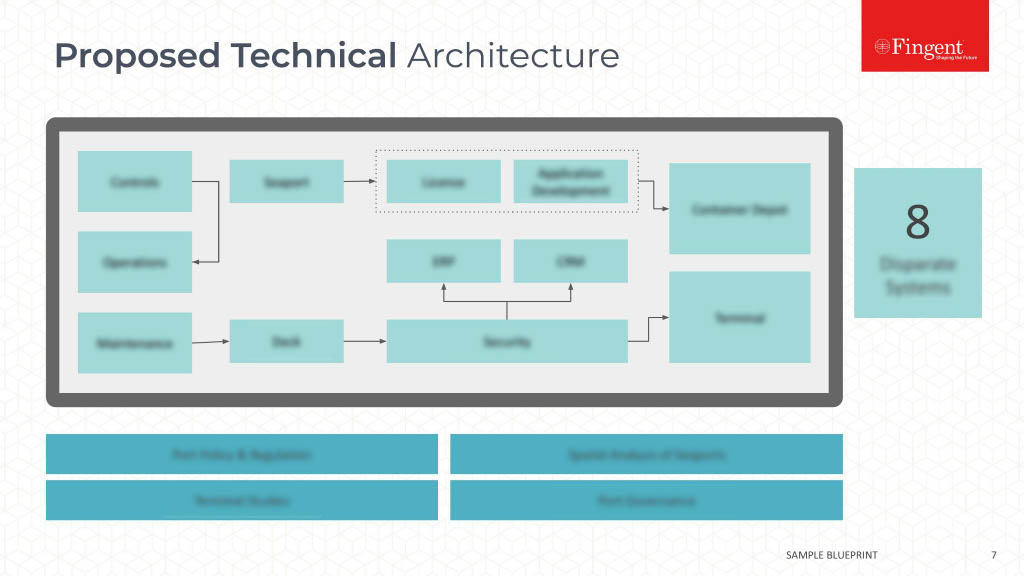
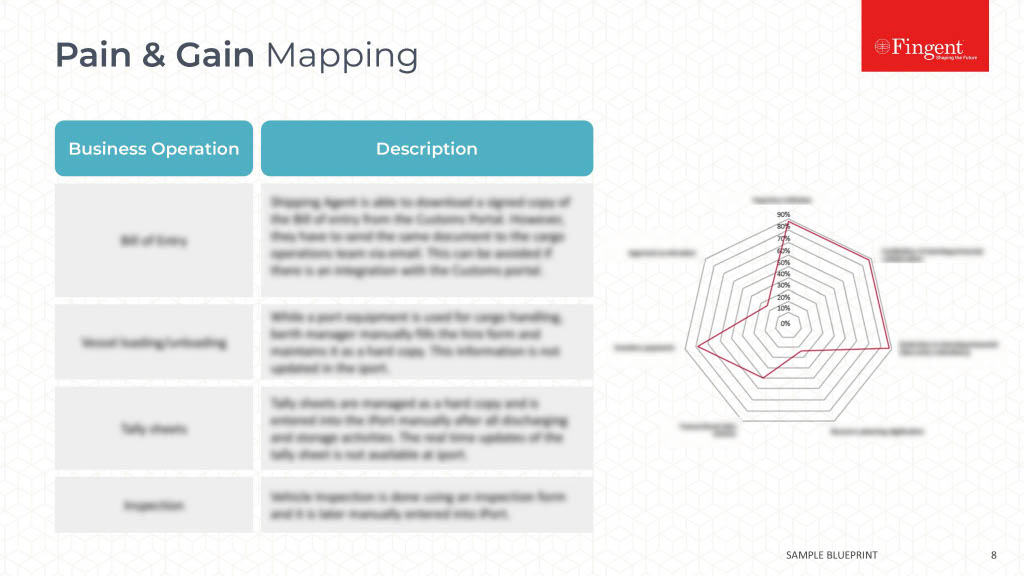
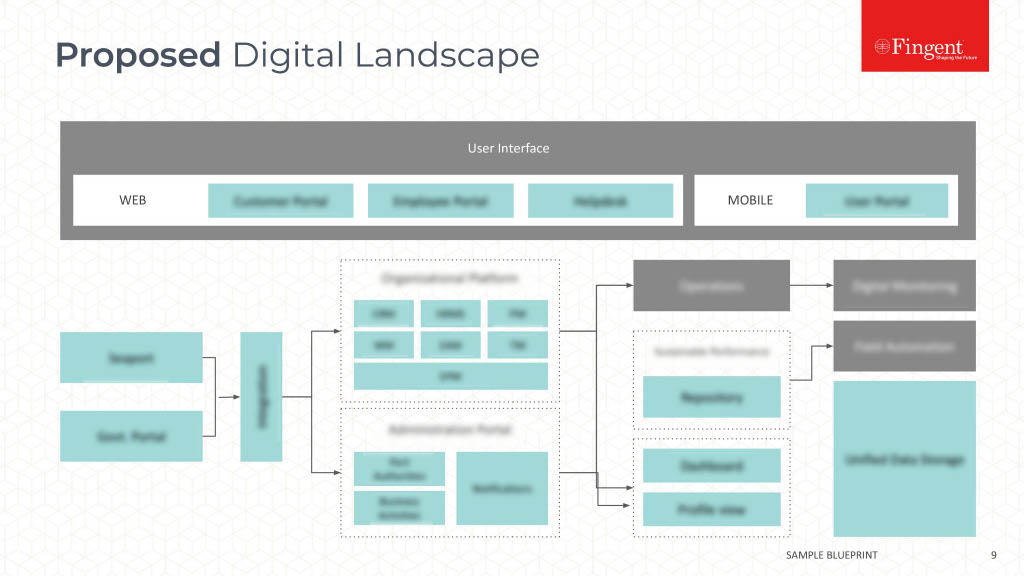
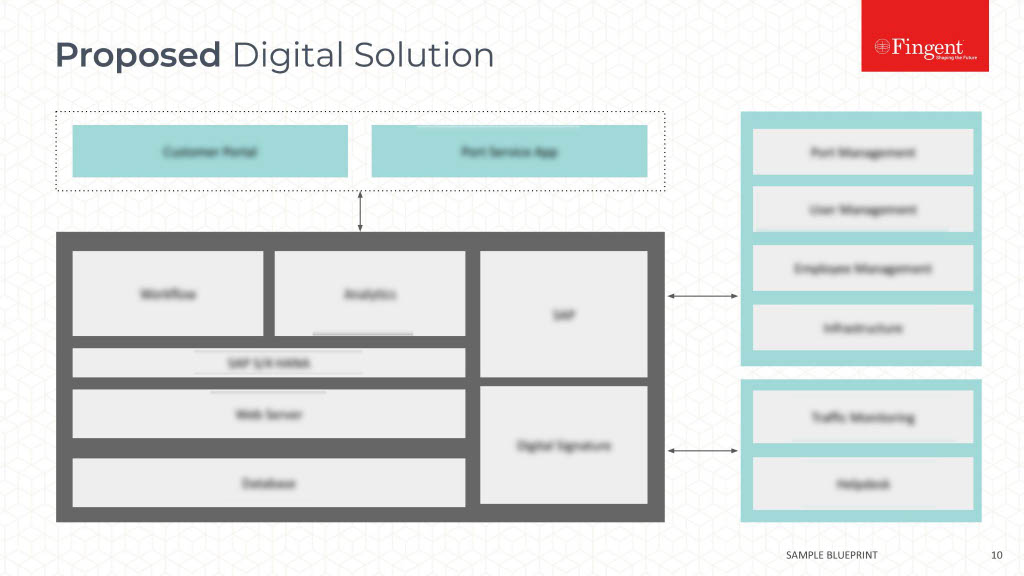
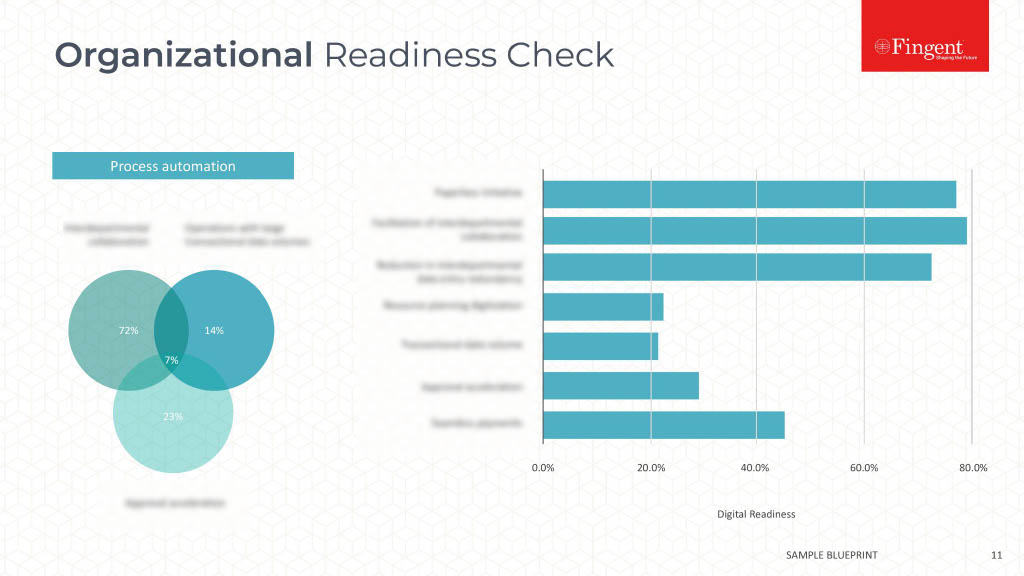
Tag: Java
How Java 12 Cleverly Upsells With New Changes And Features
Diving over the most critical areas of Java programming – The Java language, libraries, JVM and other relevant JDK features, Java 12 have come up with new and prominent features that users will crave acceptance for in these key sections.
With the release of Java 12 on March 2019, it is advised that all users deploy their applications on the newest version of Java. This will help all the tech-breathing community, especially the users in Java language, keep their programming know-how up-to-the-minute and also broaden their views on the entire performance improvements and changes that have come through with the Java 12 release!
Some of the greatest benefits you can expect from the new Java 12 and how you can prepare yourself for accelerated performance are:
- Easier coding process. For instance, the new ‘switch’ statement/ expression.
- Introduction to JVM constants API modeling for the key class-file and run-time entities, to manipulate classes and methods.
- Introduction of a new collector named ‘teeing’ which uses the teeing method to evaluate the average of input parameters.
- Garbage collection has been made easier with reduced pause times and segmentation, regardless of the heap size, than ever before with JDK 12.
- The new AArch 64-bit port, eliminating the need for two to improve efficiency and getting rid of redundant work.
- Promotes a streamlined execution of existing benchmarks and addition of new into a whole new suite from JDK 12.
Related Reading: Find a complete list of JAVA Trends rolling out this year.
To start with, there are differences, enhancements, certain APIs and features removed, and certain others deprecated. Let’s prepare for a deep dive into Java 12 features and changes:
The Unicode 11.0.0 Support
The previous version of JDK 11 supported Unicode 10.0.0. With the release of JDK 12, the most important changes include:
- Addition of 684 new characters (66 emojis, copyleft symbol, half stars for rating systems, Chinese chess symbols, astrological symbols etc)
- 7 new scripts (namely the Hanifi Rohingya, Sogdian, Dogra, Makasar, Medefaidrin etc.)
- 11 new blocks (7 for new scripts and 4 for the existing scripts like Mayan numerals and Chess symbols).
JVM Constants API
The new package java.lang.invoke.constant introduced with Java 12 brings about this new API and is used to model nominal descriptions of the class file and run-time entities, especially the constants that are loaded from the constant pool. This API will contain classes such as ConstantDesc, ClassDesc etc.) that include the information to describe the constants from the constant pool.
Compact Number Formatting Support
This feature provides support for formatting numbers in their compact form. These formats are defined by LDML’s Compact Number Formats. For instance, in the en_US locale, 1000 can be formatted as “1K”. For this, factory methods by NumberFormat are used to obtain instances as described in the above example.
The Z Garbage Collector
The ZGC has started to support class unloading feature with the advent of Java 12. Now, data structures related to the unloaded classes can be freed. This takes place without impacting the garbage collector’s pause times and also does not interfere with the execution of the application threads. This feature is enabled by default.
The Beta Switch Expressions
Pattern matching techniques were used in widespread to resolve issues that existed with the switch statement. This included the default single scope switch block, the flow behavior of switch blocks and also when the switch statement worked as a single statement. The switch statement used the fall-through semantics, which is error-prone.
With Java 12, the switch statement uses the ‘lambda’ expression to return from the switch statement. This removes the need for the usual break statements. Also, the switch is treated as an expression. That is, it can either have a value or return a value.
Related Reading: Check out some cool tips to make Android App development easy.
Promptly Return Unused Committed Memory From G1
JDK 11 was compatible with G1 being able to return some of the committed memory back to the Operating System for other applications to run. But it could do this only during concurrent cycles. With Java 12, G1 is able to retain committed memory for a longer time period, that is, during a full collection.
This happens because during low memory usage which leads to inactivity of the applications, G1 either tries continuing or it triggers a concurrent cycle to evaluate the overall Java heap usage. With this, the unused memory is now returned to the OS on time. This feature promises a more stable memory utilization for the JVM.
Shenandoah: The low-pause-time GC Algorithm
Shenandoah is a garbage collector that aims at reducing pause times because here, pause times are independent of the heap’s size. This feature was implemented and supported by RedHat for aarch64 and amd64.
The Shenandoah algorithm guarantees low response times, that is, the lower end being 10-500 ms.
Default CDS Archives
The class data-sharing (CDS) archive is built with the aim of improving the JDK build process. It is performed with the default class list on the 64-bit platform. It has a better start-up-time, prevents the need to run the default -Xshare :dump class list.
For CDS to be used, an archive that loads the classes when an application starts, is a requisite. With JDK 12, the classes.jsa file in the lib/server directory is now available.
Microbenchmark suite (JEP 230)
The Java Microbenchmarking Harness (JMH) was developed to deliver a rich framework for developing performance benchmarks for Java applications. It simplifies the execution of existing benchmarks and also supports the creation of new ones. It is based on the Java Microbenchmark Harness (JMH) and allows easy testing of JDK performance.
It includes around 100 benchmarks as a start functionality.
One Aarch 64 Port (JEP 340)
Java 12 will now support only one port for the ARM 64-bit processors. This is to get rid of redundant work needed for 2 ports as the JDK 11 had two ports for the same. The main goal is to get rid of the entire arm64 port’s sources, while keeping intact the 32-bit ARM port and 64-bit aarch64 port.
Java 12 makes the world of programming even better with these new and significant changes. In addition to boosting application performance, Java 12 offers a wide new range of added on functionalities. Read our latest articles to find out how Java 12 forms a new paradigm to sweep the application development world! To know how you can embrace the power of the latest JAVA trends for your business, get in touch with our custom software development experts today!
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
As we enter 19 years into the millennium, we find that Java has been running on 10 billion devices. The world is yet to witness innovative and user-friendly Java trends that will have a profound effect on application development in the year 2024!!
From peer-to-peer, open source and embedded to wireless and Juxtapose applications, Java has been the most popular programming language in the world of application development, with the highest rating of 16.746 percent, according to the Tiobe index!
A Retrospective Of Java Trends
Java so far has given a step-up to many of the light-weight programming platforms, as for Eclipse, Java Development Kit (JDK), the Oracle JDeveloper, as well as the Eclipse and other Open Source Applications. Let us take a look at the Java trends that made a breakthrough in application development.
-
Emergence Of EE4J and MicroProfile Projects
The Eclipse Foundation has emerged with pride with the introduction of projects like EE4J and MicroProfile.
MicroProfile has provided insight into how a more open Java EE community could flourish. Both Java EE and Spring technologies benefited out of this rise, by bringing accelerated innovation.
-
Emergence Of Kotlin
Kotlin, the JVM-compatible programming language has caught the strong attention of the Java/ Android community. Its concise coding syntax and interoperability with Java have already made it a hit in the world of application development. Kotlin is first-class support for Android and is expected to additionally improve its use for mobile application development in future!
-
Java SE 6 Updates And The OpenJDK 10 Release
2018 also witnessed the updates of Java SE 6. These updates, however, are not publicly available as yet! The code restores are only available through the Java SE Support program and in Solaris 10’s Recommended Patchset Cluster and were mainly a couple of security fixes. OpenJDK 10 was released on 20 March 2018, with the adoption of certain new features.
-
Ensuring Seamless Configuration Of Applications With Containers And Java Runtimes
The Collection framework has managed to leverage more benefits of the use of containers and Java runtimes. This offers a seamless configuration of Java applications and consistent memory management.
-
Frequent Alteration To Features – To Ensure A Well-Planned Application Development
Yet another major development was the introduction of a ‘six-month release’ interval.
This ensured frequent iterations and faster introduction of features to Java applications. These characteristics were decided to be made available through enterprising shops.
Technology Trends in Java – What To Expect In 2024
Java is a programing language that can run on nearly any system (Thanks to the platform-agnostic JVM!), it has started to get easier to use and scalable than ever before! Below are listed the major trends that we could predict for this and coming years.
-
Java Continues To Evolve – Java SE 10 Contribution
Java is a programming language that is used by more than 9 million developers. It contains extensive libraries that shape the whole enterprise application development. With the release of Java SE 10, which was created in close collaboration with the OpenJDK Community, came several new added features. Java is also ranked as the #1 developer choice for cloud, with over 12 million developers and over 21 billion cloud-connected Java virtual machines!!
-
Real-time Specification
The Real-time Specification for Java (RTSJ) is into existence.
Java creator, James Gosling, and Sun’s real-time guru, Greg Bollella have described embedded systems as “the new frontier in which predictable execution takes precedence” over other system attributes, such as speed, bandwidth, and payload-carrying capacity. They are promoting real-time Java applications for embedded use! With the RTSJ, they have managed to solve the language and runtime issues.
-
Project Juxtapose
Sun’s JXTA open source platform has gained ample acceptance among developers.
Using Project Juxtapose, Sun hopes to influence standards that will govern future Web services development. With this, Java developers will be able to focus their capability to contribute more for Java application development.
-
The Java Effect On Scripting Languages
Scripting languages such as Jython, which is a complete implementation of the Python language, is coded in cent percent Java. Python, Perl, and PHP to name a few other programming languages are receiving widespread attention.
-
Wireless Applications With Its Ease Of Use
Wireless application development in Java has gained noticeable traffic due to its open-source platform nature. The reason being Nokia, the world’s largest mobile telephone maker, has committed to using the open source Symbian OS for all of its future handsets!!
Both kinds of Wireless Java applications, Local and Network applications, is more challenging because they are developed on one platform (such as Solaris or MS Windows) but deployed on a totally different one (such as a cell phone or PDA). It is a concern that, while emulators enable developers to do some of their testings on the development platform, they need to test and evaluate the application in a totally different environment of a live wireless network. This is however made easy!!
-
Growing demand for Java developers
Java being a statically-typed language, it is faster and easier to maintain with fewer bugs. It is also backward compatible, which means old versions of the language will still run perfectly even after new versions are released. This is a big relief for businesses who would otherwise worry about rewriting their code every time a new version comes out. Coupled with its portability, developers know that investing in Java will pay dividends for a long, long time.
-
Mobile Application Development
In less than two years, the demand for mobile enterprise applications is estimated to rise five times faster!! Android currently dominates the smartphone market with 80.7% (compared to Apple’s 17.7%) and will continue its expansion! Java will, as a result, continue to be the driving force behind mobile application development trends!
-
The IoT Era And Java
The Internet Of Things is among the latest development trends in Java! As of now, Java is currently one of the few technologies that are capable of adding life to IoT. It is indeed true that Java’s future lies in the Internet of Things.
Mike Milincovich, Eclipse Foundation strongly believes that Oracle will help to develop a definite end-to-end storage data solution!! Like the Kona Project that is currently working on Java APIs for embedded systems.
The Java ME platform allows vendors to build secure mobile enterprise applications for the Internet of Things. The language is supported by the Intel IoT platform!
With all these advanced features and development, Java continues to grow and evolve. Java has undeniably achieved the top spot among the most popular programming languages in the world!
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Write once, run anywhere – the alluring catchphrase of Java still seems relevant. Since Sun Microsystems unveiled Java, it has remained the most popular programming language in use. Object-oriented and class-based, Java stood its ground even when the development space became saturated with a plethora of new languages. However, with time, programming languages do get phased out once newer and better platforms take over.
And then came Kotlin. The search for a tenable Java alternative reached fruition with Kotlin, a statically-typed programming language running on the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). Essentially, Kotlin stripped Java of its complexities and came up with a refined alternative that is as versatile as its predecessor.
The Czech software company JetBrains unveiled Project Kotlin in 2011 with the objective of coming up with a better alternative to Java. They looked to Scala, another Java alternative with support for functional programming, but were taken aback by its slow compilation times.
Kotlin Goes Public
In 2016, JetBrains launched Kotlin v1.0, its official stable release to the public. Kotlin immediately gained traction among the Android development community. They lauded its refined framework and faster compilation times, complete with added tool support, as a significant advantage over Java. Things gained momentum when Google announced Kotlin as a first class language for developing Android apps at the I/O 2017.
What followed was an outburst of mainstream apps all written fully or partially with Kotlin. Kotlin had everything that developers couldn’t find in Java or any of its alternatives like, JRuby or Groovy. It is concise and 100 percent interoperable with Java. Added to that, Kotlin came with extensive compatibility with Android Studio in which IntelliJ IDEA, JetBrains’ own Java IDE serve as the backbone.
With interest in Kotlin skyrocketing, global adoption rates point to a widespread disruption. From freelance developers to software development houses, the adoption of Kotlin has increased manyfold. In the Stack Overflow Developer Survey Results of 2018, Kotlin is just behind Rust as the most loved programming languages. In the near future, Kotlin could become the de facto standard in Android development.
Kotlin’s Development Philosophy Strikes a Balance
Andrey Breslav, Kotlin’s lead language designer at JetBrains highlighted that the goal of Kotlin is to serve as a general-purpose language, which is concise, adaptable and fully interoperable with Java. By giving these extended set of functionalities, JetBrains intends to push the developer to migrate into Kotlin. Plain old Java has numerous flaws and the developers at JetBrains couldn’t conceive things as they wanted. For them, greater interoperability and productivity in the language is the need of the hour to quickly compile and execute code.
When working with Kotlin, we could easily pinpoint its structural similarities with its parent language, Java. The brains behind Kotlin did not just want to create a new language, but one which is in all ways a “better language” than Java. Platforms like Scala, although they offered extensive feature list and functionality, failed when it comes to build times and tool support. Kotlin managed to tick all the right boxes and struck a balance on how an ideal Java alternative should be.
Kotlin borrows some elements from Scala to bring out a more upgraded version. In fact, one could find that Kotlin does contain certain instances from other programming languages as well. Pascal, an early procedural and imperative programming language remained fairly influential in the development of Kotlin. Certain elements of it, like parameter lists and variable declarations with the data type following the name of the variable could be found in Kotlin too.
Bringing Full-Scale Interoperability with Java
What distinguishes Kotlin from other languages is its full interoperability with Java and the Android runtime. It is easier to call existing Java codes from Kotlin and Kotlin codes from Java. Developers could use all the Java frameworks to build highly responsive and feature-rich apps. Both the platforms, Kotlin and Java, identify each of their classes as their own, which enables seamless interchange and compatibility. This interoperability with Java could be demonstrated with a few lines of Java code as listed below:
MainActivity.kt
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
// accessing "getSum" method from a java class
val result = SumHelper.getSum(1, 2)
}
}
SumHelper.java
public class SumHelper
{
public static int getSum(int val1, int val2){
return val1+val2;
}
}
Fig 1. Kotlin – Java Interoperability
This extensive interoperability of Kotlin with Java owes it to the fact that JetBrains worked on all the limitations of Java and sought to bring out something more refined. Together, the team worked on a new version that is different but still has Java as its backbone. Besides, Kotlin fully supports Java 6 and 7, the current versions used by Android developers.
Java Lacks Key Elements that Current Developers Need
Java has been around for more than two decades. Developers still continue to build great apps using its highly versatile and robust framework. Like every language, Java too has its limitations chiefly because it is old. Even though numerous updates were released over the years, they failed to address some essential problems associated with coding using Java.
When it comes to Android development, Java lacks support for key elements like lambdas, streams, method references, etc. Null Pointer Exception continues to be a fundamental flaw of Java, particularly in the way it handles them. Null references in code often referred as the Billion Dollar Mistake is the key reason why several apps written in Java still undergo occasional crashes.
Moreover, Java is verbose and takes a lot of code to get even a simple program up and running. The APIs involved in Java get rather complicated as the developer is forced to go through multiple steps, which take more time. Kotlin, on the other hand, requires lesser coding than Java by reducing both redundant and boilerplate code, making development a whole lot faster.
A Class Declaration in Java
public final class PersonJava {
private final String name;
private final int age;
private final String email;
private final long phone;
public PersonJava(String name, int age, String email, long phone) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.email = email;
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public long getPhone() {
return phone;
}
}
In Kotlin
data class PersonJava(val name: String, val age: Int, val email: String, val phone: Long)
Fig 2. Side by Side Comparison of Kotlin and Java Code
Lesser code means developers can write a program in lesser time and the code has greater readability combined with fewer chances of bugs or manual coding errors. Memory leaks are also a frequent problem with Java due to the way it implements anonymous inner classes and nested classes.
Kotlin Edges out over Java in Conciseness
With Google’s official endorsement, Kotlin has become the most commonly used language for Android development. The simplicity and robustness of Kotlin means both proficient and novice developers can write and debug applications with ease. Generally, Kotlin requires fewer steps or ceremonies when writing code, which simplifies the process altogether. Compared to Java, Kotlin has:
- More concise class declarations because of primary constructors and properties
- Robust type interface eliminates the need for repeating the same types again
- Function parameters with default values mostly do away with delegating overloads
- Availability of top-level functions substitute static utility classes
Being more concise than Java, Kotlin edges it out when it comes to ease of coding. It takes a redefined approach to programming to untangle several complicated workflows that developers face when using Java.
Meanwhile, Kotlin’s less verbose coding decreases the time taken to code and enhances the readability while also reducing the chances for any errors or bugs. Writing lesser code means developers can reduce the number of boilerplate codes while improving their productivity and avoiding tediousness.
Kotlin is Nothing but an Improvised Version of Java
A notable benefit of Kotlin over Java is that it does not sway from being completely independent of the latter. In fact, Kotlin is an improvised form of Java, with all its limitations sorted out. Kotlin still relies on Java libraries but refines them all together to improve their functionality.
In the existing Java ecosystem, Kotlin manages to integrate each of its elements like the Java libraries, APIs and frameworks. In fact, Kotlin incorporates Java’s procedural and functional programming aspect at the right balance. Besides, its lightweight framework combined with modern features make it a refined version of Java that is in every way better than the original.
Android Development Gets Swift and Efficient with Kotlin
Kotlin aims at being pragmatic and productive at the same time all the while serving itself as a general purpose language fully compatible with Java. Owing to its compactness, Kotlin has proved itself a workhorse among the Android development community. It steers clear of all the limitations of Java with its full interoperability with the existing ecosystems of libraries and code. Here are a few reasons why Kotlin remains the ideal platform for Android development currently.
Developer Friendly:
Novice developers can easily learn and adapt Kotlin owing to its simplicity. It takes less time to learn to code with Kotlin due to its uncomplicated learning curve. Developers already proficient in Java would appreciate the familiarity of its coding process and streamlined approach to programming. Meanwhile, the availability of existing Java libraries, frameworks and lesser coding, amps up the speed of coding, allowing developers to conceive applications faster than before.
Excellent IDE Support:
IntelliJ IDEA, JetBrains’ own platform serves as the base for Android Studio and thus offers extensive IDE support to Kotlin allowing developers to seamlessly build apps. This ready integration with the IntelliJ IDEA framework enables access to its wide range of productivity tools. Configuring Kotlin plugin could be undertaken within minutes in Android Studio. Besides, every single process of coding in Kotlin from writing, navigation, debugging and unit testing happens effortlessly with the improved support offered through the IDE.
Enhanced Versatility:
Kotlin was designed to address some of the fundamental flaws in Java and it did well. Integrated into its framework is a built-in null checking feature that helps avoid frequent errors. Kotlin’s compiler also includes a feature that automatically corrects mistakes in the code simultaneously while it is being written in the console. These rich features negate several issues in Android development giving developers a clean and versatile platform to work with. Besides, it allows developers to streamline the production process through its features like search and auto-completion of code.
Open source:
JetBrains announced open source status under Apache 2 for Kotlin in 2012. The Java to Kotlin converter tool can seamlessly convert an existing Java project into Kotlin to save on time and work. Besides, it is completely free to use for any developer wishing to expand their skill set or get acquainted with its refined framework.
Summing Up
Every new language introduced into programming has the potential to disrupt it. Developers, when faced with limitations while working on their existing language readily adopt a new language that mitigates these issues. And Kotlin proved to be just that with Java. Its swiftness and concise nature proved instrumental in its widespread adoption among the Android development community.
For them, Kotlin seemed a better Java and its great interoperable support combined with expressive nature meant they could code just like they did with Java but in a fast and efficient manner. That does not mean that it will completely phase out the former. Java will still be around as a versatile language for years.
In times to come, newer versions of Kotlin gets released, which would be more developer friendly and complete with added features and support. More apps will utilize Kotlin to develop Android apps and there will come a point where it will ultimately substitute Java. Moreover, the steep adoption rates signal an increasing prominence of Kotlin for Android development in the near future.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new