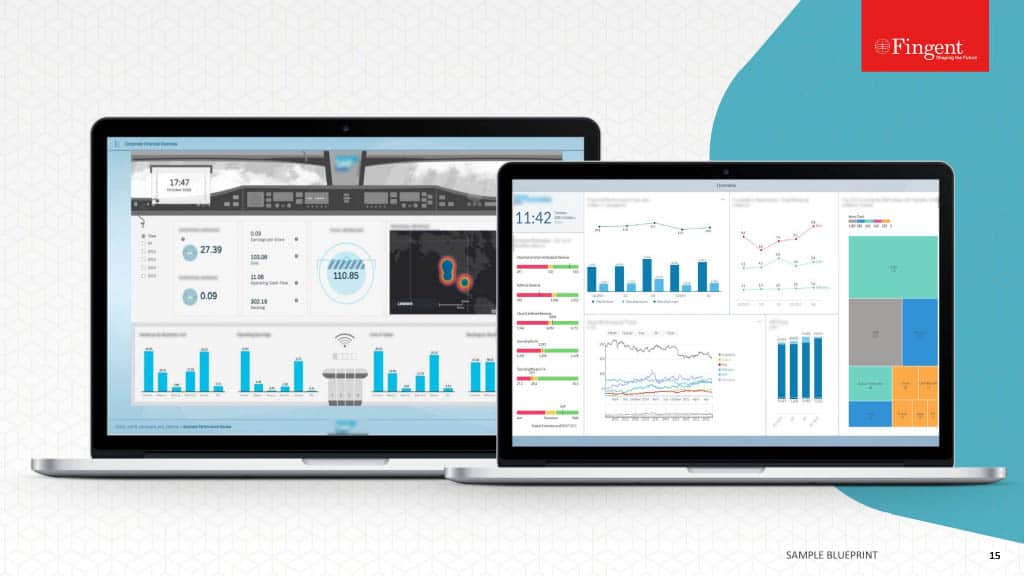
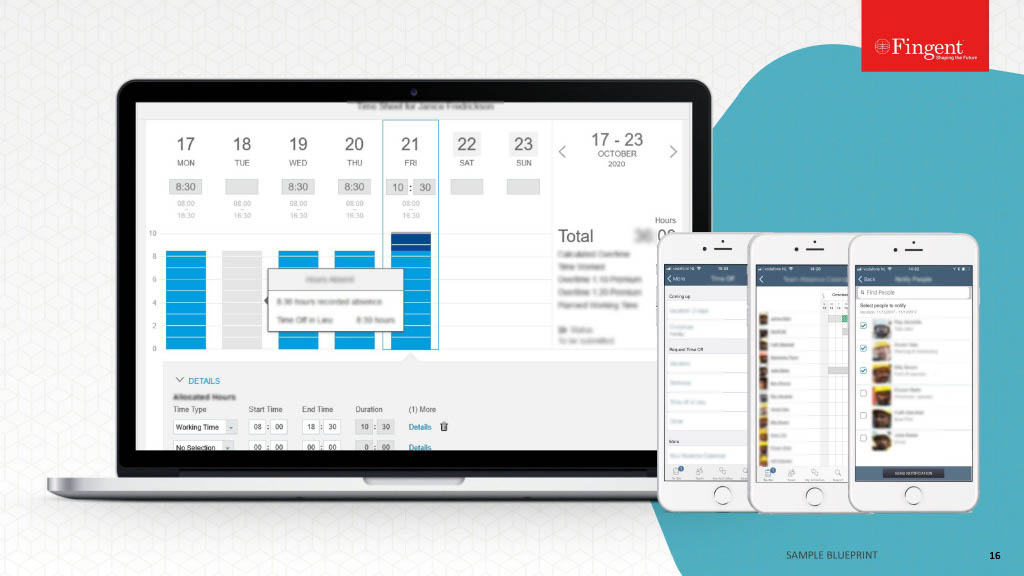
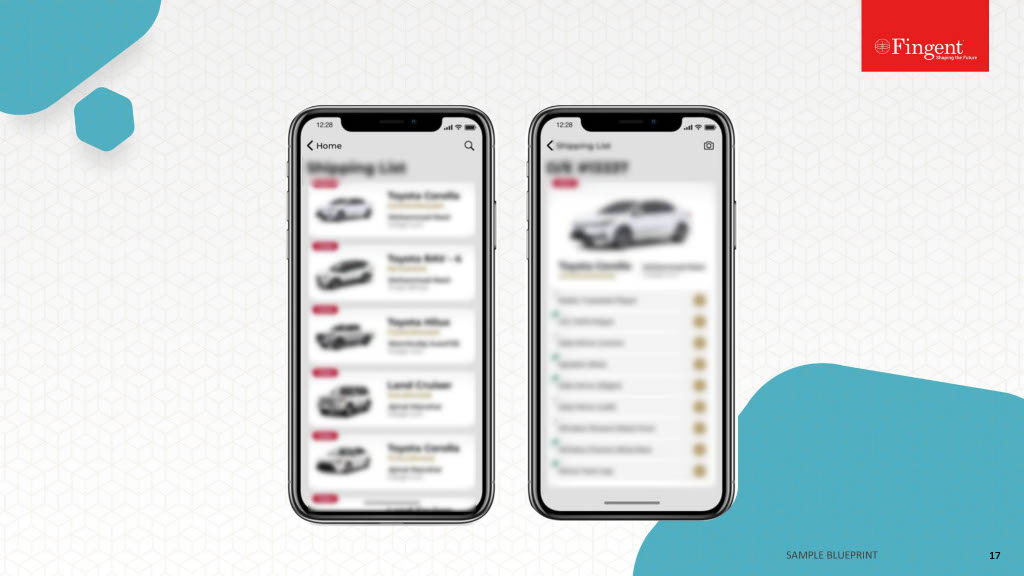
System Integration Services
Trusted by Clients, Driven by Excellence for Two Decades
















Fingent’s System Integration Services
01 Data Integration
02 Application Integration
03 API Integration
04 Cloud Integration
05 Business Process Integration
01 Data Integration

Data Integration
Let us help you bring together your scattered data from various sources into a centralized hub. This allows for a comprehensive overview, empowering better decision-making and efficiency. Let Us Help You02 Application Integration

Application Integration
We can assist in seamlessly connecting your different software tools, ensuring they work harmoniously together. This streamlines your processes, saving time and reducing errors. Let Us Help You03 API Integration

API Integration
Let us help bridge the gap between your applications with APIs. By enabling them to communicate effortlessly, we enhance functionality and enable smoother operations. Let Us Help You04 Cloud Integration

Cloud Integration
We can facilitate the integration of your existing systems with cloud services. This provides you with the benefits of scalability, accessibility, and cost-efficiency, tailored to your business needs. Let Us Help You05 Business Process Integration

Business Process Integration
We’re here to optimize your workflows by integrating your systems. This ensures tasks flow seamlessly from one process to another, improving overall productivity and effectiveness. Let Us Help YouFingent’s Approach to System Integration

Fingent, The Trusted Custom Software Development Company


Take a Glimpse of Our Client Voices
5.0
"I’ve felt that I have a real partner in this work since Fingent came in on day one with a comprehensive plan."
VP of Technology & Innovation, Impact XM
5.0
"I like the quality of their deliverables, the timeliness with which they deliver, and the budget."
Co-Founder & CTO, Chemical Safety Software Developer
5.0
"We have complete confidence in the team and plan to use them for years to come."
Director, Trade Alliance Group
5.0
“I was very amazed by what they managed to pull off from my description of our software.”
CEO, Spectrum Exchange Corporation
5.0
"Their team’s knowledgeable, responsive, and professional."
Owner & Director, Mohawk Day Camp
5.0
“I’ve never wondered if somebody else could have done it better, faster, or cheaper.”
Partner, Sapra & Navarra, LLP
5.0
“Their team is completely committed to our success as a client, and they do that with their dynamic team.”
Principal, Substantive Solutions
5.0
"We had a very complex thing that we had to break down, and they made it very easy."
Chief Creative Officer, Eskoa
5.0
“Beyond their reasonable price structure and technical knowledge, their team is reliable and productive.”
Technical Director, Click n Collect Pty Ltd
More Insights on System Integration

System Integration
Why Your Business Needs a Customized Order Management System
If you’re a business with an expanding online retail footprint, your hard work actually begins once a customer places an order....
Read More
System Integration
Legacy Application Migration: Excerpts from a CTO
A legacy system is any outdated software, hardware, or application that organizations still use...
Read More
System Integration
Outsourcing Software Development In 2022: Ultimate Guide
If you are required to develop software to run your daily business operations, you are probably left with three major choices...
Read More