Tag: Ruby on Rails Web application framework
Digital presence is no longer confined to a static website. The advent of backend frameworks has helped raise the standards of web development. The backend frameworks are an important aspect of web development. These frameworks help in creating necessary online platforms and applications. Finding a suitable framework that ensures utmost scalability and performance is the key to a successful business.
However, with many choices available in backend frameworks, finding one that suits a specific business goal can be challenging. This is why we want to help you dive deeper into the popular backend frameworks so you can make the right choice. Here is an unbiased comparison of two popular and trusted backend frameworks: Node.js and Ruby on Rails (ROR).
An Overview Comparison of Node.js and Ruby on Rails
Node.js
Node.js is a server-side open-source tool. It attributes its success to the single-threaded process used for web loads and async programming. Businesses can also use Node.js-based frameworks to enhance the backend capability of a project. This technology can build single-page applications, websites, and backend API services.
Market Stats Of Node.Js
- 66.8% expressed interest in continuing to develop with Node.js frameworks.
- A survey revealed that 85% of Node.js developers use it for web app development.
- There also has been 3.5% of stack overflow questions addressed regarding Node.js a month.
Node.js Use Cases
- Nasa: By creating a single database for any query, Nasa could reduce access time by 300%.
- Netflix: When they migrated from Java to Node.js, they decreased their startup time from 40 minutes to 60 seconds.
Read more: Learn why Fingent is recognized as a Top Node.js Company by TopDevelopers.co!
Ruby on Rails
Ruby on Rails is an open-source web application framework written by Ruby. It is the best option for beginners to help them build and deploy web applications and websites.
Market Stats of Ruby on Rails
- Ruby on Rails powers 394,000 websites
Ruby on Rails Use cases
- GitHub: GitHub has over 61 million repositories for its 22 million users worldwide. Using Ruby on Rails, they improved performance, documentation, and features.
- Airbnb: Airbnb boasts over 7 million listings in over 220 countries and regions. Ruby on Rails enabled them to reduce the TTM.
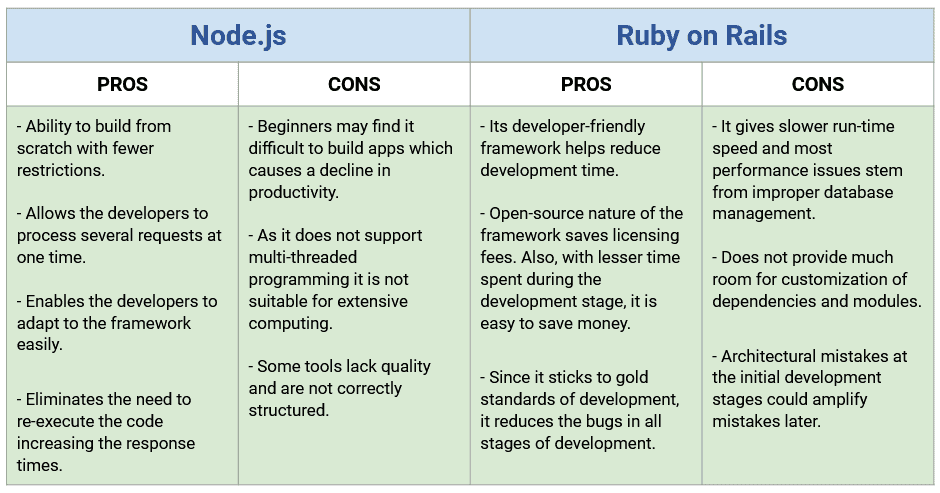
Pros and Cons of Node.js and Ruby on Rails
Now that we understand the pro and cons, let us look at a few other comparisons.
Performance and Speed
Performance is important when building complex and large projects.
Node.js creates the perfect environment for small tasks that do not affect the main application thread. Plus, the JavaScript engine can make multitasking more efficient.
Ruby on Rails can create efficient web applications with satisfactory performance. RoR applications may slow down in rare cases, like when the traffic scales significantly.
Application Architecture
It is important to choose flexibility when choosing a framework. A framework should be a guide, not a standard.
Node.js enables developers to handle multiple concurrent requests with high performance. in addition, it supports asynchronous communication between various components providing high performance. It ensures faster, flexible development modules and reduces time to market.
Ruby on Rails, on the other hand, follows MVC architecture. This architecture easier testing and decoupling because of the convenient separation of concerns. Also, since it follows the conventions of the configuration principle, it reduces developers’ legwork.
Scalability and Ease of Testing
Backend frameworks significantly influence web application scalability and ease of testing.
Node.js builds highly-scalable applications, and the event loop mechanism enables the server to process maximum requests. It is highly compatible with microservices. Hence, development teams can build applications more quickly as they scale. Node.js offers competent testing and debugging capabilities.
It is possible to scale with ROR if you invest more resources than other leading backend frameworks. However, Inadequate memory management and poor concurrency can create issues when trying to scale quickly on the ROR platform. Testing is simple and effective in ROR, considerably reducing intricacies during the testing phase.
Microservices Compatibility
Node.js builds smaller parts of services and code modules to efficiently handle multiple concurrent requests. Hence, Node.js and Microservices are an absolute combination for building enterprise-grade complex applications with higher scalability.
Though Ruby on Rails leans on monolithic architecture, it can be used in a microservices architecture. Hence, it is compatible with microservices’ needs and deployments.
Database Support
Node.js supports all kinds of databases. However, it is better to use a NoSQL database as it stores data in JSON objects because it offers more accessibility to Node.js.
Ruby on Rails comes configured for SQLite. However, it allows the use of multiple databases.
Hiring The Best Developers
The large community of Node.js and Ruby on Rails makes it easy to hire developers. If you are considering a backend tool for your project, Fingent top custom software development company can help define your project priorities to help you choose the stack that fits your needs.
Read more: How we optimized a MEAN Stack project for better performance
Fingent provides you with top performing talent pool for all your development needs for both these frameworks. If you struggle to choose, our elite consultants will help you find the right framework that suits your business goals.
Reach out to us, and let’s talk about what that is.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
The open source revolution is on. More and more enterprises are joining the open source bandwagon, to develop their internal and customer-facing apps. Free availability of source code, unbridled flexibility, gross reduction of app development time, resilience, and several other advantages prompt the move. But with great advantages come great risks as well.
The very nature of open source leaves the enterprise app development team with little control over the source and nature of their code. The odds are high that open source code may come with vulnerabilities, open for hackers to exploit.
Technological advances cut both ways. While technology may be used to beef up security, it also enables hackers to update their toolkits, and add any newly discovered vulnerability to their automated scanners. The odds of any application using flawed code being quickly found and exploited are generally high, more so when the open source library in question is a popular one. To make things worse, such hacker toolkits are freely available now.
So how do enterprise counter the hacker menace and ensure they can still reap the benefits of open source?
Be Very Careful of Downloads
With dozens of different open source libraries, tools, frameworks, and code snippets freely available over the Internet, there is a very good chance the variant chosen by the enterprise may have vulnerabilities. Even the hugely popular Ruby on Rails web application framework, with a very wide user community known for prompt updates, has been inflicted with several security vulnerabilities, placing 200,000-plus sites at risk of attacks that could lead to remote code execution.
Opt only for versions of open source libraries maintained by established consortium, dedicated to the cause of enhancing and maintaining the software. Such consortium would have a stake in the code. They would almost certainly be supported by grants from generous sponsors, enabling them to issue prompt patch updates, when a vulnerability is discovered.
Enterprises, for their part, need a clear policy on the usage of open source, loaded with:
- A white-list of trusted websites, from where the source libraries may be downloaded. The most reliable options are the websites recommended by Open Source Initiative.
- A list of security do-and-don’t, to prevent system admins and other users from downloading spurious open source software from dubious sources. Have a well-documented security policy, with clear guidelines on installation and maintenance of open source.
Prefer source code to binaries wherever possible. Most open source products are available either as source code or in package formats or binaries. Binaries offer a far greater level of risk, as there is no telling whether it has complied with the associated source code after all. The best practice is to download the source code directly, verify it against the provided MD5 checksums for integrity, and analyze the code for any latent vulnerabilities, before using it to develop apps.
Establish a System
A commercial closed sourced suite is developed through a structured and formal procedure, such as conducting a requirement analysis, defining the acceptance criteria, evaluating the product, comparing the product with competitive options, testing the functionality and security features, and more. Open source code may not necessarily undergo such kind of scrupulous evaluation or validation. There is no short cut but for the app development team to establish a method in the madness themselves.
Have a process in place to ensure adequate control, and to update all third-party code promptly.
Analyze the environment to identify possible threats. For instance, using popular open source libraries makes it that much convenient for attackers to identify vulnerabilities and launch attacks. However, at times, the biggest threat may not even be external, but malicious insiders. Understand the various ways in which the system could be attacked, and protect data accordingly.
Also, have a policy in place to govern code sources. Some teams may find they need to reduce the number of different code sources they use in order to manage them effectively. Within the framework of such policy and analysis:
- Create and maintain an up-to-date list of all third-party code in use, including all dependencies and sources. Designate a point person for each such code, to track mailing lists, news and updates.
- Avoid ad-hoc installations. Evaluate any open source considered for an enterprise use, and gather accurate information about the product.
- Institute an emergency response plan to execute critical releases. Internet facing apps often require a swift response to prevent attackers from exploiting a newly discovered vulnerability.
- Institute a dedicated team of system, network and security administrators to implement the policy and also review the policy from time to time, depending on the changes in business environment.
Apply Security Tools
Policies and safeguards can only safeguard to an extent, and require reinforcement through effective security tools.
Many open source projects do not issue patches, and rather just release a new version that fixes the problem.
The following are some of the tools worth considering:
Source code scanners such as FlawFinder and RATS (Rough Auditing Tool for Security) identify potential security problems in the source code. These source code scanners undertake pattern matching to highlight the areas of the code that has potential vulnerability and pose security risks such as buffer overflows, racing conditions, shell meta character dangers and poor random number acquisition.
- Vulnerability scanners such as SARA (Security Audit Research Assistant) and Nessus scan the network for vulnerabilities.
- Adopt a defense-in-Depth strategy, or a layered approach to securing the network, deploying the most effective security tool at all levels, from, application to the network.
- Configure the network properly. Disable all unwanted services, adopting the policy of “deny by default unless explicitly permitted.”
- Assume the network will be breached, and have effective measures in place to contain the menace, such as encryption of sensitive data.
The stakes of security breaches are high. The penalties, damaging lawsuits, and erosion of customer confidence can bring down the enterprise in itself. The most effective and risk-free approach towards adopting open-source is to partner with an experienced partner, like us. With us, you can leverage our considerable experience in not just developing cutting edge solutions using the most relevant open-source tools, but also take the most effective measures to ensure top-grade security.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new