility and convenience. In other words, the method of delivery, or the learning experience, is customized for the user or user groups.
The pull approach is relevant when learners are at different levels, have different uses for the same content, or require access only to specific parts of the available content. The focus on “pull” technique is on both the content and the learning experience equally. This, however, makes the preparation of such courses complex and daunting. However, the results are often well worth its while, provided the course is structured well.
To Push or to Pull?
At a basic level, all e-Learning is in essential a “pull” technique, since trainees have to complete the course by themselves, without being spoon-fed by a trainer in a conventional training session, at a conference venue.
However, e-Learning courses can itself be designed in a push or pull approach.
On the face of it, there are inherent advantages in designing e-Learning courses in a pull model. Push techniques generally tend to be dry and requires the users to remain motivated to grasp the content. When attention is dry, the focus tends to fade naturally. With the interactive-heavy intensive pull techniques, complete with a healthy mix of audio and visuals, attention generally lasts longer. In any case, since users access only the contents relevant to them, there is greater focus, motivation, and effort. If the trainer includes group collaborative exercises, there is a good scope to boost team collaboration as well.
However, on the flip side, there is an inherent risk with the pull approach in allowing learners to take the all-important decision of deciding what to learn. It again requires learners with a high degree of awareness and drives to self-actualization, for them to access content that is actually relevant, as opposed to what seems most interesting or the easiest. Again, there is nothing to prevent an innovative curriculum designer to spruce up the “push” e-Learning course with rich audio, video, images and real life scenarios.
Push is conventionally held as the “formal” learning method whereas “pull” still has an unconventional and informal label attached to it. The push approach, the traditional approach, akin to the school curriculum, laid out module by module, is time-tested, scores high on familiarity, and ensures learners go through the topics they really require. The pull approach in a way incorporates the latest technological advancements to training but is still unfamiliar to many people.
The best approach depends on the industry, the skills and motivation of the learners, and the course curriculum. For example, there is little scope but to memorize all the safety and fire hazard regulations in place. However, for soft skills training, there is ample room for discretion, interactivity and simulation features.
Regardless of whether the e-Learning is designed in a push or pull approach, success depends on sound design and construction of the course. The technical part of the course is often underestimated. It pays to tie-up with a competent partner who can help you deliver cutting edge curriculum and courses, which is aesthetically appealing as well. The Upskill competency based training platform is the best choice in this regard, offering the unbeatable mix of the latest and most advanced technology, quality content and expertise, helping you deliver powerful e-Learning courses customized to your needs and requirements.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Training is a double-edged sword. While training is indispensable to eliminate the skill gap brought about by the introduction of new technologies, much of the training that takes place adds no value and is water down the drain. With the business environment getting tough, and top management seeking accountability for every dollar spend, business managers are now taking a long and hard look at their training strategies.
With conventional training methods failing to deliver the desired value, need to do something different becoming obvious, and among the various options, competency based learning is gaining traction.
What is Competency-Based Learning?
Competency Based Training is basically learning by doing. The trainee is given an opportunity to implement the acquired skills or knowledge, to confirm the training or the dissemination of knowledge was indeed effective. The evaluators prepare a set of criteria, to evaluate the ability, skills, and knowledge of the trainee, based on the observed evidence.
The proof of the pudding being the eating, if the trainee can perform the expected workplace role to satisfaction, training was indeed effective. Trainees are not expected to do better than others but simply do the task well enough to pass muster.
Does Competency Based Training Actually Work?
The very reason competency based training has gained traction is because it works. Empirical evidence reveals the application of competency based training being instrumental in the transformation of many employees, enabling them to perform individual tasks better, manage a range of different tasks, respond to contingencies effectively, seize the moment, and be more proactive.
Competency-based training measures the actual ability imparted by the training process, rather than the time spent on training. It delivers a fundamental shift in approach, by conducting training at the trainee’s pace rather than at the trainer’s pace. The training is complete only when the trainee demonstrates competency to do the job, regardless of the time taken.
Competency based training scores high on flexibility. Understanding the exact extent to which a person has the required skills, through life experiences, formal qualifications, natural talent, and other sources, makes it possible to customize the training program, without the individual having to waste time with others in a conventional training session, being thought what he already knows, to understand what he does not know. The positive impact such customization has on employee productivity and organizational efficiency is worth its weight in gold. The caveat, however, is a strong mechanism to measure skills accurately.
Competency based training puts the spotlight on defining the competencies, or the ROI. By making evaluation integral to the process, there is strict accountability and a clear evaluation of the extent to which training delivered the goods. The process of evaluation also gives accurate feedback on the extent of the gap that remains, and the additional skill-sets the trainee requires, to do the job satisfactorily.
Competency based training caters to the immediate requirements very well, so essential for today’s enterprise, where training aimed at long term goals are becoming increasingly irrelevant due to employee turnover and short shelf life of new technologies.
What about the Challenges?
Competency-based learning allows learners to attain mastery of each competency or skill at their own pace. A big practical concern such an approach raises is the severe time pressure faced by enterprises. Competency-based learning is, in essence, a sort of role-playing. Neither do today’s enterprises have the luxury of giving their workforce unlimited time to gain the required competency and nor can they afford to risk entrusting critical business processes to a potentially unprepared trainee, to see if he or she passes muster. The solution is a robust technology solution which makes sure the training takes place side-by-side with the job seamlessly, without being disruptive in nature.
Another often heard criticism regarding competency-based training is its ignoring social learning. Again, technology is the answer. A strong technology backbone, where the trainee is exposed to a collaborative learning atmosphere, and empowered with competency-based learning tools ensure a more engaged learning atmosphere, complete with open communication and full transparency among trainees, trainees, and the wider ecosystem.
Need for a Technological Backbone
Competency based training requires a strong technical backbone to ensure it works seamlessly, without being disruptive in nature. Technological solutions can be put to effective use to identify gaps during the actual course of work, measure the competency levels, and design appropriate training schedules. A good technology solution enables all these without having to waste time drawing up an elaborate exercise for it.
An effective technological solution also offers the following advantages:
- Automates the key tasks, sparing HR or other managers from taking the trouble to do so manually.
- Ensures the skill evaluation and gap identification exercise is carried out on a continuous basis, always updated to reflect the real-time situation, rather than as a one-time exercise which only reflects the situation at one point in time, and would become soon obsolete in a fast-paced world.
- Offers a unified repository of all training materials and resources, assigned to trainees on a need basis.
- Facilitates a collaborative learning atmosphere, offering a unified interface to draw in experts and other stakeholders to the training process.
- Facilitates record keeping, making it easy to track the progress of each employee, and draw the most relevant training solution, customized to individual requirements.
Up-Skill, a competency-based training platform offers the right mix of advanced technology, quality content, and expertise, empowering businesses to impart highly relevant and effective competency based training. The framework uses robust technology, comes with quality assurance, and encourages the creation of innovative solutions. Up-Skill’s advanced mobile app also ensures employees have the flexibility of accessing content and training material anywhere and at any time, catering to the needs of today’s workforce who require content anywhere, anytime, through the device of their choice.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
The spread of mobility has resulted in a proliferation of mobile apps. However, are apps superfluous when there are already highly intuitive, responsive websites which deliver the goods admiringly well?
On the face of it, mobile apps and websites seem as two sides of the same coin, but scratch beyond the surface, several differences emerge.
Accessibility
A mobile website is technically a shrunken-down version of a normal website, consisting of a series of linked browser-based HTML pages, and accessed over the Internet through the browser. A mobile app, on the other hand, is generally developed specifically for a mobile OS and configuration, and downloaded directly to the device.
Mobile website pages are indexed by search engines, and as such easily found. It is also easy to list a link to mobile websites in directories, and share such links through blogs, websites, and even in print media.
The visibility of apps is largely restricted to app stores. The apps cannot easily be pushed in directories, or the links shared easily. However, once installed, the app icon remains in the mobile screen always, and users may access it even offline. Also, once the initial trouble of getting users to download an app is done, the user is unlikely to go elsewhere.
UX and Design
Websites designed for mobile devices are generally different in appearance and UX, compared to conventional websites. Such websites often have larger icons and buttons to suit the touch-screen interface and improve UX. Incorporating responsive design ensures the web pages scale up or down, to be optimized for any sized device.
Mobile websites rely heavily on browsers to perform even the most elementary functions. For instance, it depends on browser features like ‘back button,’ ‘refresh button,’ and ‘address bar’ to work, with little scope to customize such basic features. The efficiency and seamless functioning of a mobile website depend on an up-to-date browser.
A mobile app is free of browser constraints and may be designed with elaborate and customized functions, co-opting ‘tap,’ ‘swipe,’ ‘drag,’ ‘pinch,’ ‘hold,’ and other advanced gestures. Such gestures may be leveraged for innovative functionality, and to perform tasks better. For instance, moving to the next page is much easier with a swipe than by having to press the back button.
Functionality
Mobile websites display text content, data, images, and video, just like any websites, but generally, have a limited range of options compared to a conventional website. Nevertheless, mobile websites are often cluttered with dense content, popups, ads, and other content of varying nature. Apps, in contrast, are designed to facilitate a specific function, process or workflow. The best apps are highly focused help users achieve something which cannot be fulfilled easily or seamlessly through the website. Some web developers try to give mobile websites the look and feel of an app, but often end up over-optimizing the website, complete with over-designed layouts.
Mobile websites are getting increasingly better at accessing functions such as click-to-call, SMS and GPS, hitherto considered the forte of apps. However, apps are still a better bet to access device functionality in a reliable way, especially the camera and the processing power of the device. Apps also facilitate a much deeper engagement.
Use Cases
Both apps and websites can be used to deliver the same content or functionality to users. However, both are best suited for specific purposes.
A mobile website, which offers ready access, scores over an app, which have to be downloaded first before the user can access the contents, when the intention is to offer ready content to a wide audience. However, for interactive situations, and use-cases involving complex calculations and reporting, and manipulated data, charts, and reports, apps are better suited than websites.
Apps are better to drive engagement. As long as the user takes the trouble to download the app, the odds are the user would open the app before trying to access anything else for the same purpose.
Flexibility-Customization Conundrum
It is far easier to update content in a mobile website, where changes to the back-end make it applicable to anyone who accesses the website. In contrast, to make changes in apps, the developer has to roll out updates for each app and push the same to the users. The changes apply only when users download the updated version of the app.
However, what the app lacks in flexibility to update content, it compensates in personalization. App also offers scope for greater personalization. Unlike websites, apps allow users to set preferences and be served customized content. Apps have the capability to observe and track user engagement, also leverage the device’s location capabilities, to provide users with custom recommendations and updates. One of the biggest advantages of mobile apps is the ability to send push notifications. Push notifications deliver click-through rates of about 40%.
Cost – Performance Conundrum
Apps generally cost more to develop and maintain compared to websites, for the simple reason a new version of the app has to be developed and maintained for each OS or platform. The mobile app development process has to be repeated for each platform. In contrast, a single instance website runs across all devices.
Again, apps compensate through superior performance. Well-designed apps perform actions much quicker than mobile websites. Apps store data locally on the device, whereas websites have to pull in data from remote web servers. Apps, by virtue of its high customization features, take proactive actions on users’ behalf, further speeding up things.
A mobile website and a native app are not necessarily mutually exclusive. What works best for any enterprise depends on several factors, such as the preference of target audiences, whether there is a critical mass of subscribers, budget on hand, intended purpose and required features. Many functions, especially marketing related, require both a mobile website and a mobile app. Generally, the mobile website is the first step in developing a web presence, and apps follow.
Ultimately, the proof of the pudding is in the eating. Mobile users spend 86% of their time on mobile apps and just 14% of the time on mobile websites. However, while an app offers several big advantages, the advantages realize only when the mobile app development is done the right way. Do not take chances with your app development process, and fritter away both your competitive advantage and investment. Get in touch with us to leverage our highly talented, resourceful, and experienced teams, who are adept in delivering cutting-edge mobile solutions.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
The customer is truly the king in today’s hyper-competitive environment. Businesses who are too busy to pamper the customer would soon find themselves free of hassles, as customers move elsewhere and the money starts to dry up.
Improving customer service is the name of the game when it comes to retaining customers. Providing a superior product that satisfies customer wants is the basic requirement to remain in business. But in today’s tech-neutral and information age, many providers can offer the same thing. As such, service becomes the key differentiator. Businesses who can offer superior products and back it up with top-notch customer service rakes in the moolah.
So how to go about improving customer service? Regardless of how customer service is to be improved, the underlying solution is to streamline workflow.
Need for Speed
Speed is of the essence in improving customer satisfaction. Today’s customers, born and bred in a fast paced world are attuned to getting things done instantly and do not like to wait. Forrester estimates 45% of US customers will abandon an online transaction if the business fails to address their concerns or questions fast enough.
Enterprises can respond with speed and agility only if they get their workflow right. Often, the required information is trapped in silos, preventing the executive from accessing it in a timely manner to serve the customer. In many cases, the customer interaction touch points are messed up that executives delay in contacting the customer who initiates a query.
Customers who cannot get in touch with a responsible executive when they need to are invariably lost forever.
Need for Accuracy
Along with speed, it is also important to get things right the first time round. It takes 12 positive customer experiences to make up for one negative experience. The implications are more ominous in today’s highly competitive environment where a wrong move must simply push the customer away to a competitor.
Automation drives accuracy. the A main cause for errors is disjointed systems and manual working. Many processes are still done manually, simply because no one has the time to digitalize it, or because the best quick fix to overcome a disjointed system is manual intervention. Automating whatever possible, and integrating manual processes to the enterprise system contributes to accuracy in a big way.
Need for Customization
Today’s customers prefer marketers to engage with them on a personalized basis. Even without personalized one-to-one interaction, deep segmentation to offer special discounts and services, location based instant-offers, and more, reaps rich rewards. There is also benefit in understanding the customer, and offering something of value, in terms of curated content.
The role of analytics is crucial in getting personalization right. Integrating big data analytics to the workflow allows the enterprise to gain insights about the customers, their background, buying habits, preferences, and more, and enable dealing with them
Need for Flexibility
Today’s businesses have no option but to fine tune their systems and workflows around the customers. The old functional workflow, or arranging workflows and systems according to organizational departments, and expecting customers to make adjustments are today a sure-shot recipe for disaster.
A case in point is the need to offer multiple touch points for customer support. Research by Salesforce estimate 61% of customers prefer phone assistance, 60% of customers prefer email, 57% prefer live chat, 51% prefer dealing with an online customer base, and 34% of customers prefer “click-to-call” support automation. Successful businesses build their workflow along such popular channels, rather than, say, not make available live chat because it is inconvenient for the workforce and an added overhead.
How to Streamline the Workflow
The root cause for disjointed workflows and silos that impede efficiency, and by extension come in the way of improving customer service is many work processes being developed on an ad hoc basis when the need arises, and such process lingering on. The enterprise needs to bite the bullet and review existing workflows, with an aim to smoothen it, keeping the customer in mind. Keep the end in mind, and work backwards, rather than try to define an end by defining the most convenient workflow.
It helps to adopt a granular approach, breaking processes into discrete steps. Such an approach allows the top management to set policies, the middle managers to issue guidelines, and empowers customer facing staff to do what is required at the moment. Needless to say, such an approach has to be accompanied by a culture of openness and empowerment.
In today’s mobility driven age, developing mobile apps and solutions for customer support and other critical functions allow employees to react instantly, and engage with the customer at the time of their choice. Powerful mobile apps, residing in the cloud, drawing in the most relevant information from all sources empower field service technicians, marketers, top management, and others, by enabling them to engage with customers in an informed manner, without dilly-dallying for the need of information or resources. It also allows customer service and other executives to engage with customers as soon as they initiate a conversation, equipped with full data.
Having a partner who knows their stuff is essential in developing solutions for streamlining workflow and improving customer service. An experienced partner can offer proven and practical data-driven solutions to solve your workflow issues effectively. When you partner with us, you can leverage our skilled and talented team for whom developing solutions to streamline your workflows is their primary focus. You can also leverage our years of experience in the field, and spare yourselves of expensive trial-and-error, or investment to reinvent the wheel.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new