Category: Business
Automation in the retail space improves efficiency, enhances the quality of service, and reduces the cost for all stakeholders. Retailers who realize this fact strive to offer innovative products and solutions, based on automation technology, to differentiate themselves from competitors.
Here are some of the ways in which retailers leverage automated solutions to optimize their operations and cut costs.
Digitalization of Tasks
Digitalization boosts the efficiency of manual and tedious, time-consuming internal tasks. While most progressive retailers have already applied IT applications and solutions in a big way, the emergence of IoT has given rise to newer solutions that take efficiency and quality improvements to a whole new level.
IoT based solutions like leveraging components such as RFID tags, NFC, sensors, and smart devices are primed up to disrupt the retail space in a big way. Retailers apply such solutions in almost all retail functionalities, including product search, checkout, analytics, inventory management, security, PoS, and vending machines.
NFC based payments systems, for instance, facilitate contactless payment systems, speeding up the process considerably, and doing away with queues.
Amazon GO, the checkout free, fully automated grocery store in Seattle offers a prototype of the future store. The store uses cameras and sensors to track what shoppers remove from and place back on the shelves. Amazon bills the customer automatically when they leave the store, using the credit card stored on file. Check out lines, often the major pain point in a retail store, become superfluous.
Starbucks’s “Order & Pay App”, allows customers to pre-order items when on the move. The order is ready when customers enter the store, sparing them the hassles of having to stand in a line. The app, in essence, replaces the POS terminal.
Retailers who invest in such solutions reap huge savings as a result of reduced employee and infrastructure costs. They also gain through increased sales resulting from increased customer satisfaction.
Automation of Key Processes
Automation of critical processes such as inventory control, filling out employee timesheets, invoicing, entering information from various PoS terminals to the accounting platform, financial management, point of sale transactions, etc., can improve efficiency and bring about big cost savings. An integrated point-of-sale system, for instance, spares the need to manually key in transaction information into the card reader or other systems.
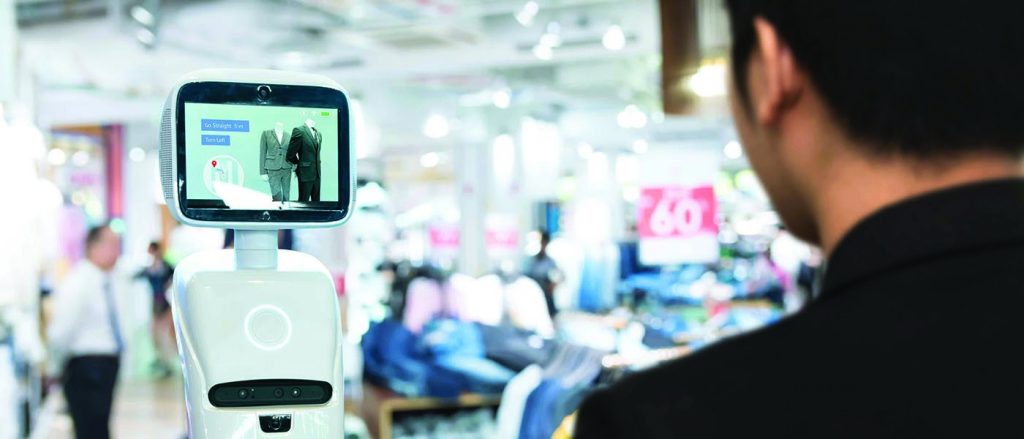
Many retailers have identified robots as a key tool to automate their processes. Evidence on hand suggests big efficiency gains and cost savings through the implementation of such innovative automation solutions.
A case in point is Walmart that has patented the use of robots in retail stores. Robots offer an effective and reliable solution to key issues such as insufficient staffing during peak hours, cleaning messy aisles instantly, and identifying theft with precision. Robots are excellent workers, and an HR department’s dream-come-true; they do not need a vacation, never get sick, arrive at work 100% trained, and do not slack. The deployment of such robots has saved millions of dollars for Walmart, in the form of reduced HR costs.
Another success story that retailers can set as a benchmark is that of Amazon’s Kiva robots. Amazon deployed these robots across its warehouses, in 2014, to automate the retrieving and packaging process. Amazon has already saved about $22 million per fulfillment center by deploying these robots, according to Deutsche Bank.
There is the added benefit of automated technologies attracting youth. A recent study by Fisch Restaurant estimates nearly one out of three customers in the 18 to 24 age group prefer ordering from the drive-thru at restaurants because “they don’t feel like dealing with people.” Likewise, McDonald’s automated ordering kiosks are a rage across Europe, relegating manual ordering to the second spot.
Personalize Customer Experiences
A major objective of applying automation technology is to enhance customer experience. Customers are the lifeblood of any business. In today’s age where choice is plenty, customers who feel dissatisfied or have to put up with difficulties to complete the transaction will leave. As such, retailers strive to create high-value, personalized interactions with customers.
The first step towards facilitating the customer is to understand their preferences and requirements. Today’s customers demand highly personalized services. Research by TimeTrade reveals 36% of shoppers do not like to wait for items to ship, 30% of shoppers prefer advice on what products to buy, and 90% of customers will make a purchase when they receive assistance from a knowledgeable store associate.
Retailers may personalize each customer’s experience by harvesting the growing volumes of customer data available across social and other channels.
Retailers could use such data to offer location sensitive offers. In the past, retailers strove to deliver contextual product recommendations. Today, they strive to rationalize the shopping opportunity. 7-Eleven, the global convenience brand targets customers based on location and weather and delivers customized and time-sensitive offers. For instance, if it has started raining in the city or a specific area, the company may offer discounts on umbrellas to customers who are outside their homes, and in the vicinity of the stores.
Lowe is all set to introduce LoweBots – multilingual, autonomous customer assistance robots. The pilot program has been announced in 11 locations across the San Francisco Bay area.
Personalizing customer experience goes far beyond creating brand loyalty and increasing sales. By understanding the customer, the retailer can target and optimize the effort and investment on the customer, without wastage. For instance, if a customer is known to prefer shopping alone without the aid of a salesperson, the retailer can spare the time and cost associated with deploying the salesperson to serve the customer.
Integrate the digital ecosystem with the real-world shop
The most common manifestation of integration of the digital ecosystem with brick and mortar shops are customer apps which aid the shopper as they shop in the physical store. Such apps make shopping easier by listing detailed product features, offering demo videos, and providing customized geolocation-based offers. Such apps also facilitate omnichannel sales. The shopper, may, for instance, opt to shop at the store and get the product delivered through an e-commerce channel.
Retailers need to complement such apps by installing beacons to identify customers who enter the store premises. They could then personalize the experience based on the customer’s preference and demographics. For instance, leading brands such as Sephora and American Eagle identifies each customer to deliver discounts on their birthdays.
Retailers would also do well to take the transaction to the customer without them having to wait in a long, slow-moving checkout queue. Even if red-hot IoT based technologies such as “Amazon’s Go cashless store” is beyond a small retailer’s budget, they can still adopt the Tablet PoS system that allows their staff to check out customers in aisles, doing away with the cumbersome check-out queues. There could also be a facility for online app-based checkout.
Examples of retailers who have applied innovative new automation-based products to enhance customer experience are many. Westfield London, for instance, applied an RFID technology driven smart card system, enabling customers to park their cars without needing a ticket. This is a big improvement over the manual process of refunding parking tickets, sparing the hassle of customers having to present the parking tickets and claim a refund from the store.
Likewise, augmented reality chat bots not just enliven the customer service experience, but also offer greater insights into the customer, reducing the effort and time for the customer service agent.
Audit and Redesign Internal Procedures
A sure shot way to boost internal efficiency and reduce costs is by reducing internal processes by adopting Lean methodologies.
The prerequisite is to conduct a thorough audit to identify supply chain strengths and weaknesses and identify and quantify waste. Retailers can optimize inventory, and pinpoint other areas of improvements.
Constructing an end-to-end lean value stream flow, focused on minimalistic procedures, improves transparency, and makes it easier to review and eliminate avoidable procedures. It creates a standardized workflow with all glitches and kinks ironed out, while co-opting abnormal workflows, catering to all contingencies such as a power failure which results in many POS terminals going down.
Automated retail workflows come integrated with analytics and a CRM suite, creating a highly powerful system, and facilitating further cost-saving methods such as just-in-time inventory, and real-time stocking.
Optimize the Workforce
Automated algorithmic-based labor scheduling tools calculate store workload and optimize staffing, with a high level of accuracy. Custom made algorithms consider factors such as store format, operating hours, backroom configurations, labor regulations, ergonomic considerations, and all other factors, to schedule shifts seamlessly. Such automated systems optimize staff at peak hours and ensure they remain at their productive best. It also reduces absenteeism. The investment is such a solution also delivers a big motivation boost for the workers, reducing turnover rates and decreasing HR costs considerably.
An advanced workforce optimization software, powered by advanced analytics, integrates the customer journey with the employee’s schedule. For instance, if an employee has already struck up a relationship or a rapport with a customer, the employee is assigned to the same customer as far as possible. Such software also ensures high levels of compliance to deliver operational control and business confidence.
Optimize Merchandising
Retailers do not make money by blindly stockpiling inventory. The inventory has to sell. When introducing a new product, smart retailers ask pertinent questions such as “Will the product sell?” “Can the store make money selling the product?”, and so on.
Having introduced a product, a retailer’s prime focus is to optimize the handling of the product inventory; the ordering processes has to be streamlined by identifying the most optimal order-quantity and should be integrated with the sales forecast to eliminate stock-out situations. A good, automated inventory management suite automates all these processes, boosting efficiency and reducing costs.
Automating the merchandising and product exposure process offers retailers the infinite capabilities offered by machines, as opposed to the finite capabilities of a human employee. It also facilitates easy integration of disparate data sources, and comprehensive analytics based on live data. Customers who enter the store are presented with the most optimal inventory, in the best possible way. The analytic engine, could, for instance, draw up the price-point resulting in maximum sales, and tweak the pricing and merchandising strategy accordingly. The net result is the elimination of wasteful trial-and-error methods and saving time. It also ensures the exposure of more products to more people, increasing sales.
Embrace analytics to improve processes
The application of IoT based sensors has taken data analytics to a new level. Retail analytic solutions now aggregate data from video camera feeds, beacons, Wi-Fi, POS systems and other components, and subject such data to big data analytics.
Retailers could gain valuable insights from such analytics. They could measure various elements in the buying process, such as the products each customer inspected in detail, tried, and compared. This information, available in easily digestible reports and graphs, allows retailers to optimize their inventory, eliminating slow-moving inventory. They could also fine-tune prices to boost uptake of inventory. More importantly, such processes become automatic and precise, with a high degree of accuracy, reducing the costly trial-and-error methods usually associated with the processes.
Mindtree’s 2017 study, “Sixth Sense of Retail“, reveals how rapidly evolving digital trends such as social media, mobile applications, and automation reshape the way retailers engage with customers. About 51% of young shoppers (16-24) are comfortable with automated technologies and would visit robot-driven stores, but as high as 78% of older shoppers (55+ years of age) were apprehensive about this trend. Likewise, while 44% of men, cutting across age groups are comfortable with automated technologies, only 30% of women are similarly comfortable. As such, retailers would do well not to blindly embrace automation, just because someone else is also doing it. Rather, they should study their business, understand their customer, and apply automated technologies judiciously.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
The perennial build versus buy question continues to haunt enterprises in search of software solutions. Off-the-shelf software is ready-to-use once they are installed on a computer or device. Custom software, on the other hand, is developed according to specific requirements and specifications.
There is a huge gap between these two technologies in terms of performance, functionalities, and usability. Each option has its own merits and demerits, and here is a rundown of the same.
-
The Question of Cost
An off-the-shelf product will typically be moderately priced when compared to a custom developed product; the obvious reason being that the cost involved in developing an off-the-shelf product is distributed among a large number of buyers, and thus pricing is spread across several licenses to be sold. A tailored product, on the other hand, is specifically developed for a client, and as a result, all the development expenses will be borne by that individual client. Hence, considering the costs, it might seem that an off-the-shelf product is a right way to go.
Purchasing software off-the-shelf also offers an accurate estimate of the cost and valuable support for everything that lies ahead throughout the lifecycle of the project. But, in terms of performance, they might not be as apt as custom-made products.
Many enterprises underestimate the time and resources required to develop custom software in-house. The development team needs to take into account, not just the initial design, build, test, and implementation costs, but also the lifetime cost required for support, headcount enhancements, patches, and general maintenance. There is also the issue of costs for the inevitable functionality enhancements and upgrades in future to consider.
Even when the enterprise has the adequate budget for in-house custom software development, they still have to consider the availability of a skilled team in-house, or access to such a team through outsourcing. The outsourcing route in a way offers the best of both worlds, or the availability of ready resources to develop software the way the enterprise wants it.
-
Which is easier to implement?
Coding is getting easier by the day. Gone are the days when programmers spend weeks on end ruminating lines of code even in their sleep. Today, coding is taught at the high school level, and the proliferation of open source means code snippets are readily available for just about any functionality. What’s more, intuitive drag-and-drop interfaces make it possible to roll out highly advanced applications without even writing a single line of code. Many such platforms, such as QuickBase, Zoho Creator, Salesforce Platform, FileMaker, make the task of developing highly intuitive apps and software solutions easy. A basic level of code knowledge would suffice to make the required customizations, quickly.
However, the ease of coding doesn’t mean app development is a piece of cake. Coding is just one aspect of the overall app development process. Requirements gathering, app design, UX, testing and other critical aspects of the software are all challenging tasks which require highly skilled and experienced professionals.
While, theoretically, developing a custom software may seem like an attractive and manageable proposition despite the high level of skills required, on the ground, enterprises could find such developmental tasks to be a distraction from their core focus. The internal IT resources may already be engaged in routine maintenance activities, and development works could pose a drag on their efficiency. With custom software, the enterprise will have to bear the brunt of all the drawbacks until the glitches are ironed out, and the software finally matures. With off-the-shelf software, the enterprise can learn from the mistakes of others.
Moreover, the core focus of the developers of off-the-shelf software is the software itself, and they incorporate agile and other best practices. They also keep abreast with changing technology to remain ahead of the game. Therefore, before it’s released to market, the software will be tried and tested extensively, and glitches ironed out.
However, purchasing software ‘off-the-shelf’ is also not as easy as picking apples off a supermarket shelf. The procurement process is elaborate, with the source-to-contract process raising specific challenges. The in-house team would still have to perform the requirement gathering exercise, to find a suitable product. Such ‘off-the-shelf’ programmes also have to be evaluated for UX, ease-of-use, supporting infrastructure required, and other parameters, all requiring considerable effort from the enterprise.
-
The Need for Deep Customization
As a rule of thumb, developing the software in-house is a good idea if the software requires extensive customization. Enterprises which seek to develop basic and generic software to support common routine functionality, such as solutions for emails, discussion forums and file sharing are ‘reinventing the wheel’. It is foolhardy to develop software in-house when industry majors such as Google, Microsoft, and others offer advanced, scalable and secure solutions, customizable with the enterprise name. Likewise, those seeking a CRM suite would do well to pick up any of the ready-made CRM suites available in the market, such as a Salesforce CRM, HubSpot CRM, Insightly, or Zoho CRM. Most of such suites are highly matured products offering a high level of functionality and the option to pick-and-choose the required modules.
However, the devil lies in the details. When the off-the-shelf software is not matured or modular enough, it may clog systems with unneeded options even when fitting organizational needs well. In such situations, creating a custom software can eliminate the excess and ensure bloat-free software, optimized to the exact needs of the business.
-
The Challenge of Integration
In an age where data analytics is a valuable source of competitive advantage, enterprises need to ensure seamless integration of the software with other enterprise systems, especially the back office and finance systems. Marketers and other customer-facing representatives require complete access to real-time interactions, without being hindered by data silos, for which seamless integration is imperative.
The extra time and investment in developing custom software may well be worth its while, considering the benefits of seamless integration.The developer would consider the existing system when preparing the blueprint for the software development project, and make sure the new software functions smoothly within the existing IT ecosystem.
-
Upgrades
Off-the-shelf products have regular updates, which might not be all that heavy on the pocket. Also, if you go for a quality product, you might also enjoy flawless customer support. But sometimes, they might not get updated for a long period of time, due to which you might end up working with an outdated product causing a negative impact on your business.
With custom software solutions, you have the freedom to make whatever changes you want, whenever you want. You are always independent regarding the decisions you take for the software. You don’t have to wait for new releases and introductions, to add features to your software. Whether it is an upgrade or changes you need to make to include new tasks and operations, you can get them done by custom software experts at any time.
-
Nature of the Enterprise
The technical factors and benefits notwithstanding, the nature of the enterprise can also have a big say on whether to opt for developing custom software or purchasing software off-the-shelf.
Smaller companies rarely have the budget, time, or resources to create custom software. Their requirements are unlikely to require complex integrations either. As such, an off-the-shelf solution would probably fit their needs. However, at the same time, the extra effort and investment in developing custom software may be worth its while, if the business has to expand its footprints. Developing a custom platform can create a more streamlined process for a business. Custom software is easily scalable and replicable. Off-the-shelf software is unlikely to provide such scalability without duplicating the investment.
Another important dimension to consider is the end-user or the people who use the software. The off-the-shelf software comes with a complete ready-to-use package, tested for all bugs and has gone through extensive usability tests. Whereas, the custom software requires extensive investment in training users. The process may also involve some trial-and-error, with each version improving on previous versions. The implications on business operations during such a trial-and-error phase can be debilitating.
Custom-made products are generally quite flexible and of course best suited for companies with specific requirements. Some other benefits of custom software solutions are:
-
Scalability
Scalability is one of the most important factors to consider while choosing technology for your business. Your software should be scalable enough to accommodate the present requirements of your business and also make room for future additions. As your business grows, you might have to add features and maybe even departments to the software you use. Hence, it is always better to get your software built in a scalable way. Off-the-shelf solutions do not have this facility.

-
Competitive advantage
You get to use a software made exclusively for your business with all kinds of unique features and specifications that other businesses don’t have. Hence, you gain a competitive advantage over your competitors, with your unique solution.
If you are building a solution just for your business over its specific requirements, a custom software would be perfect and hence satisfaction would be guaranteed. As experts once said, you need to adopt software and align it with your business process and not the other way round. You don’t just adopt a rigid software and try aligning your processes around it.
To cut the story short, there is no conclusive winner in the build versus buy dilemma. The best option depends on the circumstances. However, making the wrong decision can be costly. For this reason, it is imperative enterprises carefully evaluate the pros and cons of both options, and rationalize based on the specific circumstances surrounding their enterprise. When making the trade-off, the primary concern should be the on the efficiency with which the software allows them to serve their customers and other stakeholders in the most effective manner.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Why do retailers undertake operational improvement?
Enhancing operational excellence will improve customer satisfaction, reduce compliance cost and optimize procurement. Today, retailers are taking a closer look at different aspects of their operations to improve customer experience. Top-notch retailers implement new technologies and processes on a continual basis to boost operational excellence.
This infographic lists 8 ways to boost operational excellence in retail stores.

If you are into Retail, sell things online or plan to start doing so in near future, or is a consumer of any type, this infographic is a must-see.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
We are living in an era of unprecedented changes.The industrial revolution brought in an entirely different range of new material good which improved people’s lives. Today, we are witnessing the next big revolution which is transforming the lives of millions better known as revolution 4.0 or popularly coined the Internet Revolution.
The e-commerce dilemma
The e-commerce Industry faces a bunch of problems like maintaining customer loyalty, unwanted product returns, price wars & the real competition with brick & mortar based businesses.
Let’s focus on one problem for now & understand how we could solve it properly. Customer loyalty is very core to many businesses, as they believe that their customer is their king. But, customer loyalty between e-retailer and customer is built on various factors like shopping experience on the mobile app/website, prompt delivery of goods and finally the real quality of goods as well.
When it comes to building customer loyalty, e-retailers don’t solve the basic problem i.e on-time customer support. Instead, e-retailers usually try to build customer loyalty by offering hefty discounts, unwanted promotional activities and at times with gamification.
Taking customer support offline
Customer support should be the first priority in any type of e-commerce business because at the end of the day your customers should remain happy. Any business can provide support to its customers based on the infrastructure and resources available. It can be done online & offline depending on the support requests received every day. Offline Support can be done simply by sharing a helpdesk/customer support number with your customers.
Few things to take care while setting up an offline support desk is as follows:-
-
24/7 availability
A 24-hour open hotline is an added advantage as well as a USP for e-commerce business, usually, customers tend to buy things from places which provide round the clock support. The hotline reaffirms the trust and raises the credibility of the customers online.
-
Special number
It is very easy for people to remember a special or fancy number. The key here is to have a number that resonates the brand value of the website as well. Moreover, with a special number, the brand positioning of your website gets a certain level of upliftment.
-
Open lines
Generally, customer support centers miserably fail to provide support to everyone who calls in. The call drop rates are very high for support centers which receive a high number of requests. It would be impossible to attend to each and every call so that customers need not wait for a long time and have enough support staff to take support requests.
-
Interactive Voice Response System
IVRS is an “easy to implement” the system for businesses who receive more than 150-200 calls/day. IVRS has many options which can be configured manually and the IVRS System can be integrated to the main Support Network of the business to make things easier for the customers as well as the support staff. Care should be taken about how perfectly the IVRS can be integrated into the existing system.
-
Customer support script
Customer support script which reflects the values & ethics of the business must be followed by the support staff and customer support managers should ensure that the script is being adapted promptly because they are the voice of the business and whatever they say has a direct impact on the reputation of the business. If the median age of users in your user base is more than the age of 40 years then offline support is the best, because that generation still believes in the power of telephone.
Taking customer support online
Online Support can be provided using many platforms which is readily available in the market. Conventionally, online support is done using support tickets & Live Chat, essentially a helpdesk software where support agents resolve or escalate the support request from the customers ensuring that every customer is given equal priority. Innovation in this space is always a plus provided it increases customer loyalty, retention and most importantly brings in value.
Few things to take care when providing Live Chat or Ticket Based Support is as follows:-
-
Proactive & quick response
Customer support executives must be trained to provide support proactively & ensure that the customer doesn’t have to wait for a long time to get the response.
-
Think of the customers as brand ambassadors
The sole reason a customer leaves a place of business is based on the way they are treated hence always think of customers as your brand ambassador.
-
Controlling the nerves
There would be moments when the customer might be on a rage and is berserk with different kind of provocative words. Responding to the customer with a cool head and best way out is to think ahead and provide a solution for the customer rather than respond aggressively to the moment. Always be prepared for such scenarios.
-
Staff training
Training the staff to use the helpdesk software is an added advantage it would reduce the fatigue in the initial days of support
-
Self-service
Maintaining resources online like a knowledge base, FAQ, forums, tutorials which to close to users and in doubt-generating places.
-
Measure, monitor and improve
It is often forgotten that support efficiency can be measured. Keeping KPIs and finding ways to constantly improve them would certainly add tremendous value to your business as well as the Happiness Index of the customers. Come what may, the ultimate goal of the customer executive should be to provide 100% customer satisfaction.Taking support online or offline completely depends on the nature of business & the value addition you wish to give your customers. And, it is important to keep a check on the additional expenditure incurred to keep the support infrastructure in place.
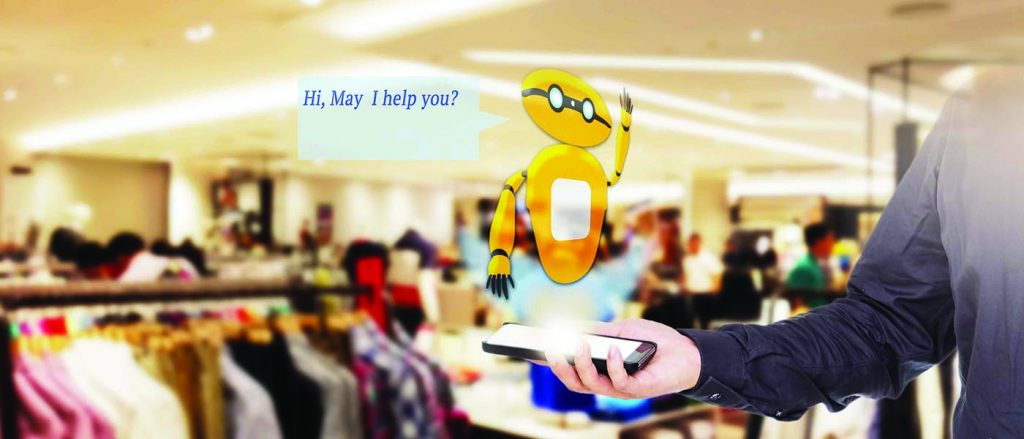
The era of chatbots is here
Powered by cutting-edge Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning Algorithms presently there are many chatbot services available in the market which can be easily used by any e-retailers to give an immersive & intuitive support mechanism for the customers in almost any messaging platform.

Chatbots are a simple to setup and can be integrated into any website, with many services online chatbots are presently being used by many small-scale e-retailers to run their support system. The advantages of having chatbots are the control you get over the scripts and the knowledge base the chatbot has access to. Moreover, compared to real human, the cost required to maintain a chatbot support system is very less. Chatbot certainly is a lucrative option for entrepreneurs who wish to cut cost on the operational side but customer support without a human touch has its own limitations as well.
Major Takeaways from Having a Support System in Place:-
-
Retains customers
When your customers are happy, he would come with repeat orders often. The relationship you build with the customer would have a lifelong impact on the success of your business
-
Creates word of mouth
A good customer service certainly generates excellent word of mouth and there is nothing better than word of mouth to promote & market your business. If we look at the success of many e-commerce websites, we would find that word of mouth has played an exceptional part.
-
Profitability
When the service is good, word of mouth and references are also good. It is very certain that your business would acquire more customers at a fraction of a cost you were supposed to. The returns you earn would be certainly much more than the returns you get by using the conventional form of marketing to promote your business.
-
Motivation for you and your employees
When a customer praises your business, it also boosts your employee morale. Naturally, over a period of time, your confidence rises on your business and you now know that giving good customer service is the key to build confidence in your employees, who will be empowered enough to keep their customers happy.
-
Competitive Advantage
Last but not the least, your customer service and the manpower that you employ for service can become your competitive advantage. If your employees themselves are building relationships with customers, then they will not allow a competitor to enter or place toehold. Hence, your business becomes sustainable and competitive and difficult to beat.
Thus, as you can figure it out yourself now, an extraordinary support system is key to the success of your business and it not only impacts your customers it keeps your employees also on the run to grab a pie in the market. Grow your retail firm multifold by seeking our expert advice. The sooner you build a competitive advantage, the better it is for you and your business.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Making a detailed business plan is a tedious process that takes a long amount of time and doesn’t exhibit dynamic properties. Apart from the hassles of writing a traditional business plan, there is no guarantee that someone will read it properly. Also, due to the ever-changing market, chances are that the plan is outdated by the time it has been finished. To resolve this issue and help kick-start businesses in very little time, Lean Business planning is the right way to go.
What is Lean Business Planning?
As the name suggests, the Lean Business Planning is one of the latest and effective methods that replace lengthy business plans with a 20-minute planning process. It basically takes the essence of major points in a business plan and focuses on the smaller steps to review results and create incremental results. Such a dynamic planning that is simpler and faster helps in starting and growing successful businesses quickly and at the same time reduce the risk of failure.
How does it work?

Lean Business Planning is a method that uses smaller steps with consistent course tracking and corrections. It wastes very little time by streamlining the essential points required for the business to function or start smoothly. The plan will include answering the following questions –
1. What does your Business intend to do?
This is highly important as it forms the key value proposition to your customers. Your identity for the business is the beginning of any lean plan and should be described in a single sentence. It is pretty much identical to answering a personal ‘What do you do?’ question.
2. What are the problems you are solving?
Every business’ intention should be to solve a problem that a customer faces. This should be the space where you define the problem that you have surveyed and plan to provide a solution to.
3. What is the solution?
Here you have to define the product or service that you will provide in a single line. Basically, it should end up being a solution to the above problem question. The answer should be crisp and clear without adding too much meat in the description.
4. What is the market you have identified?
Here you will have to put a few pointers that will describe your ideal customers. This is an important part that shows how much potential you have to build a sustainable business plan. It requires In-depth market research that helps in putting forth your point in a strong way.

5. What is the competition in this segment and how are you different?
This section should be used to put forth the competition you have identified in this segment. Also, phrase down a sentence or two describing how your business will be better or different than them to achieve market dominance.
After you have dived into answering these questions, you will have to strategize a way to start testing these plans. Float these plans across and go to the market to see the response. A good thing about a lean plan is that it doesn’t take a lot of time to read and get feedback. Once you have a list of issues identified, you can start to revise the plan. Remember, Lean Business Planning is a continuous process where you keep revising and testing the plan over and over till you achieve the most efficient of result suitable for your business.
If you still have doubts, a good way to make a plan is to check few online template or better to seek help from professionals who are highly trained in making foolproof plans and suggest the right path to help start or grow your business.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
The open source revolution is on. More and more enterprises are joining the open source bandwagon, to develop their internal and customer-facing apps. Free availability of source code, unbridled flexibility, gross reduction of app development time, resilience, and several other advantages prompt the move. But with great advantages come great risks as well.
The very nature of open source leaves the enterprise app development team with little control over the source and nature of their code. The odds are high that open source code may come with vulnerabilities, open for hackers to exploit.
Technological advances cut both ways. While technology may be used to beef up security, it also enables hackers to update their toolkits, and add any newly discovered vulnerability to their automated scanners. The odds of any application using flawed code being quickly found and exploited are generally high, more so when the open source library in question is a popular one. To make things worse, such hacker toolkits are freely available now.
So how do enterprise counter the hacker menace and ensure they can still reap the benefits of open source?
Be Very Careful of Downloads
With dozens of different open source libraries, tools, frameworks, and code snippets freely available over the Internet, there is a very good chance the variant chosen by the enterprise may have vulnerabilities. Even the hugely popular Ruby on Rails web application framework, with a very wide user community known for prompt updates, has been inflicted with several security vulnerabilities, placing 200,000-plus sites at risk of attacks that could lead to remote code execution.
Opt only for versions of open source libraries maintained by established consortium, dedicated to the cause of enhancing and maintaining the software. Such consortium would have a stake in the code. They would almost certainly be supported by grants from generous sponsors, enabling them to issue prompt patch updates, when a vulnerability is discovered.
Enterprises, for their part, need a clear policy on the usage of open source, loaded with:
- A white-list of trusted websites, from where the source libraries may be downloaded. The most reliable options are the websites recommended by Open Source Initiative.
- A list of security do-and-don’t, to prevent system admins and other users from downloading spurious open source software from dubious sources. Have a well-documented security policy, with clear guidelines on installation and maintenance of open source.
Prefer source code to binaries wherever possible. Most open source products are available either as source code or in package formats or binaries. Binaries offer a far greater level of risk, as there is no telling whether it has complied with the associated source code after all. The best practice is to download the source code directly, verify it against the provided MD5 checksums for integrity, and analyze the code for any latent vulnerabilities, before using it to develop apps.
Establish a System
A commercial closed sourced suite is developed through a structured and formal procedure, such as conducting a requirement analysis, defining the acceptance criteria, evaluating the product, comparing the product with competitive options, testing the functionality and security features, and more. Open source code may not necessarily undergo such kind of scrupulous evaluation or validation. There is no short cut but for the app development team to establish a method in the madness themselves.
Have a process in place to ensure adequate control, and to update all third-party code promptly.
Analyze the environment to identify possible threats. For instance, using popular open source libraries makes it that much convenient for attackers to identify vulnerabilities and launch attacks. However, at times, the biggest threat may not even be external, but malicious insiders. Understand the various ways in which the system could be attacked, and protect data accordingly.
Also, have a policy in place to govern code sources. Some teams may find they need to reduce the number of different code sources they use in order to manage them effectively. Within the framework of such policy and analysis:
- Create and maintain an up-to-date list of all third-party code in use, including all dependencies and sources. Designate a point person for each such code, to track mailing lists, news and updates.
- Avoid ad-hoc installations. Evaluate any open source considered for an enterprise use, and gather accurate information about the product.
- Institute an emergency response plan to execute critical releases. Internet facing apps often require a swift response to prevent attackers from exploiting a newly discovered vulnerability.
- Institute a dedicated team of system, network and security administrators to implement the policy and also review the policy from time to time, depending on the changes in business environment.
Apply Security Tools
Policies and safeguards can only safeguard to an extent, and require reinforcement through effective security tools.
Many open source projects do not issue patches, and rather just release a new version that fixes the problem.
The following are some of the tools worth considering:
Source code scanners such as FlawFinder and RATS (Rough Auditing Tool for Security) identify potential security problems in the source code. These source code scanners undertake pattern matching to highlight the areas of the code that has potential vulnerability and pose security risks such as buffer overflows, racing conditions, shell meta character dangers and poor random number acquisition.
- Vulnerability scanners such as SARA (Security Audit Research Assistant) and Nessus scan the network for vulnerabilities.
- Adopt a defense-in-Depth strategy, or a layered approach to securing the network, deploying the most effective security tool at all levels, from, application to the network.
- Configure the network properly. Disable all unwanted services, adopting the policy of “deny by default unless explicitly permitted.”
- Assume the network will be breached, and have effective measures in place to contain the menace, such as encryption of sensitive data.
The stakes of security breaches are high. The penalties, damaging lawsuits, and erosion of customer confidence can bring down the enterprise in itself. The most effective and risk-free approach towards adopting open-source is to partner with an experienced partner, like us. With us, you can leverage our considerable experience in not just developing cutting edge solutions using the most relevant open-source tools, but also take the most effective measures to ensure top-grade security.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Few lines about Varghese Samuel -CEO of Fingent Corp
Mr. Samuel is the Founder and CEO at Fingent Corp, a Global Technology company founded in 2003. Samuel’s ability as a leader, to span a breadth of businesses and technologies has enabled Fingent to build and deploy technology platforms which realize tangible business benefits for Enterprise businesses across the globe.
Over the last couple of years, he has led Fingent’s transformation to the cloud-based services business – Products and services that Fingent currently offers leverage modern cloud platforms and frameworks. Samuel has been a Technologist and an Entrepreneur leading technology innovations over the last 20+ years. He has a diverse background in the broader financial services and healthcare industry, and a proven track record of transforming businesses by creating innovative technology solutions. Samuel received a Master’s Degree in Engineering from Indian Institute of Technology, Mumbai India.
1. Give us a brief introduction about your company.
Since our inception in 2003, Fingent has pioneered custom solutions that have become central components in our client’s business success. Our technology and industry expertise enables us to partner with clients to deliver sophisticated solutions rapidly and on budget. We apply modern design principles, together with the latest in mobile, cloud and desktop technologies to help create solutions. As an organization, our primary focus is to build technology solutions that help businesses simplify/streamline their existing business processes, prepare for future growth, offer new services, reduce operational overheads, lower costs and help organizations connect better.
Fingent has been a recognized force to reckon in the technology space as we have made significant investment in producing advanced software products and platforms that will transform the technology industry.
2. What are the services you offer to your clients?
Fingent has been building custom enterprise business applications since inception for major corporations, small/medium businesses and startups across the Globe. As a pioneer in delivering technology driven innovations, we have segmented our focus areas into 8 Strategic technology Business Units, to better respond to client requirements. Our Strategic Business Units are as follows
● Microsoft
● SAP
● Enterprise Mobility / Digital
● Open Source
● Dev Ops and Infrastructure management
● QA
● Product conceptualization, including UI/UX
● Data Analytics
Most of our clients prefer to opt-in for services spanning across BUs for a single program or for multiple projects. Key areas include:
● Technology consulting ( including strategy, review, and intervention)
● Software product development including PLM
● Business process automation
● Digital Marketing
3. In this intensely competitive era, what technologies, services, and project model can give you an edge over your competitors?
Our vision is to be acknowledged by our clients, people and our shareholders as the leading strategic technology partner in our market.
We will deliver this vision by providing high-quality Software & product development, IT infrastructure, project management & IT Consulting services enabled by our people, technology, and assets and supported by our committed vendors and partners.
4. After service is a necessary part of development. How do you provide customer support to your client?
We have always prided ourselves as our client’s extended technology wing. We have always focused on, not just building solutions, but, delivering value. And as extended partners of our client, we ensure that our solutions and products are always catalysts to their growth. We have account managers and business analysts who act as single point of contact for every client need. Our dedicated infrastructure and quality assurance team ensure that we deliver quality solutions that keep our clients a step ahead in the market.
5. Give your opinions on how far this app revolution can make a difference in the technology world?
We already have many personal-use apps exploiting the hyper-connected, hyper-local, hyper-personalized environments provided by mobile devices. Apps and the connected cloud-based ecosystems have dramatically transformed the personal-tech space.
However, the Enterprise Tech world has barely scratched the surface in exploiting apps for innovation and business value creation. While Enterprise users demand mass market like apps and their cloud counterparts, security and cultural challenges remain key obstacles. The challenge is to find the delicate balance between controlling mobile devices and yet freeing employees to use them efficiently. CTOs and CIOs managing Enterprise IT teams can leverage the app (and cloud) revolution to deliver significant value by:
- Placing mobility and mobile devices at the heart of their digital workplace strategies
- Deploy management policies while educating users and bringing transparency to compliance
- Provide the best Rewards versus Risks balance for the apps deployed across various employee segments
- Manage the device lifecycle – purchase, usage, and disposal
Enterprise mobility is complex. At Fingent, we can help traditional IT teams upgrade their Enterprise Mobility strategy to deliver tangible business value, by leveraging the app revolution.
6. What latest technologies and tools you’re planning to implement for mobile app development?
We prefer to use tried and tested robust technologies to create both native and cross-platform apps across – iOS, Android, Windows and Blackberry devices. We carefully evaluate new and bleeding edge tech before considering them for production use on client projects. While there are a number of tools we are evaluating, we are excited by the recently announced Azure App accelerator and Telerik Progress platform. Long term – we believe that AI and Machine learning will significantly alter the app development process. On a slightly different note, there is a lot happening on the wearables, AR and VR space. We successfully delivered our first Hololens project a couple of months ago.
7. What’s your approach to creating interactive and addictive UX/UI of mobile apps and websites?
We approach UX/UI from the perspectives of -Understandability, Learnability, and Operability under real user conditions. On mobile, we try to imbibe business features with the natural advantages provided by the mobile ecosystem – GPS and location tracking, Voice recognition, Cameras for Scanning, Gyro and Accelerometers, native connectivity option like Wifi and Bluetooth – in a secure manner. From a UI techniques perspective, we are looking at circular design patterns, interactive content layers, intelligent manipulation of content, cognitive interfaces and a few other areas to provide good learnability and operability.
8. What are the challenges you see in the outsourcing industry and how much you’re prepared to face those challenges?
I remember reading a report recently that 70% of CIOs expect to change their mix of sourcing providers to get more business value and innovation from new partner relationships. While this is a challenge for incumbents, it is good news for the outsourcing industry as a whole. For customers, outsourcing is no longer just about cost, but also about innovation and partnership. Today, most Enterprise software outsourcing is based on the staff augmentation approach. As customers demand result oriented and value driven partnerships, we see a slow but steady shift back towards the project-based approach. This requires a greater understanding of the customer’s business and higher accountability and ownership of business results.
At Fingent, we are built ground up to focus on the business outcomes that our clients wish to achieve using the product we develop for them. Our processes secure the continuity and coherence across the CX cycle from- Sales to Account Management to Operations and Delivery. This, together with our focus on technology competence development ensures that we provide innovative solutions to add value to our customers’ businesses. We are happier to provide our customers with solutions that add value to their business, to be accountable for the entire solution, than to body shop. We are ready.
9. Mention the ways you use to introduce new updates to your team.
We have many different mechanisms depending upon the source, the context, and the impact. Technology updates are managed within the BU and the teams unless it has a wide-ranging cross-functional impact. Project-specific updates are introduced from the PMO since every project has a single point of contact ( for the client) who is responsible to secure that project changes are communicated and understood by the project team. Communication channels for an update may include one or more of- meetings, emails, blogs or updates within our PM tool. We prefer face to face communication to the extent possible, either in person, or using modern video communication tools.
10. Nearly 70% users engage in wearable tech. What’s your step to enter into this revolution?
We have already started working with clients on Augmented Reality. We recently delivered a Hololens based facial recognition system for a client. We see opportunities across the entire technology stack- from chipsets to applications to cloud to data analytics and learning. Our strategy is a bimodal approach –
- Leverage competence in areas where we are already strong. For e.g. Our strengths in data analytics and visualization, help us manage the structured, semi-structured and unstructured data that flows in from wearables. Our expertise in data security helps provide Security consulting services to Wearable tech manufacturers.
- To focus on a few niche areas, where platform technologies are likely to succeed. For e.g. creating Augmented Reality applications for the HoloLens.
11. Examine the success and failures that your developers are facing while wearable app development?
The key challenges that we face in the wearable tech industry include:
- Lack of standardization. Fragmented platforms create an overhead due to the learning curve and lack of interoperability.
- Cultural challenges. Many users are not aware that by connecting wearables to the internet, high-risk information is placed in highly insecure and vulnerable environments. Risk assessments are often overlooked in an attempt to cut costs.
Nonetheless, we are optimistic about the opportunities here. These are challenges faced by any nascent industry.
12. There’s a boom in native apps for wearable devices, what’s your move to this technology?
Given the tight hardware integration required for many wearables, I would argue that in most cases, native is the only option. We are looking for more cross-platform tools to create apps that can be deployed across platforms at lower costs for our customers, But these are early days and we believe that such cost efficiencies will soon be created.
13. Define your future prospective and vision regarding new technologies like wearable and IoT apps?
I believe that we are at the beginning of the mass market wearable and IoT revolution. Privacy issues may lead to a temporary backlash, but these issues can be resolved.
We are looking forward to enterprise applications of wearable technology, especially in AR. Challenges around Security, Interoperability and Data mining/analysis have to be solved for Wearables and IoT to deliver tangible benefits at low risk.
14. What is your go-to-market scheme at a global level?
Currently, we are operating globally with offices across the globe. We have built many innovative solutions for our clients which are attracting other business with similar needs to reach out to us. We have a market research team that does industry research to identify the potential leads/opportunities based on the various matrix that we have developed internally. Some of the advanced project management and delivery processes that we developed with proven history convince our clients to work with us. We have most of our clients working with us for many years as a trusted partner as the organizational culture that we developed over the years focus on trust, integrity, and transparency with our clients along advanced technology capabilities.
We also share our knowledge and experience through blogs, white papers, case studies which has helped many people. We are also tapping into the power of social media platforms.
We also recognize that there is so much more than can be done to establish the Fingent Brand across the Globe.
Please tune in to hear about some major platform launches coming soon which we have been hard at work.
15. Mention the name of some of your successful projects?
We are grateful to have worked with large enterprises like NEC, Johnson and Johnson, CBN, Sony, WRI Capital, PwC and many more. We take a great deal of pride in having played a significant part in the explosive growth of successful startups like RentMoji, MFS, Lindsey Jones, Sweden Academy, Teachucator and many others. We believe that true success is about adding value to people’s lives, be it in ways large or small, at work or at home – our work with our clients has helped us do exactly that.
This post originally appeared at https://www.itfirms.co/interview-with-varghese-samuel-ceo-fingent-corp/
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
The psychology of color in human beings is a subject of’ research and ‘has been under study for long periods. The color scheme that is selected by the retailers for decoration, the design of the logo, content on the website and mobile applications etc. can have a direct impact on the sales.
Importance of Color
According to a research, the first impression of the customers plays a significant role in retail and 62% to 90% of it is based on color. Aesthetic appeal is of utmost importance for the shoppers and 52% do not return to the store if they dislike the aesthetics. The primary and deciding factor for 85% of the shoppers while making a purchase is the color. Signage is also an important factor for retail and it is often observed that the ads and banners are designed using red as the primary color.

Color Schemes
There are various color schemes that the retailers may use in their store and on the web applications. Some of these color schemes are as listed below.
- Monochromatic Colors: Varied tones of a single color are used under this scheme.
- Complementary Colors: The opposing colors on the color wheel are used in this scheme.
- Analogous Colors: The colors that are placed at left or right of a color on the color wheel are used.
- Triadic Colors: The colors placed at 120 degrees apart on the color wheel are used as per this scheme.
- Split-Complementary Colors: A color is selected as a base color and two colors that are adjacent to the complementary colors are used.
- Rectangular Colors: Pairs of two complementary colors on the color wheel are used.
- Square Colors: Four colors placed evenly on the color wheel are used.
There are also combining color schemes that are often used by the retailers in order to enhance the visual appeal and attract an increased number of buyers.
Influence of Color
Color is a critical variable that has the power to impact the psychology of a human at conscious and subconscious level.
The colors can be used in the following ways to have a positive and appealing influence on the customers.
- The retailers shall select an effective theme for their store and shall then decide upon the colors to explain the concept to the buyers.
- There are certain colors, such as green and blue that may have a calming effect on the shoppers while orange and brown can have a reassuring impact.
- The retailers must understand the ability to alert and appeal their buyers through the use of adequate colors. The use of bright colors like red and yellow can grab the customer attention.
- Brand recognition can be enhanced by 80% with the correct use of colors. Logo colors and color scheme should be intelligently selected.
- The category of product and the choice of color shall go hand in hand. For instance, the sleek look of an electronic product may vanish with the use of bold and bright colors.

Consumer Reaction to Red Color
Red is a color that is usually associated with love and power. The color also has the ability to enhance the heart rate and also activates the pituitary gland. The use of red color in the retail stores visually appeals the buyers and grabs their attention.
A majority of retailer use red as the color for sales signs and for displaying other significant details. It is because more value is added to the aesthetics and it can be easily read from a distance.
A research was carried out to understand the importance of the color in a better manner. A male model was selected as the communicator and was asked to pose for two different pictures wearing a red sweater in one and white sweater in the other. Persuasive arguments were used to understand the color psychology of 94 undergraduate students and the picture with red sweater was rated more persuasive.
The use of web and mobile applications has increased in the recent years and the color of the website or application logo along with the choice of text color shall also be judiciously picked up. The online shoppers make their purchasing decisions largely on the basis of the color scheme used.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Improving the customer experience is the mantra for survival in today’s highly competitive business environment. More and more businesses have identified machine learning as a reliable tool towards this end.
Machine learning is in essence software coded differently to traditional software. Rather than a long list of if-then-else statements typical of traditional software, machine learning predicts what humans would do given a specific set of inputs.
Currently, marketers and others leverage machine learning to further customer experience through improved personalization, enhancing the computer vision, improving natural language, greater decision support, through analytics optimization, and augmented analytics.
1. Machine Learning Aids Personalisation
Today’s highly pampered customers prefer and even demand personalized engagement and experiences. Machine Learning facilitates it to the hilt. Data and analytics allow marketers to understand customer preferences. Using machine learning in combination with new data sources from the Internet of Things (IoT,) telematics, geolocation beacons, and social data improve the insights.
Several marketers now apply machine learning based algorithms to understand the nuances of their customer’s preferences and engage them on their terms. Marketers use such algorithms to develop highly relevant marketing campaigns, such as a matching audience profile with highly targeted video content. These steps improve the call-to-action.
Customers receive tailored offers rather than irrelevant non-contextual offers. Such non-contextualized offers have a very low probability of conversion.
Segmentation gets better. For instance, insurance companies do not have to go by general assumptions or time-honored conventions to offer the highest automobile insurance premiums to a 16-to-25-year-old male. They can factor in everything specifically related to the customer, and tailor the premium based on individual rather than class factors.
The creation of such relevant content is the godsend at a time when over 90% of online users in the U.S. and Europe feels advertising is more intrusive today compared to two years ago.
Related Infographic: Machine Learning- Deciphering the most Disruptive Innovation
2. Machine Learning Facilitates Computer Vision
Machine Learning technology detects everything and anything, from objects and people to complex scenes within the images and videos. Applying the technology to enhance the quality of digital assets is a sure-shot way to win the customer’s heart.
One big success story is Twitter’s Magic Pony, which leverages machine learning technology to make pixelated images sharper, and enhances the quality of video captured on mobile phones in poor lighting conditions. Apart from delighting the customer, the spin-off benefit of Twitter is lower data usage, and by extension improved streaming abilities.

3. Machine Learning Aids Natural Language Processing
The next big thing revolutionizing human interactions with computers is speech recognition technology. The ability of computers to recognize human speech and act on it not only spares the hassles of keyboard typing but also unlocks a host of new possibilities. While speech recognition technology has been around for a while, the application of advanced machine learning technologies has made the system highly accurate, with error rates far lower than humans. Google’s Cloud Speech API now recognizes over 80 languages and variants, with a high level of accuracy.
Marketers can, and are leveraging advanced linguistic data and cognitive technologies spawned by speech recognition capabilities to create highly engaging content, targeted at the customer. In a sense, it furthers the cause of personalization in a big way.
Marketers benefit from natural language capabilities in myriad other ways also. A case in point is the intuitive new tool launched by Relative Insight, a UK based start-up. The tool converts natural language into data, offering marketers a wealth of information to connect with specific audiences instantly and deeply.
4. Machine Learning Improves Decision Support
Machine learning allows the marketers to predict the future. The “machine” becomes capable enough to predict the customer’s likely course of action, based on the data at his disposal, and his present behavior. The market is now flooded with several digital tools and services which provide advanced recommendations on this front.
On the anvil is “copyless paste,” where machine learning will save users time by proactively offering to share information between apps. Marketers will leverage the concept further to offer proactive product suggestions. Integration with other systems also offers the scope for proactive and automatic delivery.
5. Machine Learning Facilitates Analytical Optimization
Businesses leverage the immense analytics opportunities offered by machine data to fine-tune their operations, deliver new business models, and offer new products and services in tune with customer demand. The insights gained, predict not just how a customer may behave or act, but also how the competition may move in the future.
One sector where machine learning algorithms are already in widespread use is the financial sector. Financial services companies use various machine learning algorithms such as random forest and gradient boosted models for a host of applications, from predicting the probability of being ranked at the top of aggregator portals to predict midterm cancellation rates on policies, and more. These applications have a direct bearing on customer satisfaction. For example, banks and financial institutions predict volumes for credit card lines, to adjust rates and terms, and thereby attract the right type and volume of customers for the specific product.
Related Reading: Top Artificial Intelligence Trends to Watch Out for In 2019
6. Machine Learning Facilitates Augmented Analytics
The scope of machine learning improves with the development of technology. Neural networks support better classification and forecasting, decision trees support more complex rule and relationship-based customer experience programs. All these improve the organization’s ability to support complex decisions, forecasts, and optimizations.
Augmented analytics, which co-opts these latest and emerging technologies, combines various elements of the ecosystem, such as data preparation, business intelligence, predictive analytics and machine learning capabilities into a single, automatic and seamless process. Enterprises would be able to cleanse their data easily, to uncover latent insights and patterns.
Today’s huge data create millions of variable combinations impossible to process manually or even with traditional tools. Augmented analytics, powered by machine learning, deliver quicker insights, reducing customer frustration.
What exists now is just the tip of the iceberg. The future holds a world of possibilities. A case in point is the fragmented nature of the machine learning ecosystem being all set for a big churn. Increased competition, the hyper-fast paced changes in technology, and the proliferation of big data at an alarming frequency force many open source machine learning libraries, algorithms and frameworks to join forces and deliver a better deal to their customers. The lower-level personalization commonplace today will make way for a more robust collaborative filtering, delivering a much higher degree of personalization and contextualization than present levels.
Side-by-side, the machine learning ecosystem is becoming increasingly easier to use, and more affordable. Hitherto, only enterprises with large analytics teams could really afford to play around with machine learning. The advent of various solutions delivered in a cloud-based subscription model makes the power of machine learning available to the masses, including start-ups, freelancers, and even individuals.
Marketers and brands can leverage the improved ecosystem to generate a better picture of their customers’ true context, and serve them better. Simply put, customers will get better food, movie, music, travel, product and purchase recommendations.
Related Reading: AI To Solve Today’s Retail Profit Problems
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the simulation of human intelligence processes with the aid of machines. These machines primarily include computer systems and tools that carry out learning, problem-solving, reasoning and perception.
Customer service is one area where AI tools and technology can be used efficiently. As per a recent study, it is estimated that nearly 85% of the customer interactions will be handled without the presence of a human agent in next three years. There are approximately 38% of the enterprises that are using AI and the number will grow to 62% by the end of 2018. AI has the capability to accomplish the following set of tasks and activities in customer service and interactions.
Pre-emptive Action
AI embedded monitors can provide the customer service team with the ability to analyze the primary customer issues. The systems can offer real-time support to the customer for the resolution of such issues. The huge clusters of web applications can be gathered and studied to resolve the issues even before their occurrence. This empowers the business organizations to reduce the customer abandonment rates and enhance the level of customer engagement.

Messaging Applications
The use of messaging applications is not restricted to connecting with friends, family, and colleagues. The brands are using these applications for customer interaction and the usage is set to increase further. The use of social media applications and in-house messaging applications allows real-time interaction with the customers and thus resolve their queries and issues.
One-time Training
The expenditure on hiring the customer service agent and training the member is quite high. It is also necessary to organize training sessions at regular intervals. However, with the use of AI platforms, a one-time training is sufficient which in turn would bring down the costs to a huge margin.
Related Webinar: Artificial Intelligence in layman’s termsNon-stop Services
Customer service agents cannot be made available for a non-stop period of time. The human resources work for specific hours in a day and may remain unavailable at the time of an incident. These limitations can be resolved by the use of automated support and customer service tools which interact with the customers at any hour of the day. The queries and incidents reported by the customers are automatically recorded and a suitable response is also provided that matches the reported query.

Self-service Options
A recent customer service study revealed that over 72% customers do not prefer phone calls for the resolution of their query or issue. Self-service options for customer service are on a rise and the use of chat-bots and forums have rapidly increased. AI has enabled the easy development and usage of such options. The companies that are still not utilizing such platforms will be required to incorporate the same in the future for enhanced customer relationship management and service.
Reliability & Scalability
Customer service and interaction have a great role to play in customer engagement and relationship management. According to a survey, 42% of the customers increased their purchase after a good customer service response. On the other hand, 52% customers reduced their engagement with the organization after a poor experience. AI platforms can enhance the reliability of service with their non-stop availability and unbiased customer interaction. The AI tools can also be scaled up or down as per the requirements. These applications can simultaneously handle a wide number of customers without any impact on the speed and performance.
Cost-Savings
There are advanced customer services that can be provided by artificial intelligence. The use of automated applications can reduce the costs. Resource and training costs along with the cost of the infrastructure are eliminated with the incorporation of AI tools.
It is often assumed that Artificial Intelligence will replace the jobs currently being handled by the human resources. There are over 10 million jobs that will be replaced by AI tools and applications in next ten years. However, in the case of customer service, automated assistance can only resolve 10-35% of the customer queries. Human assistance and capabilities will be required in the rest of the cases. The business organizations must research the AI applications and platforms that can be incorporated into their customer service interactions.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new