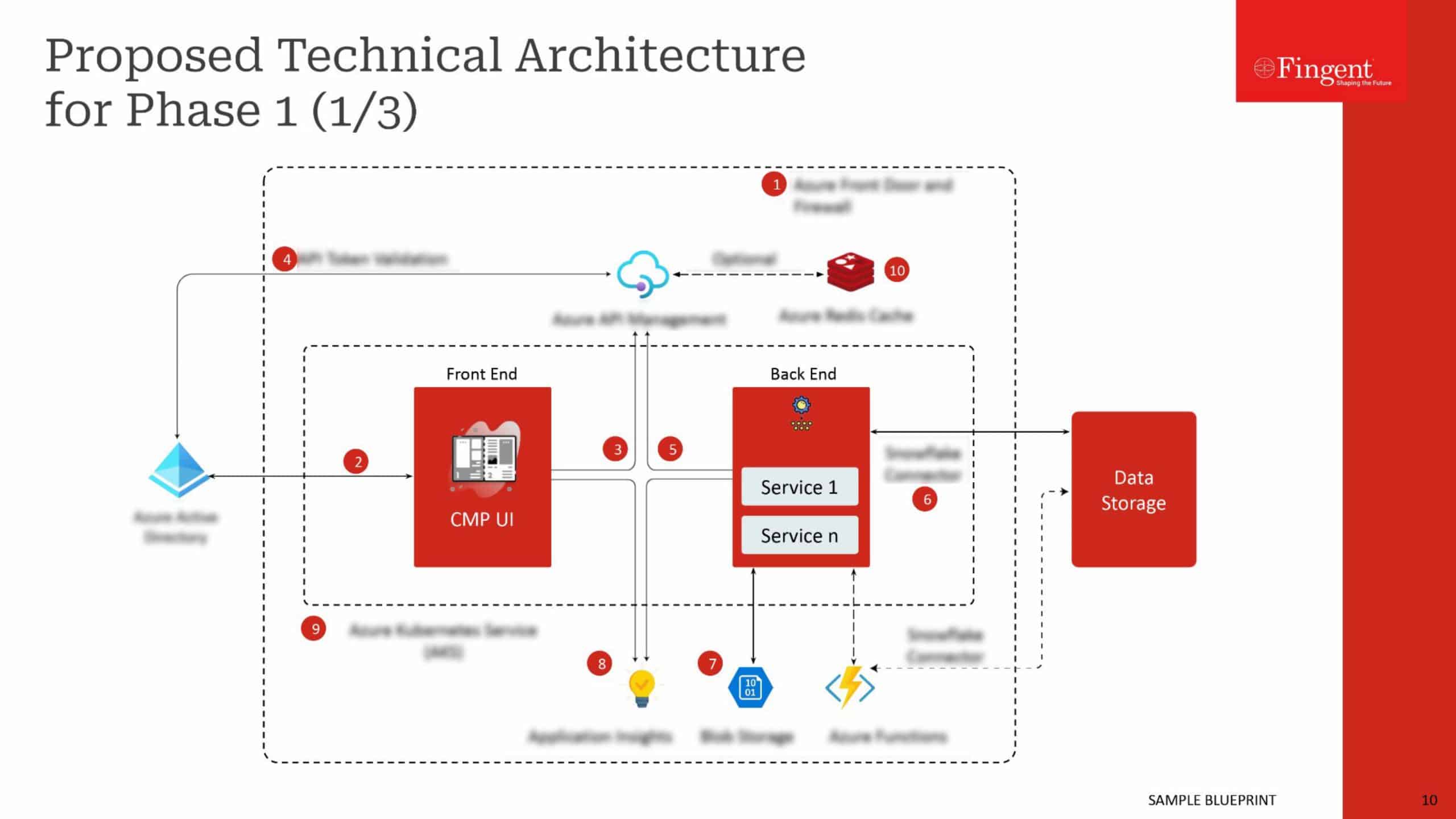
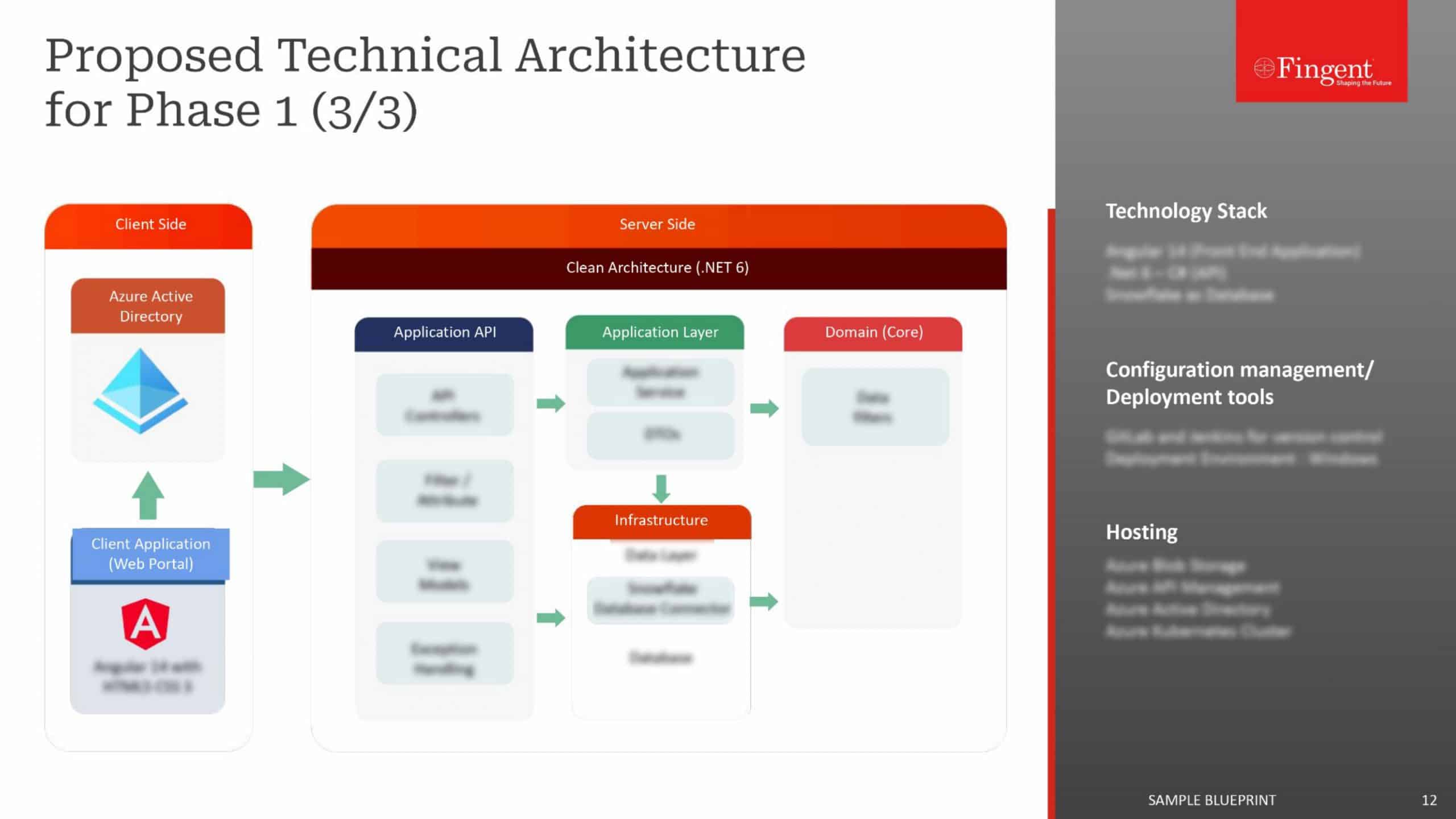
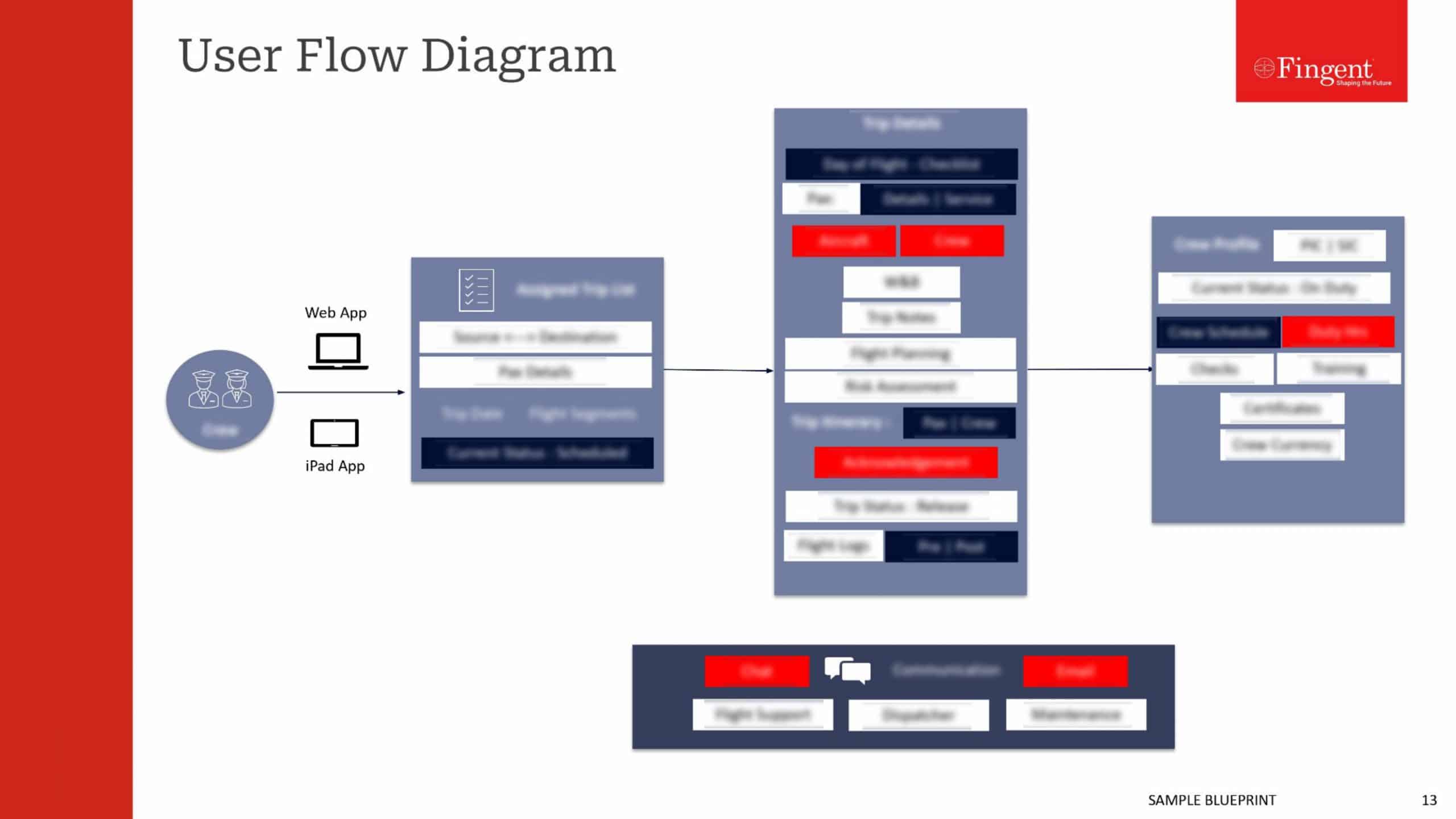
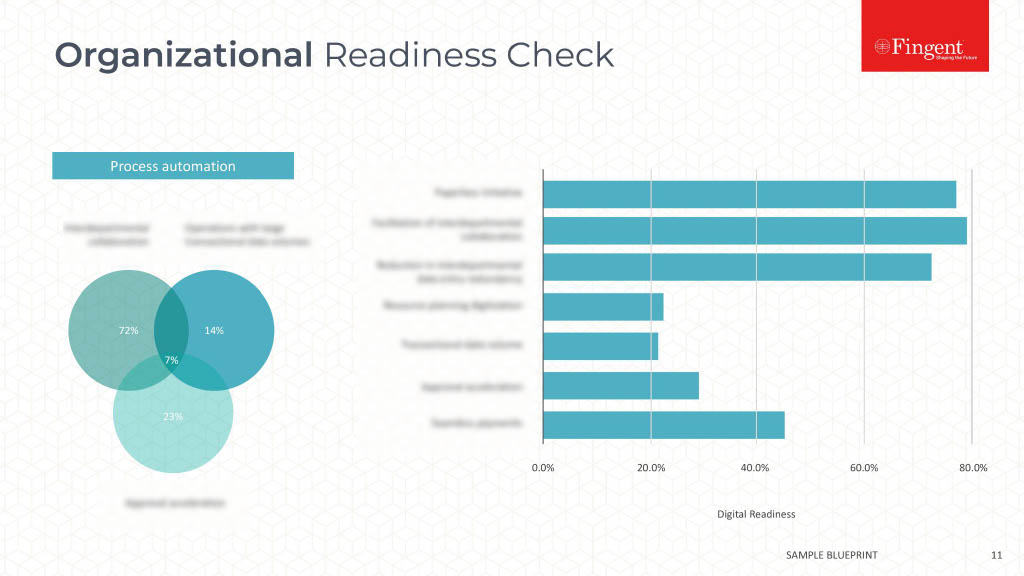
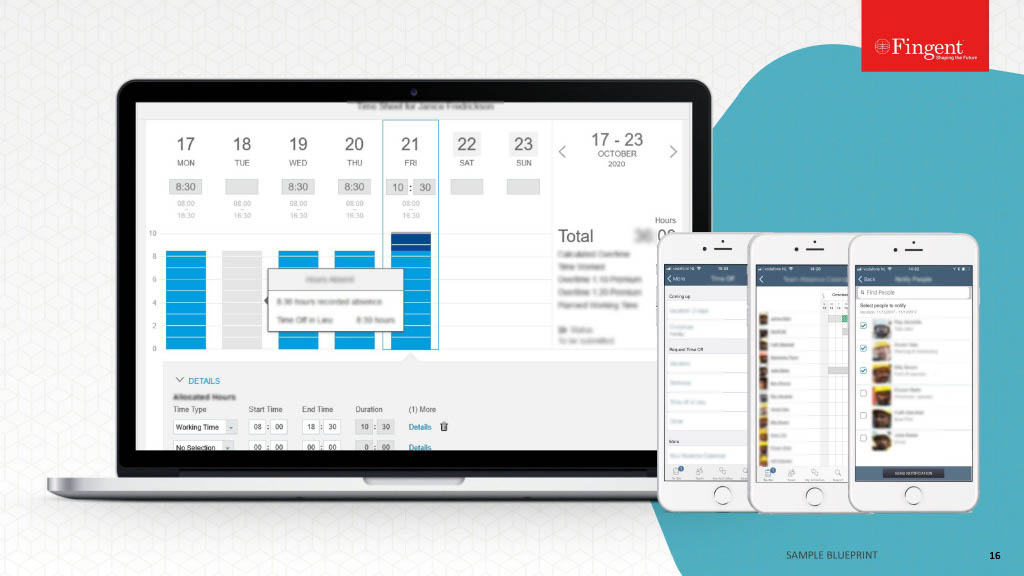
Tag: React.js
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
All that you need to know about React Developer Tools
React is an incredible framework for frontend development. It also facilitates mobile app development for multiple platforms. React was a game-changer for IT companies in the USA and across the world, and developers were thrilled when Facebook announced its launch. This post explores the features of React developer tools.
If you are into React development, you must have tried the official chrome React developer tools. This React devtools extension lets you debug your components and is available even as a standalone application. React developer tools help us smoothly create interactive UIs and React is able to reconcile changes to the DOM in a performant way.
The React Developer tool is undergoing constant development with new features added to it regularly. It is an essential instrument you can use to inspect a React application. This article lists out the features of React Developer Tools that you might like to try out and also discusses the best IDE for React.
Read more: React Native App Development – React Native Or Flutter – The Better Choice For Mobile App Development
Inspect and Debug
It is possible to use breakpoints, step-through, and logging to debug a React app. But it can become difficult especially if you have to debug an application that you haven’t seen before. By installing React developer tools, you can overcome some of these challenges.
Installing React Developer Tools
You can install React developer tools on the browser you are using to run the application. One of which is the chrome React developer tools extension. It is available in the appropriate extension store. Once it is installed, either as a browser developer tool or as a standalone application, two new tabs will become available: Components and Profiler.
Components Tab
The Components tab allows you to see the root React components that were rendered on the page and the subcomponents that they rendered. You can inspect and edit its current props and state in the panel by selecting one of the components in the tree. It allows you to inspect the selected component, the component that created it, and the component that created the second component and so on.
While inspecting a React element, switching over to the React tab will automatically select that element in the React tree.
Profiler Tab
The Profiler tab is an incredibly powerful feature introduced in 2018. React Devtools provides a profiling feature that allows you to see a summary of how your application re-renders. Just like the regular JavaScript profiler, you will have to “record” a set of interactions. Once you start the recording, React Devtools will automatically gather the performance information each time your application renders. You can continue to use the app as you normally would. Once you’re done with profiling, click the ‘stop’ button. Now you will be able to see a visualization of each re-render with accurate timing information and color-coded flame graphs.
Read more: Web Development Stacks – Top 6 Tech Stacks That Reign Software Development in 2020
Best IDE for React
A good IDE for React is a must to get started with the React ecosystem. Selecting the best IDE for React from among the many that are available out there can be a daunting task. This section will help you make a choice from both the free as well as the paid IDEs.
1. VS Code
VS Code is a Microsoft product and is available for free under open-source MIT license. You can download and set-up VS Code on Mac, Debian, Windows, Ubuntu, Red Hat, SUSE, and Fedora. It can be used for various programming needs. Being the most used free IDE, it is loaded with many useful features.
The plugins enhance JavaScript programming as well as the development experience with React and React native and more.
2. Reactide IDE
Reactide is comparatively new but is gaining popularity among the community of React web app developers. It focuses on web apps development. It is entirely dedicated to React-based application development. It is a one-click setup that installs and runs a custom browser simulator. It spares you from switching between code files and the browser to check the changes made. It is a cross-platform, open-source, free tool.
3. Atom
Atom is among the most popular open source text editors for modern programming. Built by GitHub, Atom comes with Git control and hence fits seamlessly in the GitHub ecosystem. It is a desktop-based application that is used for building apps using web technologies.
4. Rekit studio
Rekit studio is focused specifically for developing apps using React. It works both as an IDE and as a toolkit that can be used for developing scalable web apps using React Router, React, and Redux. Since Rekit has its own Rekit studio, things remain simple and controlled. It is a favorable solution for small scale developments.
5. VIM
Although it is one of the oldest IDEs, VIM has remained the favorite for some developers. Its popularity can be gauged from the fact that Facebook developers used it in the early days. It comes with many features for fast code writing using a keyboard. Using various available plugins for JavaScript and React, VIM can be transformed into a powerful IDE.
These are some of the features that we hope you will find helpful. If you have any questions on React Developer Tools or want to see how this can benefit your business, please let us know.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Ok, so we’re all very well acquainted with our friend, the web browser. It has helped us with so many things in life, answered so many of our questions (well, technically it is Google, but nevertheless), and kept us entertained. It simply became a huge part of our lives. And how?
Through its well-built web applications. Our web browsing experience is influenced a great deal by these two factors, the web application and the web browser. And over the years, we have seen a hell lot of improvements in our browsing. The kind of browsing experience we have now is not something we imagined a few years back. To explain how it has changed, let’s take a quick look at how web apps used to be in the past.
While growing up
Ever since the introduction of the web, browsing worked something like this; when you type in the address for a web page, the browser requests for the page, say for example “Fingent.com”, which causes a server somewhere on the internet to find and create an HTML page and send it back to the browser. Back then, browsers weren’t all that powerful and HTML pages were basically just static and independent documents, so this set up in the back end worked well. Later on, Javascript (the programming language) came to be used, which allowed web pages to be more dynamic. Even then, web pages used nothing more than image slideshows and date picker widgets.
After several years of technological advancements in computing, the web and the web browser have evolved so much that, it has become a platform for fully featured and rich applications. With the introduction of HTML5 standards, put together with fast JavaScript runtimes, developers have been able to create richer apps that used to be possible only with native platforms.
Single page apps
Much later on, developers started building full-fledged applications on the browser using JavaScript and its advanced capabilities. Single page apps (like Gmail for example), were able to react or respond immediately to user actions without having to go to the server to bring up a new page. Such applications used libraries like Backbone.js, Ember.js, and Angular.js, all of which come under the client-side Model View Controller (MVC) architecture model.
In this case, the mass of the application logic (like views, controllers, templates etc.) lies in the client side and communicates with an API for data. The server, which may be in any language like, Ruby or Python, handles the creation and serving of an initial bleak HTML page. Javascript was the basic and traditional language of the web browser, and computations were directly performed on the user’s machine. This was called “client-side processing”.
Such apps were actually very good for the user as all they needed was the initial loading time. Once that was done, then navigation between the pages would become pretty easy and smooth without refreshing the page and it even supported offline browsing if everything was done right. Even for the developer, such apps were perfect, as there was a clear cut division between client and the server and there was not much sharing of logic required between the two (which are often in different programming languages), which facilitated the smooth workflow.
However, there were a few flaws in this perfect approach for web applications:
Trouble for the spiders
An application that works only on the client side is not capable of serving the web spiders or web crawlers. Web spiders are automated programs or scripts that run to search the web in an automated and systematic manner. The process is called web spidering. A lot of search engines and even sites use this process as a way to provide up-to-date data. What they basically do is request the server for a page and interpret the results. If however the result is a blank page or an undefined page, then it is of no use. Now, as such apps cannot support web spidering, their SEO (Search Engine Optimization) will be poor or not up to the mark by default.
Slow applications
If the application is requested for by the user, and if the server is unable to provide the full HTML page and hence waits for the JavaScript on the client-side to do so, then it causes a delay in loading the page by a few seconds, which could actually cause huge losses. There are several statistics that prove how drastically sales get affected as a result of a slow web application. Need I say more.
Apart from these, there were several other minor limitations like for example, as there was a clear distinction between the client and server sides, there were chances for duplication of application logic and data, such as formatting of date and the like. Such things were more problematic in case of huge and complex applications.
THE SOLUTION
With all the above-mentioned limitations, there was a need to find a solution that surpassed these issues and yet maintained the efficiency and smoothness of client-side application logic. Thus emerged Isomorphic web applications developed using React.js.
A word about React.js first – It is basically an open source JavaScript library used for creating user interfaces for web applications. It intends to overcome the issues in developing single page applications and is maintained by Facebook, Instagram and similar communities of individual developers.
An Isomorphic application is one that can run on both the client side as well as the server side. The code for an isomorphic application can be used or shared by the front end and the back end. A major difference in such applications that make them much better than other applications is the way they process requests. An initial request made by the web browser is processed by the server and all other subsequent requests are processed by the client side.
Now there are a number of benefits associated with Isomorphic applications due to which they are rising in popularity and becoming a huge hit among developers as well as users. Let’s take a look at some of these benefits:
- Speedy– Isomorphic apps are faster to provide HTML content, as the request is not always handled by the server-side. Only the initial ones reach the server whereas subsequent requests are handled by the client-side. This makes browsing faster and more efficient. Moreover, as opposed to common Single Page Applications, where the first request is used majorly for loading the application and then further steps to gather the required data, Isomorphic apps have fast first page processing and even faster further processing.
- Versatile – New devices, as well as old devices, can browse Isomorphic apps, as they return HTML which is compatible with every device, irrespective of features. Single Page Applications returned tags that contained JavaScript which proved to be a problem with older devices.
- SEO Friendly – Isomorphic apps are supportive of web crawling and hence contribute to better SEO. And from 2014, Google can crawl JavaScript applications as well.
- Less Code – As the code is shared between the client side and the server side, there is much less code required as against Single Page applications. This makes it a lot easier to develop as well.
Another major factor is the fact that Isomorphic apps can be easily maintained. As there is no need for duplication of application logic between the front end and the back end, it makes handling of even complex applications much easier.
A lot of these benefits make Isomorphic apps very popular among developers, as they all point in one direction – that is, making development easier. They also give the expected results, and that put together with less coding, makes it a favorite among developers.
As for the users, speed and efficiency are the essential drivers. If you have an application that loads fast and gives excellent features, what more do you need?
The future
Node.js seems to be becoming mainstream with most organizations around the globe. This means that it is slowly becoming inevitable that web apps share code between the front end and the back end. Isomorphic JavaScript is essentially an array that may start with simple sharing of templates and then go on to even handle an entire application’s logic. Applications that live on the traditional back end can also use Isomorphic JavaScript by creating sensible APIs and making it exist along with Node.js. Thus, “Isomorphism” is slowly but surely taking over browsing and soon, there will be a time when not a single advanced web app exists, that does not make use of some JavaScript running on the server.
Tiny flaws
Just like any application, there happens to be a little flaw with Isomorphic apps as well. It’s just that debugging is a bit of a problem for such apps. There is probably a need to use separate debuggers for the server side and client side of the application. Like for example, for the server side, a node.js debugger would be sufficient while for the client side, maybe the web browser’s debugger would do. It depends on the kind of application as well.
Another possible difficulty could be in managing the settings on both sides. For example, the setting for the server side such as API keys and for the client side like the hostname of resources used such as CouchDB, could vary according to the production environments and it could be quite a task managing them.
Conclusion
Just like any other application, Isomorphic applications have their own share of advantages and disadvantages. In spite of the minor flaws, these apps are definitely increasing in popularity with each passing year because of its ease in development and speed. It is an exciting technology that comes with the option of various isomorphic libraries available, that can be chosen according to the scenario. What do you think about Isomorphic applications? Share with us in the comments below.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new