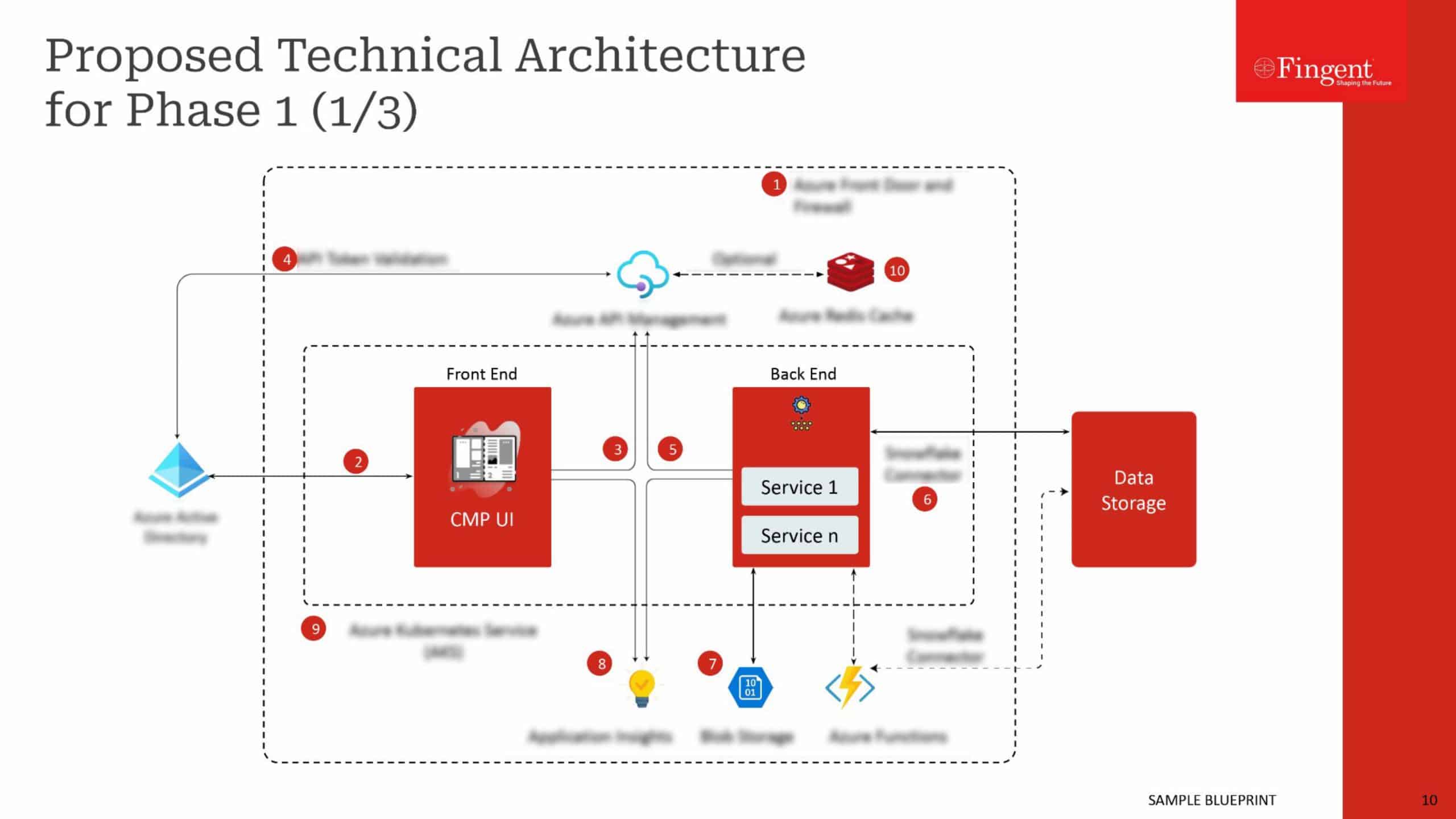
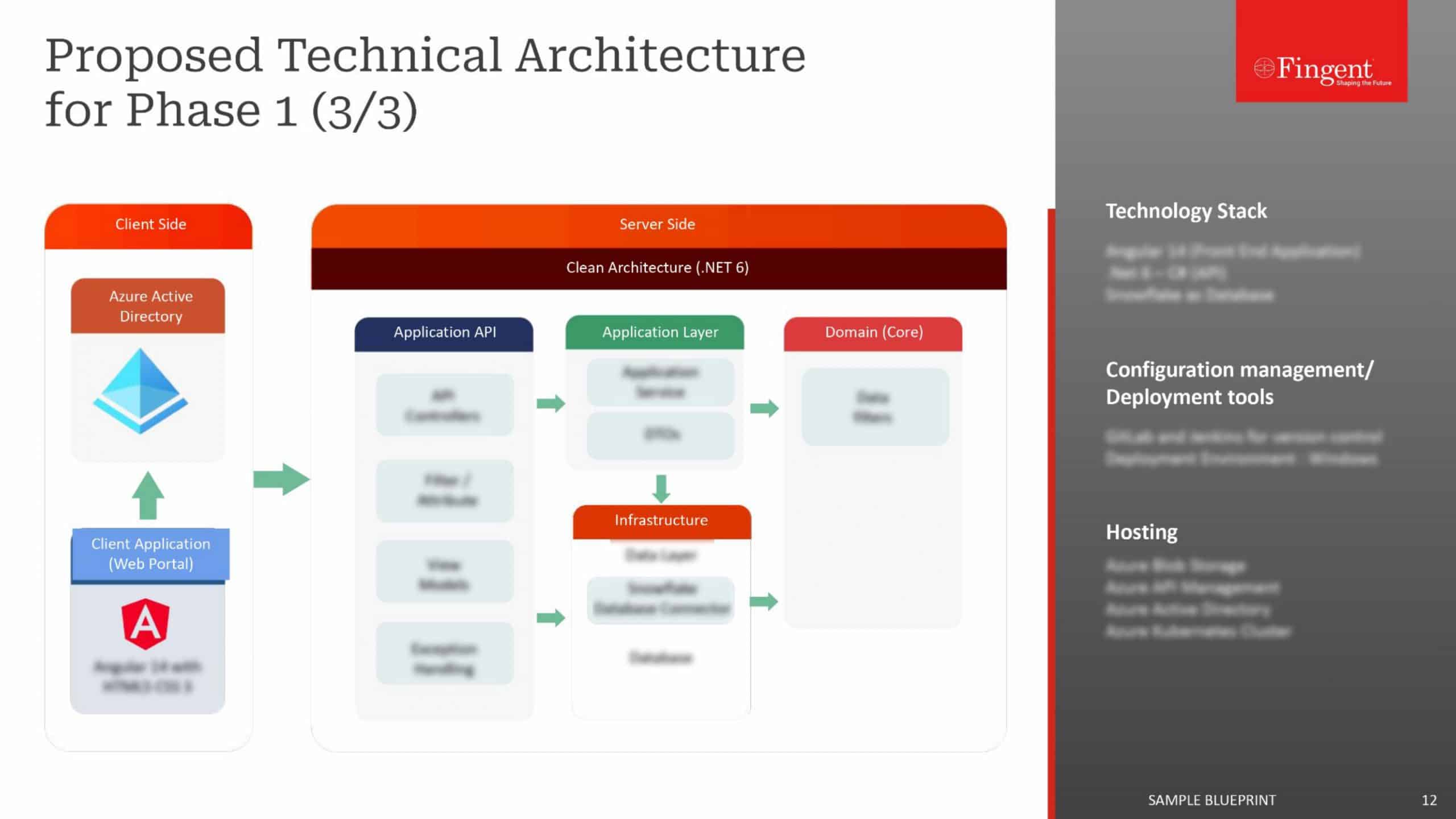
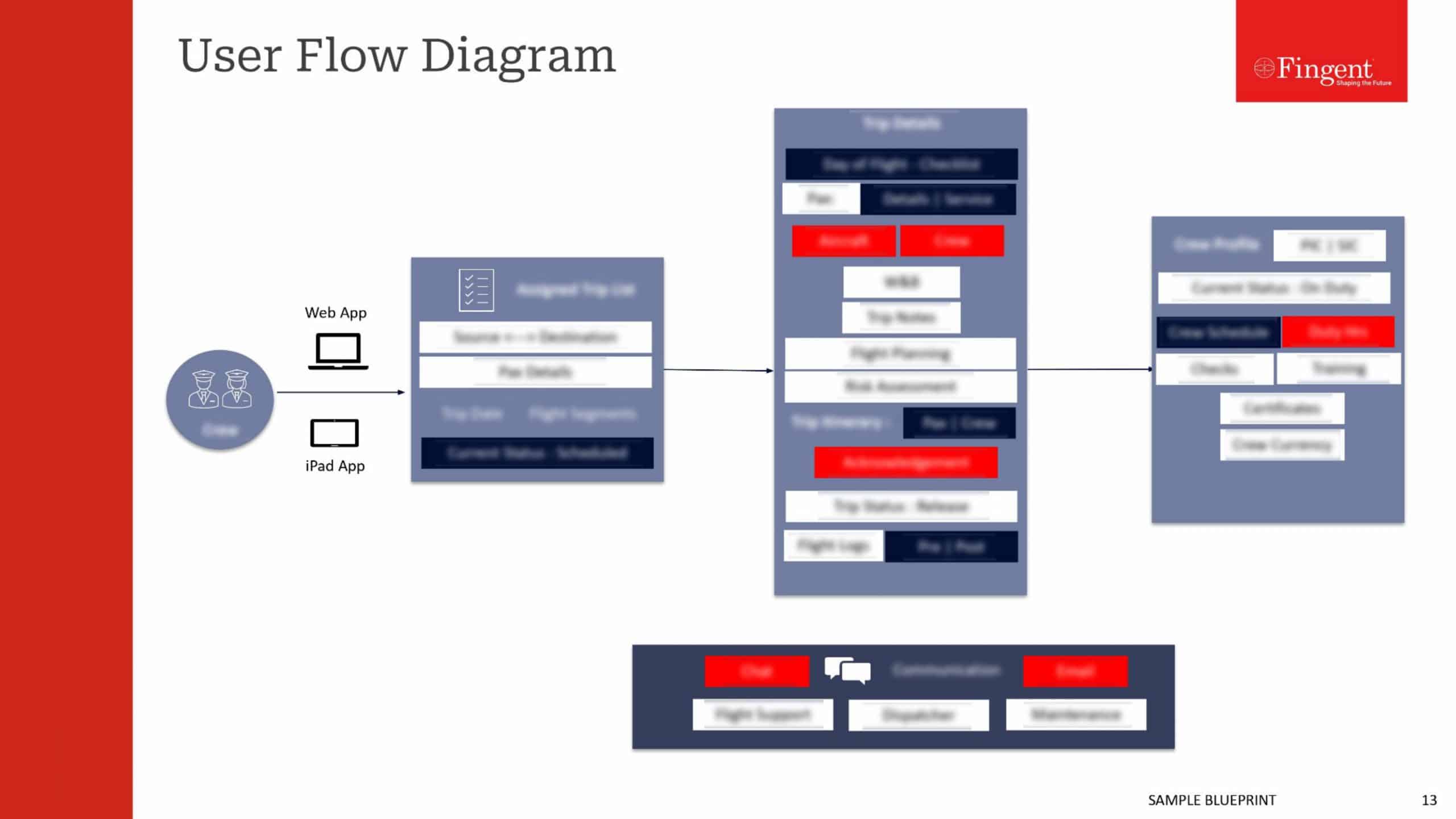
Tag: enterprise mobile apps
Technology successively progresses all around us; from the simplest basic Google searches to the working of aircraft, technology has indented its value in everyday life. Biometric APIs are not a foreign idea to us, and 81% of all smartphones have biometrics enabled. Passkeys (on Apple) and Google’s new standards will enable a new class of security with protection like never before. This article will discuss the rise of this form of authentication and its benefits over traditional passwords.
Security – A Major Concern
A big chunk of our daily lives revolves around our mobile phones; sometimes, it is the key to our survival. Once technology grew and mobiles were planted in people’s hands, brands and organizations became smart and decided to adopt their services into these devices. Online banking and payment methods, personal detail locks, and private picture archives evolved. These are just a few generic examples of the important things we trust our mobile phones to hold. This being the case, is it not all the more important to ensure that this technological linchpin is protected at all costs?
Cybercriminals can hack into almost anything today – cars, security cameras, door locks, baby monitors, smart TVs, and even healthcare devices. Mobile devices can be extremely vulnerable to hostile software, viruses, data leakage, and other mobile threats without tight security measures. In such situations, one can not rely only on traditional password-based systems because they will crumble under a brute-force attack.
The Rise of Biometric Authentication
In very simple words, Biometric Authentication is essentially authentication that utilizes biometrics modalities (fingerprint, facial recognition, retina scanning, voice recognition, and more) to detect and authorize the identity of the user trying to access an electronic gadget. An individual’s biometric features are unique to only themselves, and authentication based on them is guaranteed to be effective.
Here are some advantages of biometric authentication over traditional passwords:
1. High security and assurance – Traditional passwords and security codes are generally harder to remember. The biometric system eradicates this problem by offering different modes of verification instead. Additionally, since fingerprints and iris scans cannot be forged, sensitive data will remain more protected.
2. Offers The Best ROI – The biometric authentication system is famous for its matchless ROI. It is a single device that keeps a check of every employee’s whereabouts in a large enterprise. The device is significantly better than a human resource representative who would claim a hefty salary to do the same job.
3. User Experience – Using this system is very convenient as it is built into most devices. This system is highly cost-effective and extremely fast in processing. In addition, forgetting a password is an infamous mistake of most users, but with biometrics, it’s impossible to forget them.
4. Prevents forging – Since everyone has their own set of biometrics, the forging of authorization is very slim. (Unless someone decides to pull a 007 move and trace fingerprints)
Current Adoptions and Usage
The Cisco Report of Trusted Access in 2022 stated that 81 percent of all smartphones have biometrics enabled. Mobile biometric authentication can be used in numerous industries, some of which include –
1. Mobile Banking – Banks use biometrics to authenticate transactions taking place through mobile banking. They also use biometric authentication to verify customers when they try to access their mobile banking app or bank accounts. Most popular banks now introduce the fingerprint and touch method for signing into their mobile banking app.
2. Retail Shopping – Online shoppers tend to abandon their shopping cart or any purchases when they can’t remember their passwords, but facial biometrics can resolve this problem for online shoppers by providing a simpler login experience. This can directly increase retail business. Mastercard has recently introduced its Identity Check Mobile, a mobile-based biometric authentication solution that allows customers to verify their identity by sending a selfie to the online retailer’s website.
3. Healthcare – Biometric information from fingerprints, iris scanning, and facial recognition are helping hospitals to identify patients and retrieve their past medical history. Northwell Health exemplifies this use case by using iris scanning and face recognition to identify emergency patients.
Read more: How Businesses Are Using Facial Recognition to Create An Impact!
Enabling Secure Authentication with Biometric APIs
API stands for Application Programming Interface and when used in conjunction with Biometrics, it refers to the Programming interfaces of websites and applications that are powered by biometric modules. Mentioned below are the three main types of biometric authentication:
- Fingerprint Authentication – It is the most common biometric authentication method and involves scanning a user’s fingerprint.
- Face Recognition Authentication – As the name suggests, this uses the mobile device’s front-facing camera to scan the user’s face. It is very simple to use and offers a high level of accuracy.
- Iris Scan Authentication – The user’s iris is scanned for authentication in this method. Iris scan authentication is the most secure biometric authentication method as it is extremely difficult to forge.
As Biometric Authentication provides such enhanced security, almost all mobile phone brands have adopted this feature to enhance the security they can provide, thereby building more concrete trust with their customers. For iOS-running mobiles, the availability of biometric options such as Face ID and Touch ID depends on the device. All Android 10 and newer devices have biometric authentication for face and fingerprint identification.
Three distinct areas highlight how biometric APIs will potentially replace passwords:
- Security – Since each individual has unique biometric modalities, it comes as no surprise that security in biometric APIs will be far better than traditional passwords.
- Convenience – The main reason that most people despise passwords is because they can be hard to remember. Further, remembering the login passwords for all of these can be tedious since most have multiple accounts on numerous platforms. Here the use of biometric API helps again because with these APIs the need for remembering a password does not exist.
- Future proof – Progress in AI, sensor technology, and IoT will ultimately enable seamless biometric authentication. When seen this way, biometrics stands out as catering to current and future demands, unlike traditional passwords.
Benefits Of Biometric APIs For Mobile Applications
Traditional password-based authentication presents multiple challenges, including password fatigue, poor user experience, and pressure on support and IT teams when passwords need to be reset.
Biometric APIs address these issues with the following benefits –
- Reduced password fatigue – Customers are not required to memorize all their passwords when matters lie in the hands of biometric APIs. An added advantage is the mitigation of password-related risks such as weak passwords and password reuse.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) – SaaS companies can now imbibe another wall of security by collaborating the power of biometrics with other methods.
- Improved customer satisfaction – it goes without doubt that all these advantages of biometric authentication will ultimately win the hearts of customers.
- Enhanced security – the concept of ‘no passwords’ renders cyber attackers helpless as they have a much harder time invading laptops and smartphones that are protected with biometric authentication.
Few Successful Implementations of Biometric Authentication
Biometric systems are great and immensely beneficial wherever identification and authentication are critical.
Let’s quickly look at the most typical use cases of biometric technologies today:
- Law enforcement and public security (criminal and suspect identification) through the work of forensic analysts.
- Military (enemy and ally identification) under the leadership of the DoD Automated Biometric Information System.
- Border, travel, and migration control (traveler, migrant, and passenger identification) in the form of electronic passports.
- Healthcare and subsidies (patient, beneficiary, and healthcare professional identification) are seen with national identity cards used in European and Middle Eastern countries.
Concerns And Considerations of Biometric Authentication
Like any developing technology, biometric authentication has its fair share of considerations. Discussed below are a few of those:
1. Privacy and Data Protection Considerations – challenges in privacy arise when one realizes that biometric APIs can use your information without warning you about it at the time of registration.
2. Ensuring Accuracy and Reliability of Biometric Authentication – these are seen when there is an evident bias in the training data and declining access due to erroneous scanning and compromise of the biometric, for instance, a cut finger.
3. Regulatory Compliance and Legal Implications – when intermingling emerging technologies with biometric APIs, unexplored legal territories are bound to emerge and transcend the domain of human health.
Future of Biometric Authentication
Biometric Authentication, from its dawn, has shown true potential for progress, and it continues to be adopted into various fields of life. A TMR study predicted that the biometrics market will efficiently boom to $136.18 billion by 2031. Listed below are some trends in biometric authentication that will paint the sky in the coming years:
- Verification of Physical Identity – Biometrics powered by AI using cameras installed on-premises.
- Use of Newer Identity Markers – Modalities such as odor recognition, heartbeat pattern recognition, DNA signature, and hand geometry are being developed.
- Identity Proofing – the use of ‘liveness’ testing to guard against identity theft. This can also be accomplished with the help of AI.
- Healthcare Applications – Biometrics will verify the patient’s entitlement to specific medical treatments and medications.
Biometric systems have the untapped potential to enhance cyber functioning with biometric authentication and identity management systems. The list of actual benefits of these APIs is miles long, and the right use of these applications can benefit the entire world. Countries across the globe are adopting Biometric Authentication and systems. Will you?
Connect with Fingent top software development company to learn more about how you can leverage technology to enhance your business operations and customer experiences.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
With the internet, especially mobile internet now a way of life, businesses are going overboard developing enterprise apps. A 2015 Gartner survey reveals 79% of enterprises increase their mobile spending by 36%. These numbers are increasing every year and for good reasons.
Here are the basic reasons why enterprises are going overboard, developing mobile apps for their internal and external stakeholders.
1. Enterprise Apps Improve Productivity and Efficiency
Very few businesses can get away with slack in today’s highly competitive business environment. Enterprises looking to remain competitive have no option but to go all out in improving internal efficiency and boosting employee productivity, and enterprise apps contribute in a big way on both these fronts.
Enterprises apps increase employee productivity, help to optimize business processes to bring in process efficiency, and unlock insights which drive new business models. It facilitates a lean business model, with greater transparency, facilitating operations with reduced inventory and just-in-time inventory fulfillment practices.
Often, employees hit a roadblock in their quest to do something by being unable to access the required data. Enterprise apps make it easy to retrieve data. Moreover, one of the important pre-requisite before developing enterprise apps is removing data silos and fostering transparency, for apps to retrieve the data in the first place.
Mobile apps simplify what would otherwise be convoluted and even confusing processes. Armed with an app, the employee would know exactly what to do and how to do, without the risk of errors or procedural delays.
The single biggest drag on employee productivity is searching for information, preparing reports, and other routine “maintenance” tasks. Enterprise apps automate most of these processes, leaving the employee free to work on their core responsibilities.
2. Enterprise Apps Empower Field Workers
Today’s businesses are extremely mobile. They often work from multiple locations and have no option but to become go-getters, reaching out to customers at their site rather than expect them to visit their premises. The importance of sales and service has also increased manifold. A vast number of businesses, from delivery services to long-haul truck drivers, and from airport mechanics to courier companies, have agents or technicians on the field.
Until recently all these businesses were constrained by lack of real-time access to their technicians. Scheduling remote work was hit-and-miss, with the site visit depending on many variables with the main office having no control or visibility into what is going on.
Smart devices, such as tablets and smartphones, powered by enterprise apps, not just allow remote workers to remain connected to their office, but also offer real-time insights into the process. They feeding first-hand data from the ground to the enterprise system, and get analyzed data, in a recursive cycle, to gain unparalleled insights. At the customer end, full transparency and visibility into the field workers movements make the wait for service to arrive less agonizing.
Sales executives get all insights related to the customer he or she is about to visit. Their mobile app taps into all relevant data, subject it to real-time analytics and makes it available in easily consumable formats. Likewise, the executive, during the course of the meeting, can crunch data, make follow-ups, make commitments, or show projections, instantly, without having to make follow-up visits and lose the momentum.
It gets better. With IoT soon coming into the mix, remote devices can communicate with the main office, sending signals on what exactly is wrong, allowing field service technicians to make the site visit with the right tools and spares, sparing the need to make re-visits. Likewise, augmented reality (AR), artificial intelligence and other cutting-edge technology enable even rookie field service technicians to perform complex tasks, with support from experienced hands situated even in another continent, with AR powered enterprise apps offering seamless connectivity.
3. Enterprise Apps Increase Engagement and Sales
Customer facing enterprise apps drive sales and improve customer satisfaction manifold.
E-commerce apps make it easier for customers to buy. Often customers, wanting to buy a product, are put off by the complexity of the whole process, or the need to take time out to visit the e-commerce website. The easy-to-use mobile app makes the product available in just a few easy and convenient swipes. The same convenience holds true for reaching out to the company to make inquiries, and log complaints or support tickets.
4. Enterprise Apps Unlock New Insights
In today’s information heavy age, all businesses end with up tons of data. Such data could be a source of competitive advantage if subject to analytics, to derive actionable and relevant insights. Much of the big data is unstructured in nature, in the form of MS-Word documents, emails, videos, and embedded sensor data. Using intuitive enterprise apps powered by highly intuitive analytic tools, business managers and executives may subject such data to backend analytics, and gain actionable insights, allowing them to make more informed decisions that take guesswork and “gut-feelings” out of the equation.
An automated data analysis and presentation system collect data from a variety of sources, from shipments to warranty claims, and from failure analysis reports to bills, analyze the data automatically, and offers the insights to those who benefit from it. It requires custom apps to establish the data flow, make the required analysis and personalize the presentation mechanism.
For instance, when a customer enters a store, the executive who engages with the customer enters the customer’s name or telephone number into his app, which runs on a tablet or smartphone. The intuitive backend gathers all information residing internally, including purchase history, customer support ticket information and more, and also access the latest social media information to understand current taste and information. Such information is processed in real time, analyzed to identify the product range, price range and other preferences of the customer, allowing the executive to showcase relevant products and offer deals that really strike a chord. Without an app, powered by analytics backend, such information would be near-impossible to obtain, and definitely not in real-time.
5. Rolling out Enterprise Apps is Pandering to the Market
As the adage goes, “nothing is as powerful as an idea whose time has come.” Mobility is an idea that has gained currency and is now well entrenched. Today’s sophisticated users, both internal employees and external customers prefer simple interfaces as a means to deal with the underlying complexity, and they see intuitive web apps as the solution. Businesses who does not invest in enterprise apps stand the risk of alienating their stakeholders.
While conventional web-based interfaces may offer a solution to a limited extent, the changing nature of business and internet, especially the increasing number of people on the move make mobile apps expedients. Most users today anyway expect a higher level of usability and performance than what a web-based interface can deliver.
The best enterprise software is reliable, robust and up-to-date. Blindly rolling out apps left, right, and center, for the sake of it does no good. The enterprise app strategy succeeds only when there is clarity on what an app actually delivers that other touch points cannot, and then executing the app development process well, with an easy interface and powerful functionality. It helps to outsource the app development process to a competent agency who has experience and expertise in the work, and for whom developing an app won’t be a distraction from their daily routine.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Mobility is the rage among enterprises, as the benefits of anywhere-anytime connectivity and productivity-efficiency improvements start to sink in. However, amid the hype, the hard reality of user engagement is starting to bite. The challenge is to produce mobile apps that drive user engagement and produce it quickly, to keep pace with the fast-changing business requirements.
Driving user engagement requires offering a compelling experience for the target users. Here are the ways to do so, and thereby meet enterprise mobility demands in a successful way.
Fix the Scope
The very purpose of rolling out apps, as an alternative to the website, is to offer enterprise users the convenience to focus on a specific function or purpose, without being cluttered or distracted by unnecessary features. As such, the scope of any app is all important. A proper definition of the scope of the app, or what the app does, can make or break it.
The apps in highest demand by enterprises, cutting across industries are customer relationship management apps for sales, marketing and services, customer engagement and general employee productivity apps. However, even within such classification, the best apps facilitate only specific tasks.
A key consideration when deciding on the scope is to evaluate the benefits various segments of the workforce expect from the app, and how such benefits sync with the overall objectives of the enterprise.
Although employee job satisfaction is critical, the success of the app ultimately depends on the scope of the app, and deployment decisions having a direct correlation with the overall business objectives, be it improving customer service, increasing productivity, driving costs down, or anything else.
The best mobile apps leverage the power of simplicity. They may have a complex backend, with integration and cross-links to several enterprise function and resources, but still deliver a simple, neat, and clean user interface. The user gets a clear cut menu, allowing them to do powerful things with amazing simplicity. User experience is ultimate to ensure high adoption
Demolish Data Silos
An app is only as good as the data it handles. Even the most intuitive of apps will not gain sufficient traction if it is unable to access meaningful data. A big bane of enterprises and a key reason why enterprise apps fail is data trapped in inaccessible silos. Demolishing data silos, and centralizing data to an easily accessible location is an important prerequisite before launching enterprise apps.
It is also important to deliver content in a mobile experience that ties into the content management system, to ensure seamless sync. For instance, a mobile app to offer added value to a field marketing executive, he needs to access the latest information regarding the client, when engaging with the client at the client’s office. Likewise, the information of such meeting needs to be updated into the CRM in real time, for the enterprise to take action on the latest and updated information.
Need for Proactiveness
No matter how intuitive apps are, users need to be coaxed into using it. The most successful apps are “proactive,” leveraging an integrated set of engagement services such as in-app messaging, push notifications, dynamic use of analytics, and more. The best apps keep tracking what the user will most likely do, and issue timely reminders and prompts in this direction.
Method in the Madness
With the craze for apps, an enterprise will invariably find themselves saddled with a plethora of apps, and things can quickly get out of control. An average enterprise in Europe and USA would deploy around 10 or more enterprise mobile apps during the next two years. A good way to manage existing apps is by leveraging the mobile capabilities of Adobe Experience Manager, which helps to centralize all apps in a singular, unified dashboard.
A Hybrid Strategy
Most enterprises have limited capabilities to conjure up intuitive mobile apps on their own. Their in-house IT team in almost all cases is invariably neck-deep in routine tasks without having time to take up the time-consuming app development process.
Enterprises always have the option of promoting a resident mobile app team, by either hiring the right talent or investing in training the right people with the required skill-sets. However app development skills are hard to come by, and technology is any way in a constant state of flux for investment in any specific skill set to deliver long-term ROI. Other limitations such as budget and resourcing limitations, legacy infrastructure, technology fragmentation and immature lifecycle workflows also contribute to making internal development teams a non-starter.
Outsourcing the development task to a contractor is a far more cost-effective, and offers enterprises the best of both worlds – access to talent without the associated overheads of hiring.
Considering such factors. it comes as no surprise Forrester Research estimates enterprises spent $18 billion to contractors in 2016 to build and maintain mobile apps. The global market for enterprise mobility is expected to touch $284 billion by 2019, a four-fold jump from the present levels of $72 billion. Even large companies, with personnel requirements for app development and maintenance, and budget on their hands, adopt a hybrid approach, using outsourced skills to build mobile apps, and side-by-side train employees on building and maintaining mobile apps.
However, unless the enterprise selects the right contractor, the money spent goes down the drain. Ensure the contractor has the right expertise and has a track record of having implemented successful mobility projects. We tick all boxes, bringing with us our wealth of experience, a pool of highly talented and resourceful development team, and the latest cutting-edge tools to get the job done well in double-quick time. App development is our core competence, and our team comes fully conversant in the latest development styles, user experience best practices, and more.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new