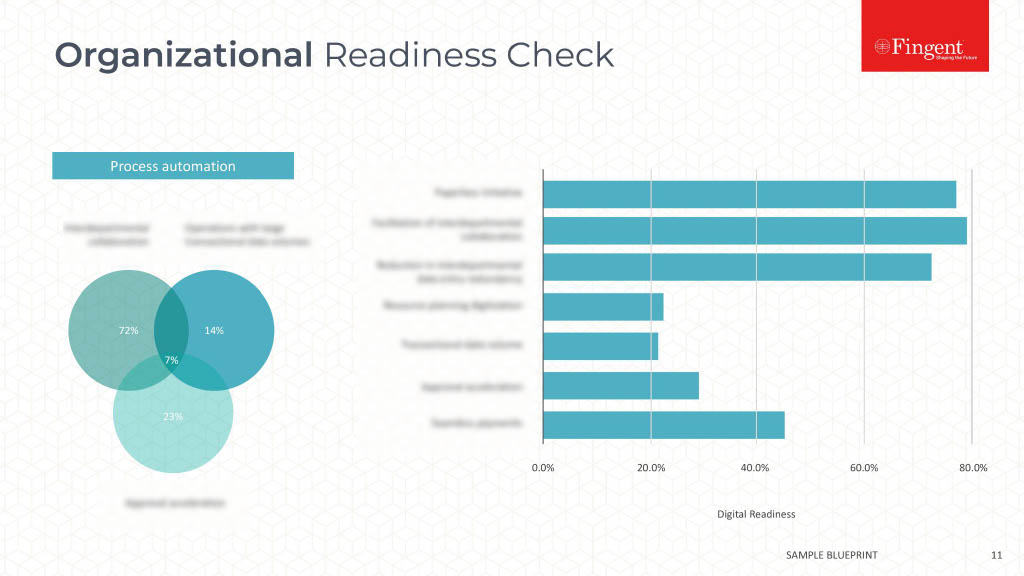
NATIVE Vs. HYBRID: Things to Know Before Building Your Next Mobile Application
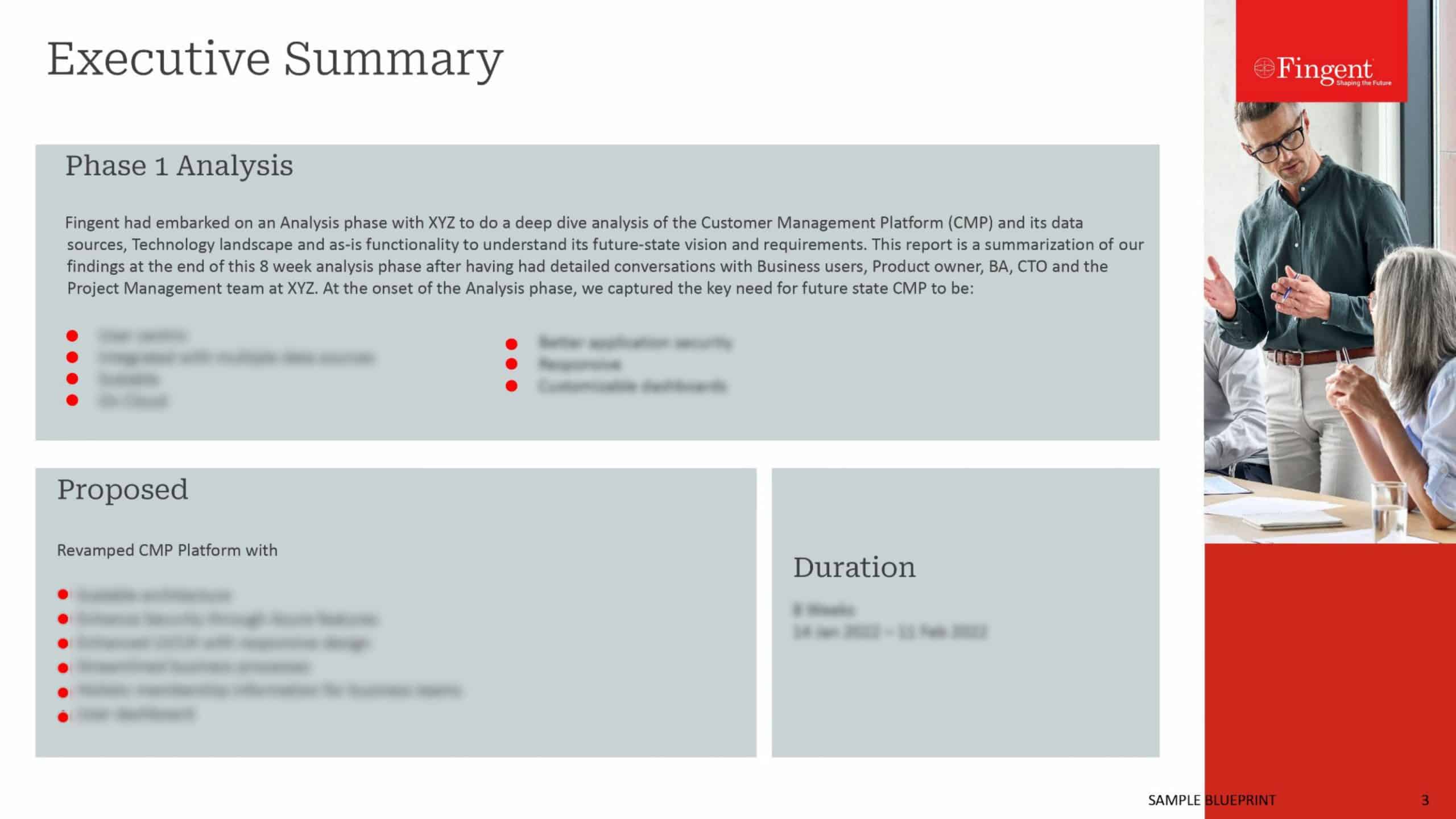
How often have you come across a situation where you needed a mobile application and had to choose between a native or hybrid application?
We as developers, have come across a number of business heads and managers, who have had a tough time deciding on the approach they had to take for the mobile application they required. More often than not, business officials are seldom aware of the technical specifications of native as well as hybrid apps. Hence, they are often confused and unable to decide between the two.
For example, one of our clients from the mining industry specialized in providing cut and fill earthworks for residential, commercial and industrial development projects, faced a similar problem. They needed a software that enabled them to move from their paper-based project management system to an online one. They also required a mobile application that enabled their field agents to gather information from their sites and also access project information contained in the main application as well. The client was confused as to what approach to use for their mobile application. After detailed analysis of their requirements, we churned out the best possible approach for their business. Similar issues persist among most entrepreneurs today.
Hence, in this article, we take you through the significant aspects of native and hybrid applications that have helped us advice our clients in deciding between the same.
Native apps
A native application is basically one that has been developed for use on a particular platform or device. And for the same reason, they are able to make use of the specific features of the operating system as well as other software installed on the device. This also implies that native apps can make use of specific hardware features as well, that are part of the device and the latest technology available with the device like the Camera, the GPS, the contacts, the accelerometer etc. Some of the general features of native apps are as follows:
They are coded in a specific programming language such as Objective-C for iOS, Java for Android and C# for Windows operating systems.
They are easily available on an app store or a market place specific to the device and they can be installed from there.
Each native app requires its own development process depending on the platform it is being developed for.
Hybrid apps
A hybrid application is one that has combined features or elements of native and web apps. Unlike native apps, they are not built for use on a particular platform, but they are made available over multiple platforms just like a web app. The major difference between a hybrid app and a web app is that hybrid apps are hosted within a native application that makes use of the mobile device’s Web View. It is more like a browser that runs full screen. Hence, they are able to utilize most of the device capabilities just like native apps. Some of the general features of hybrid apps are as follows:
- They are coded using a combination of technologies like HTML5, CSS and Javascript.
- They are easily available on the app store to be installed.
- It uses hybrid technologies like PhoneGap (or Apache Cordova), which provides APIs to gain access to native platform features like the camera and contacts.
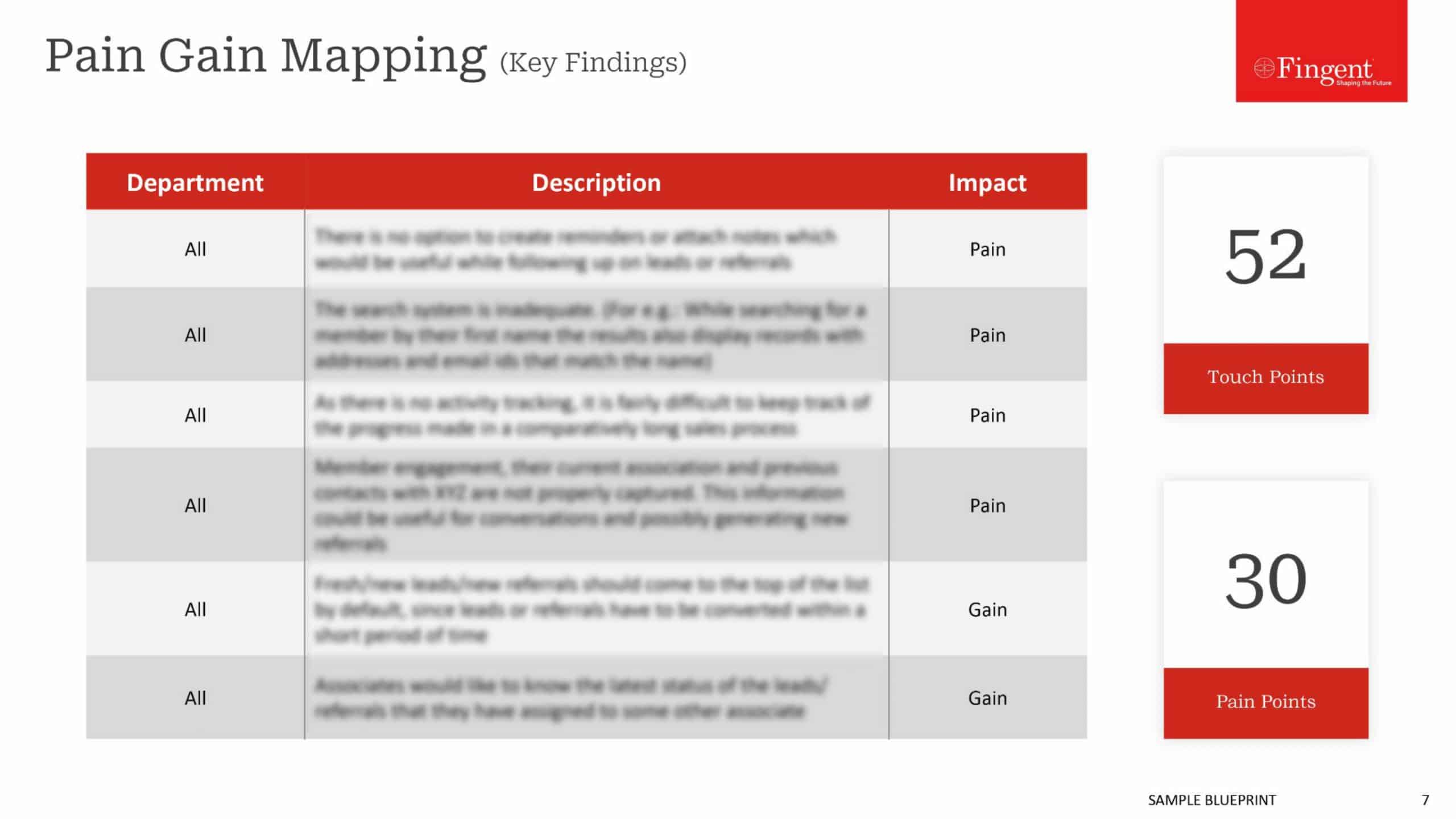
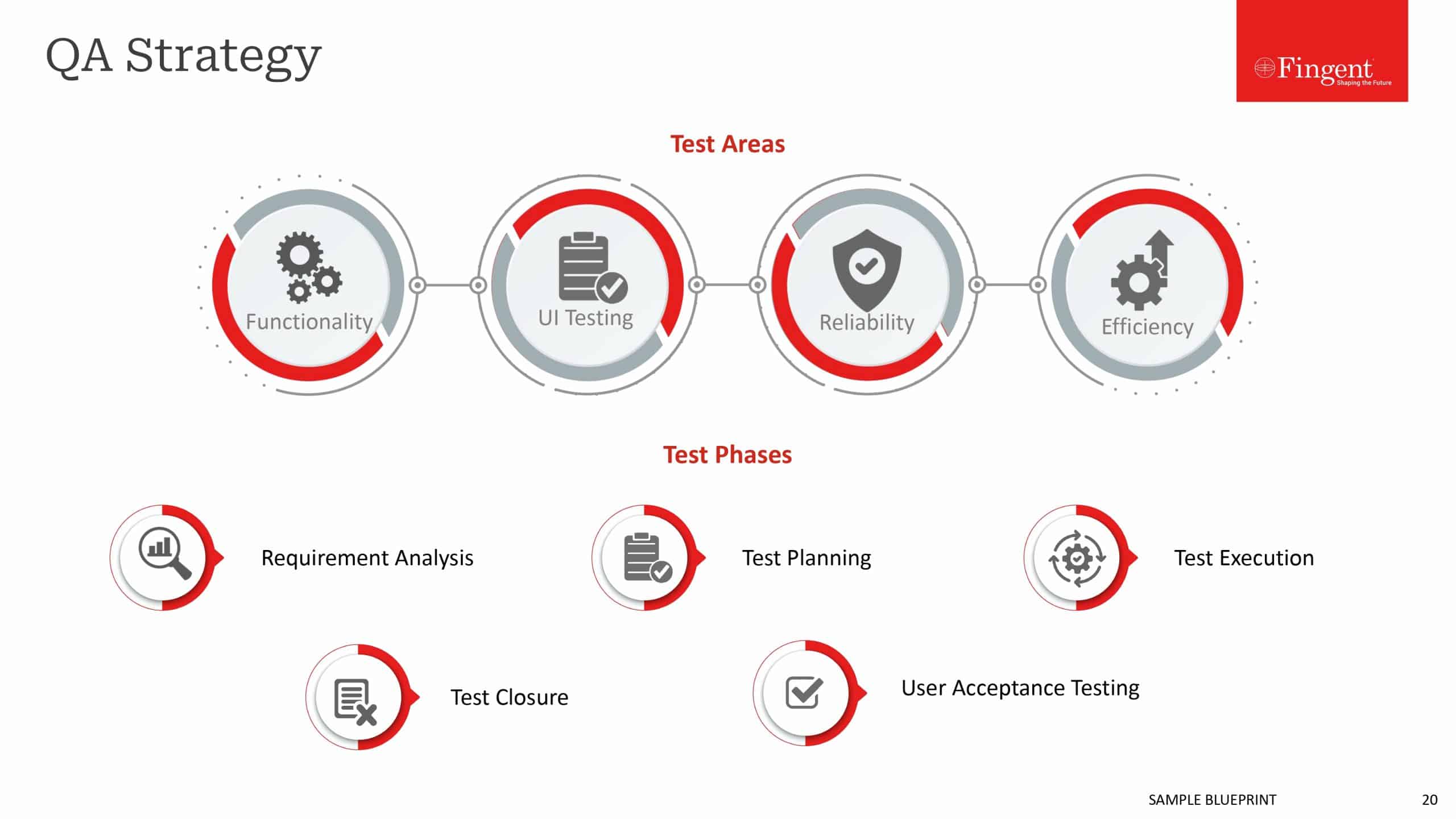
COMPARISON OF NATIVE AND HYBRID APPS
Now that we have a basic understanding of both kinds of apps, here we have a comparative study of the features and elements of the two.
User Interface
In terms of user interface, there is not much of a difference. There may be minor differences in the looks and the like, to enable a consistent user experience depending on the platform. Apart from that, both native and hybrid apps are designed to look and work the same way in terms of user interface and experience.
Development
Native apps, as mentioned before are developed using specific programming languages for specific platforms, such as Objective C for iOS, Java for Android and Visual C++ for Windows operating systems. They make use of standardized Software Development Kits (SDKs), user interface elements like buttons and text boxes, and other development tools provided by the manufacturer of the respective platforms in the process of development. They are developed using code specifically written for the app. It basically means that native applications are harder to develop and take more time.
Hybrid apps on the other hand, are developed using HTML or CSS or Javascript or a combination of these. As mentioned before, they are made to work inside a native app container so that they can have access to the hardware capabilities of the device. More importantly, most of the functionalities of hybrid apps are taken care of from the back end or server side, unlike native apps.
One of the most popular platforms that is being used for hybrid applications these days is Apache Cordova, which was earlier known as PhoneGap. It helps to provide a consistent and reliable set of Javascript APIs in the form of plug-ins which are built using native code, so that the app has sufficient access to hardware capabilities on the device. They take lesser time and effort to develop, as they make use of already existing code segments across multiple platforms.
Delivery method
Native apps as well as hybrid apps can be downloaded from an app store and installed on the device. Since hybrid apps make use of plug-ins to enable the hardware functionality as a native app does, even hybrid apps are available on the store, unlike web apps. For the same reason, the users need to manually download and install updates as and when they are ready.
Accessibility
Native apps, as they are developed for a specific platform, have access to all hardware and software functionalities of the device or platform on which it is installed. Hybrid apps on the other hand need plug-ins to have access to device specific features.
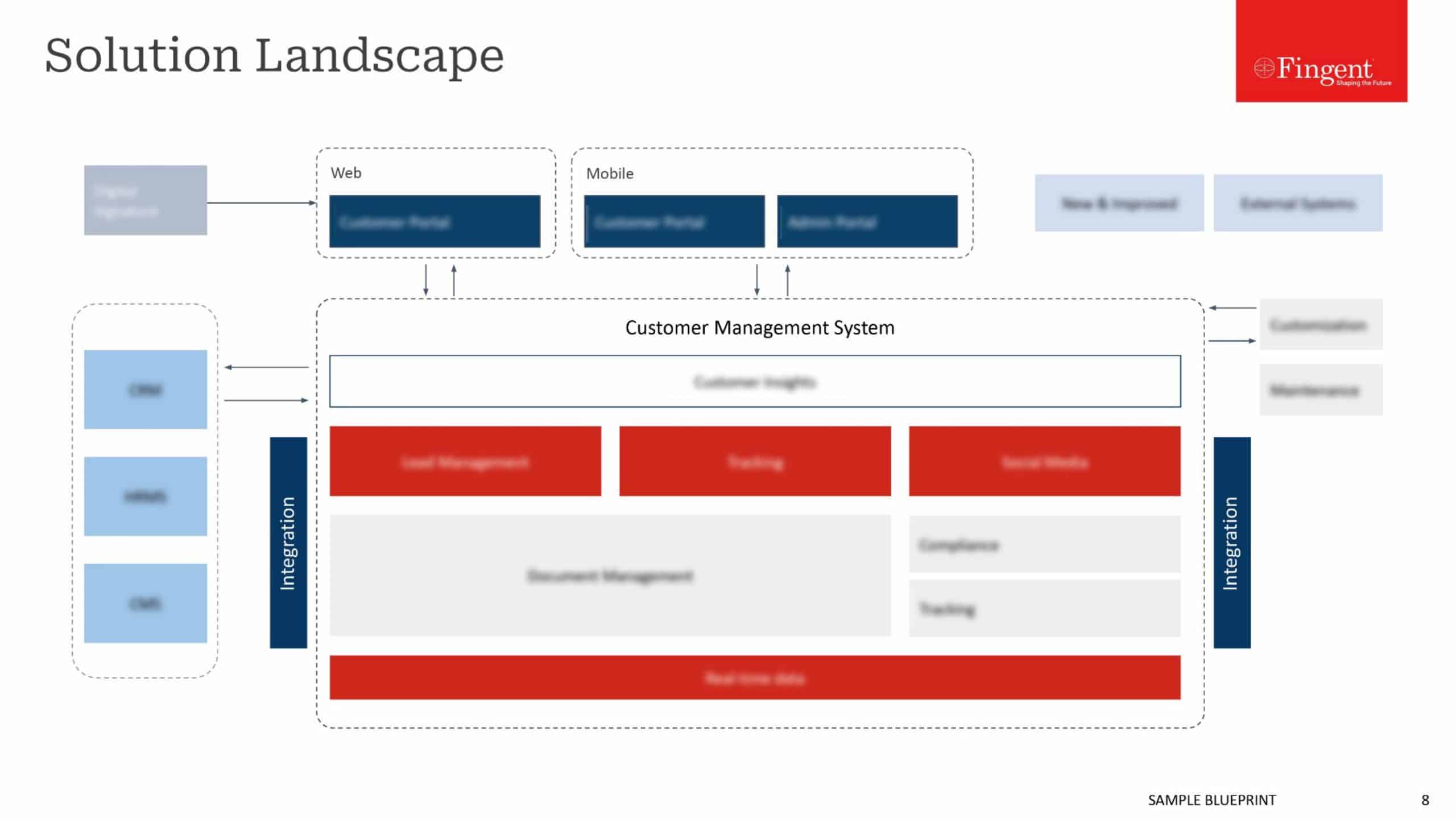
While choosing between native and mobile apps, some of the factors that you need to consider are as follows:
- Time – Native mobile applications require a longer duration of time to be developed because we need to start it from scratch. There is a lot of effort involved in building a native app as the entire code needs to be written to program the whole app. Hybrid apps on the other hand require much lesser time as they can use already written HTML code components across various devices. If you are looking to develop a mobile application and you want it done within a short period of time, then, a hybrid app would be a better option. This is one of the reasons that make hybrid apps popular.
- Budget – Native mobile applications are more expensive to build for the same reason why they require more time to develop. The effort that has to be put into making a native app is a lot more when compared to hybrid apps. Hence, the costs involved in developing native apps are more than that for hybrid apps. If you have cost concerns regarding your mobile application, then it is always better to go for hybrid applications. They are usable across multiple platforms and are available at a lesser cost.
- Requirements – If you need an application that uses features like video editing and trimming, or if your application needs access to in-device features like contacts, then you need to go for a native application. Hybrid apps do not have that capability.
- Scalability – This is an extension of the requirements factor. Native applications are more scalable than hybrid applications. If you plan future expansions to your application with more native features or features that require more communication with the Operating System of the device, it is always better to go for a native application. Hybrid apps can be made to have native features to some extent, but if you are planning to integrate many more features and add more functionalities to your app in the future, then you need a native app.
- Speed – Native applications perform faster and are easier to work with as they use the device’s built-in features. Hybrid apps, on the other hand, may not be as fast.
The basic advantages of a hybrid application over a native application are in terms of cost and time. Although, you get more efficiency and accuracy through native applications. These points will definitely help you choose better between native and hybrid apps..
Nevertheless, what matters the most is your requirement. And your final decision is entirely dependent on the kind of requirement you have.
Need more help? Talk to us! We can create powerful custom mobile applications or help you decide what works best inline with your business goals.
Stay up to date on what's new

Recommended Posts

21 Sep 2017 Retail
Different Phases of Mobile App Development for Businesses
Mobile applications have become mandatory for every business in the current times irrespective of the nature and size of the business. These apps allow businesses to create a direct marketing……
08 May 2017
Native Apps vs Web Apps: Choosing the Best For Your Brand
Mobility is growing at an exponential pace and mobility apps are the flavor of the season. However, it is still important to get the development right, to reap the benefits……

03 Nov 2016 Financial Services
Trends Shaping Mobile Payments Market Worldwide
Mobile payments are of a recent origin but have caught on like wildfire. Mobile-driven commerce now exceeds US$972.25 billion, and mobile payments are expected to touch US$3 trillion by 2021.……
13 Oct 2016
Is UX More Important than Security Considerations?
While security remains a pressing concern in the mobility space in continental Europe, UX is now emerging as a bigger investment area, in the English-speaking world of UK and US.……
Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new