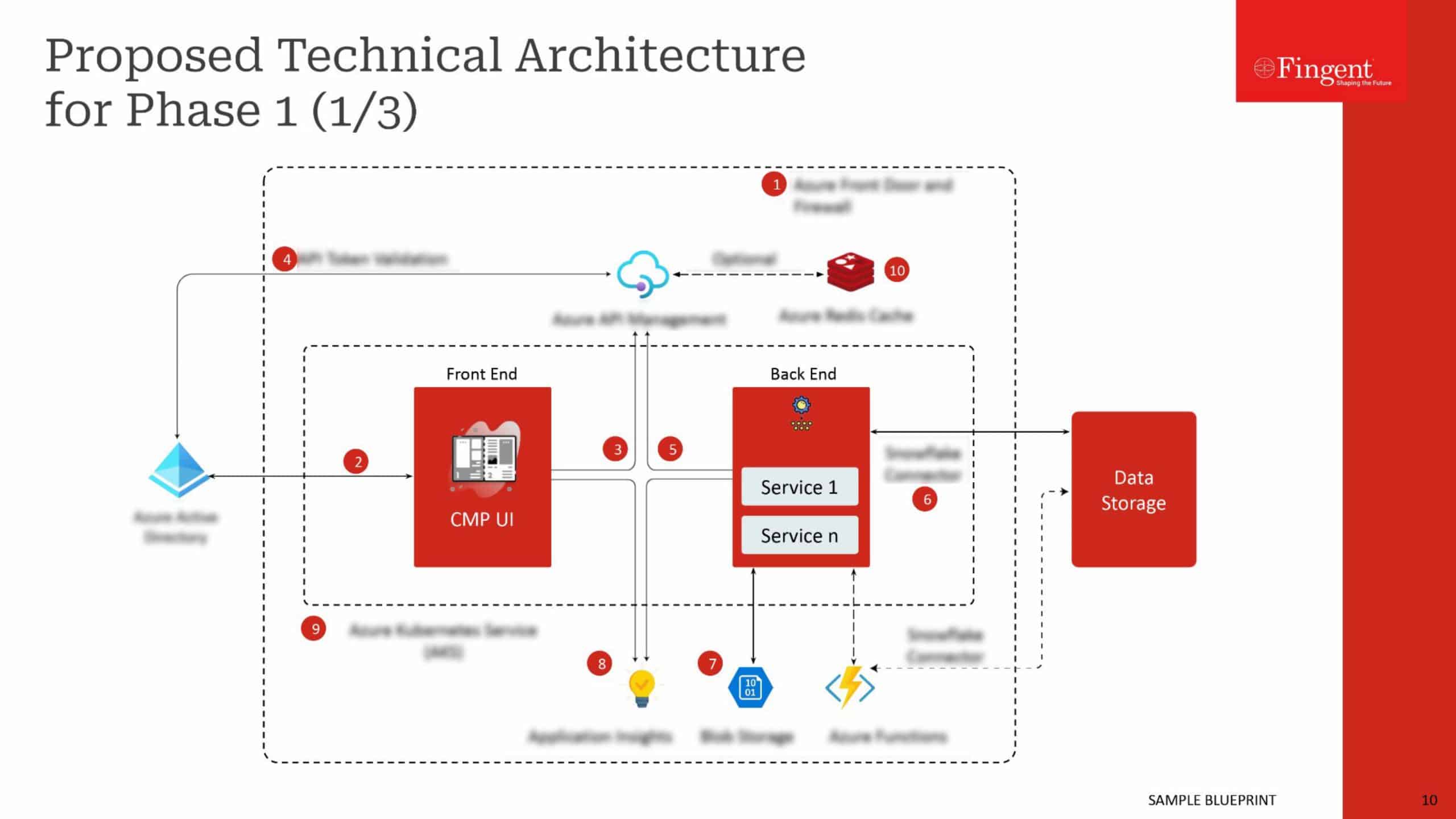
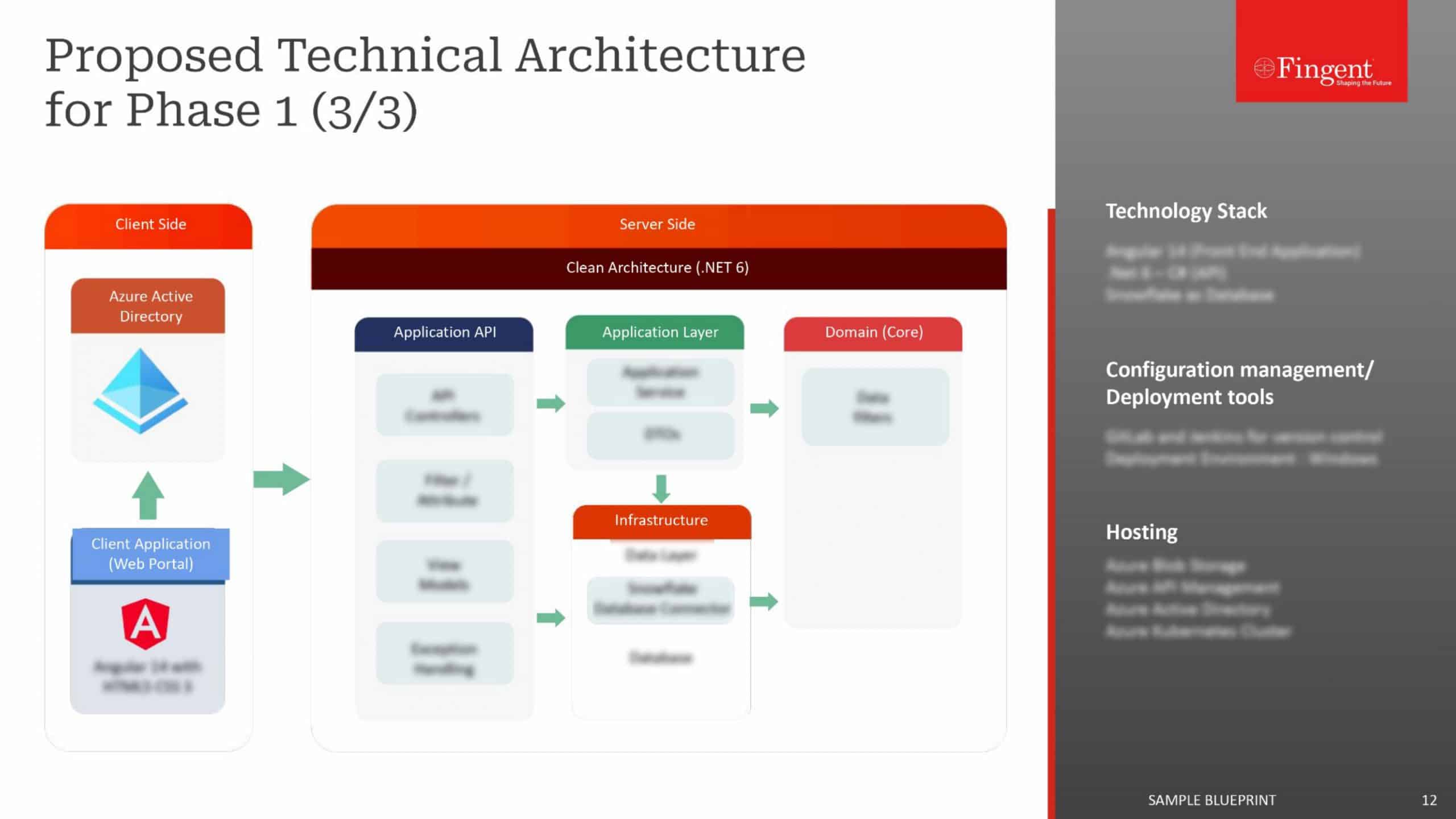
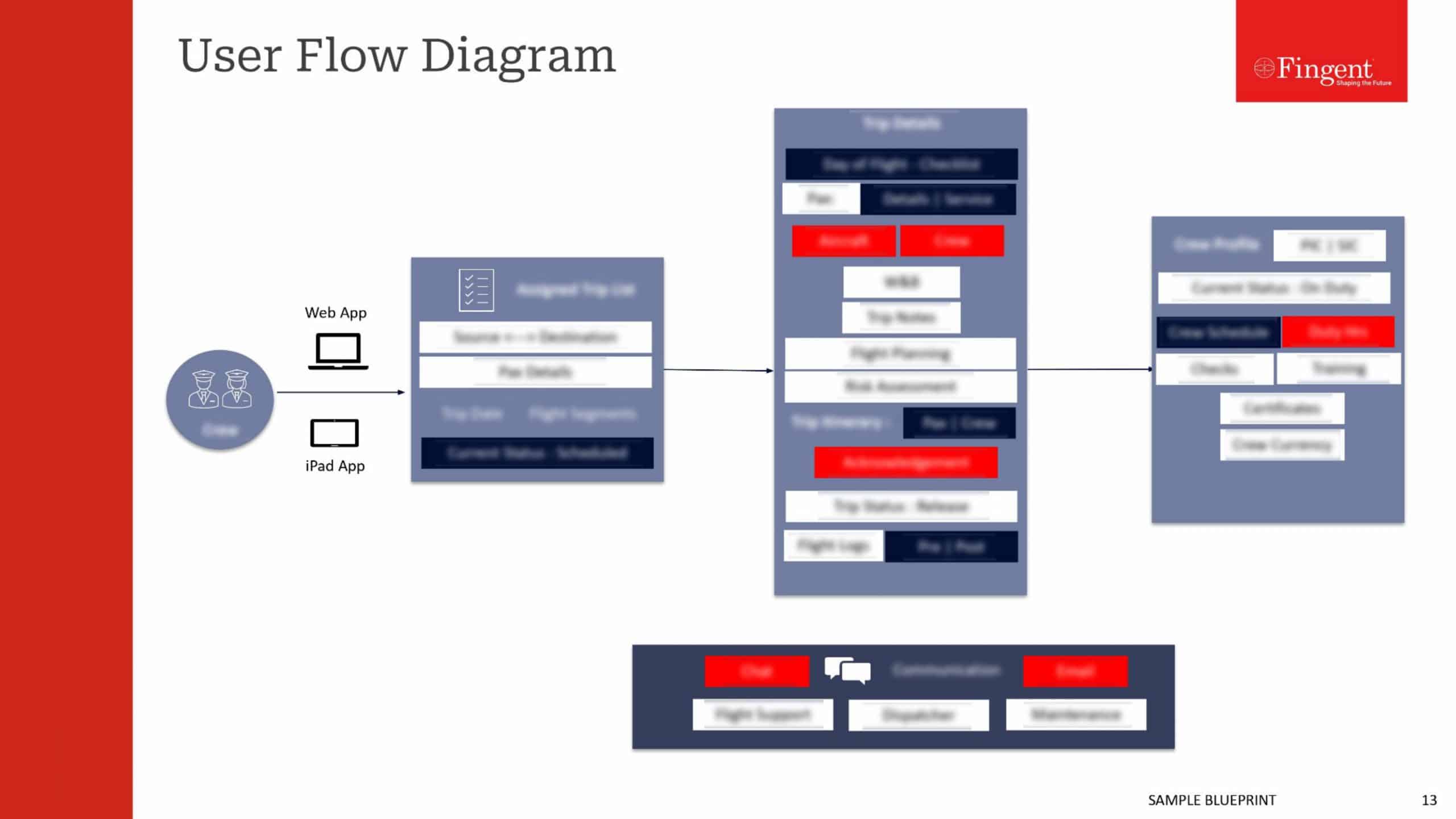
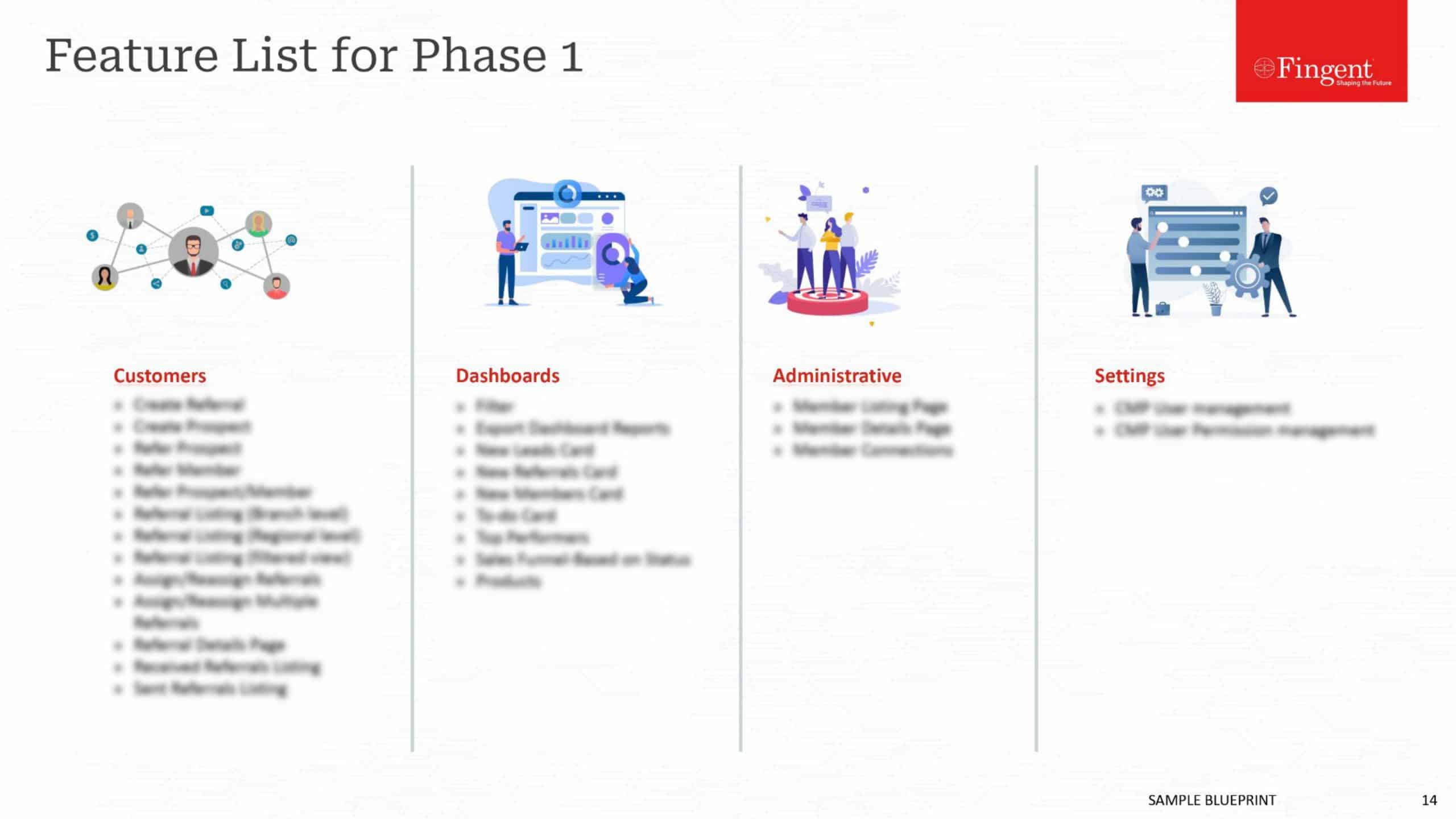
Tag: Mobile
Mobile applications have become mandatory for every business in the current times irrespective of the nature and size of the business. These apps allow businesses to create a direct marketing channel and to provide them with an opportunity to enhance the customer base. There are various business organizations in every sector and the utility of their respective mobile apps provide a competitive edge over the rest of the industry. Customer engagement along with the brand value also improves with the presence of a usable mobile app. Because of these reasons, it is of utmost importance that the mobile app is designed in such a manner to fulfill certain parameters to emerge out as a winner in the market.
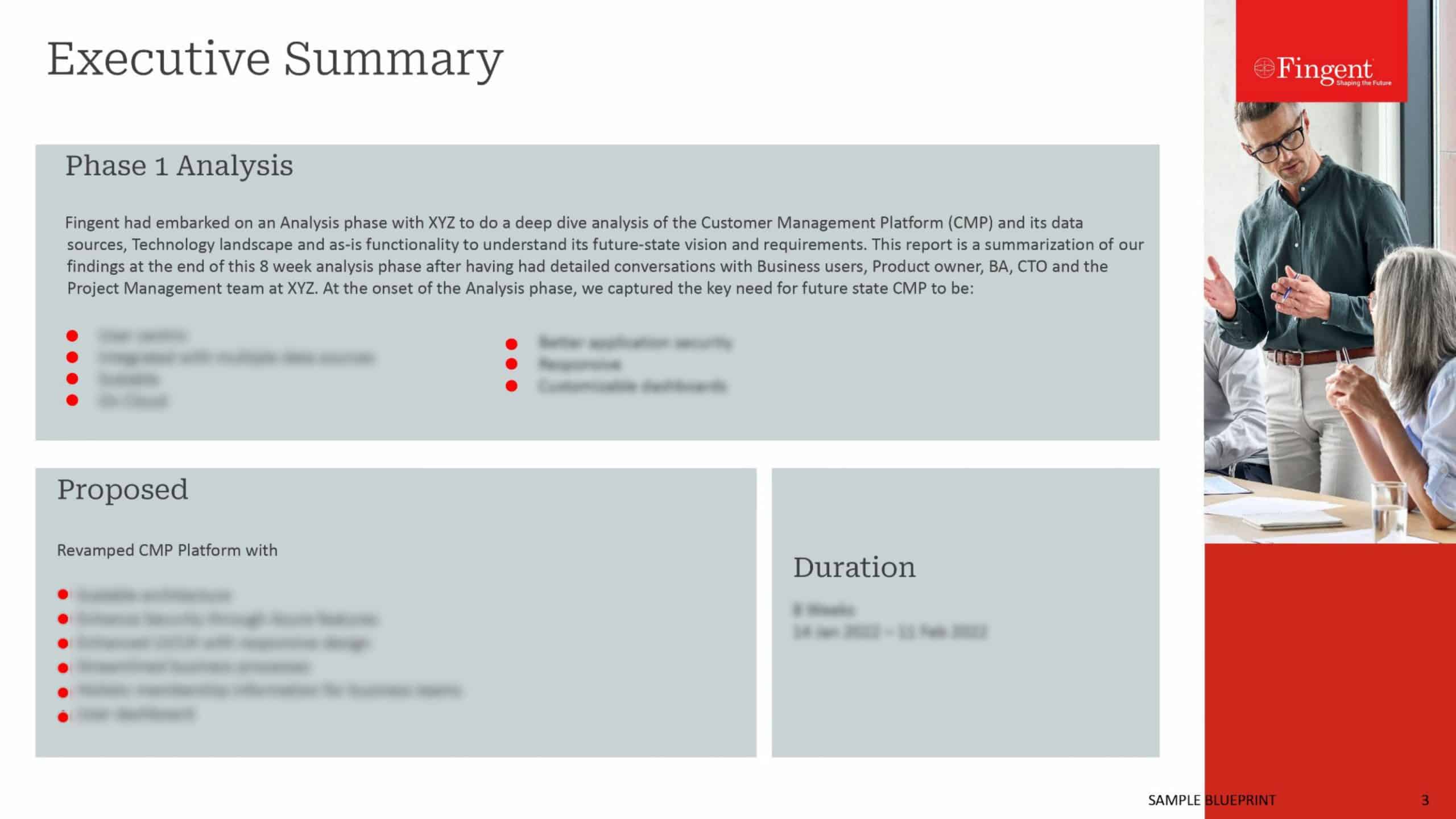
The Lifecycle of a Successful Mobile App
A successful mobile application is an amalgamation of latest technology, tactful planning, and management along with the excellent user experience. There are different phases in the creation of a successful mobile application
Planning & Analysis: It is necessary to ensure that extensive planning and analysis are involved in the design, development, and deployment of the mobile app for a business. Business requirements along with the target audience shall be identified at this stage to make sure that the outcome is as per the client’s specifications. Problem statement shall be carefully analyzed and a solution according to the same shall also be planned. Features of the app shall be classified in three broad categories as functional requirements, non-functional requirements, and user-interface requirements.
Feasibility study of the application in terms of technical, operational and economic feasibility shall be carried out as the first step.
Identification of Mobile Platforms & Revenue Model: There are various mobile platforms and devices that are available and are being used by customers. The mobile app that has to be developed for a business shall identify the target mobile devices and platforms in terms of device support, performance and other quality parameters.
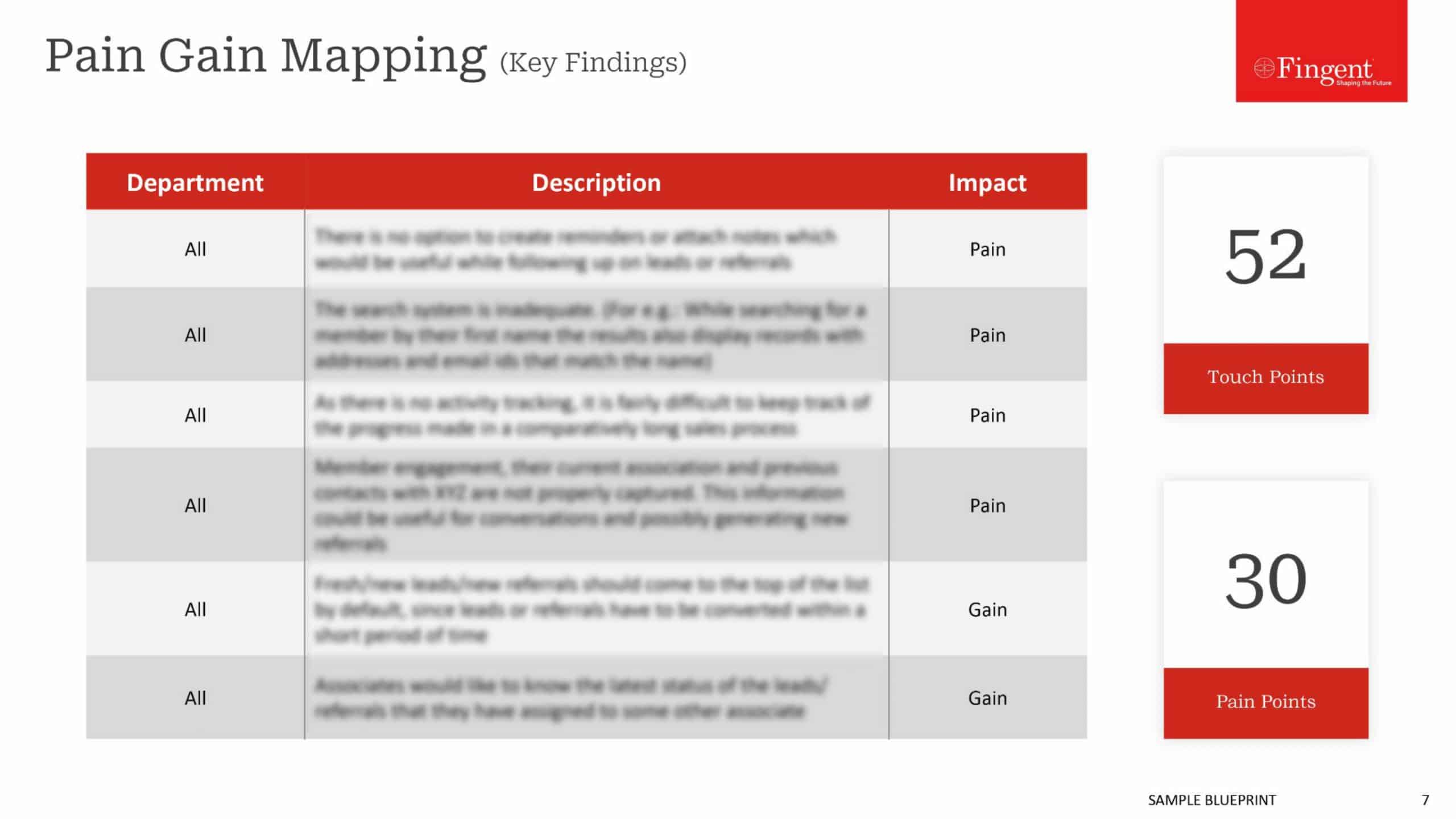
The primary purpose of the development of a mobile app for any business is to enhance the customer base and earn maximum revenue out of the application. The revenue model shall be pre-identified such as paid application, in-app advertisements, pay per download and likewise.
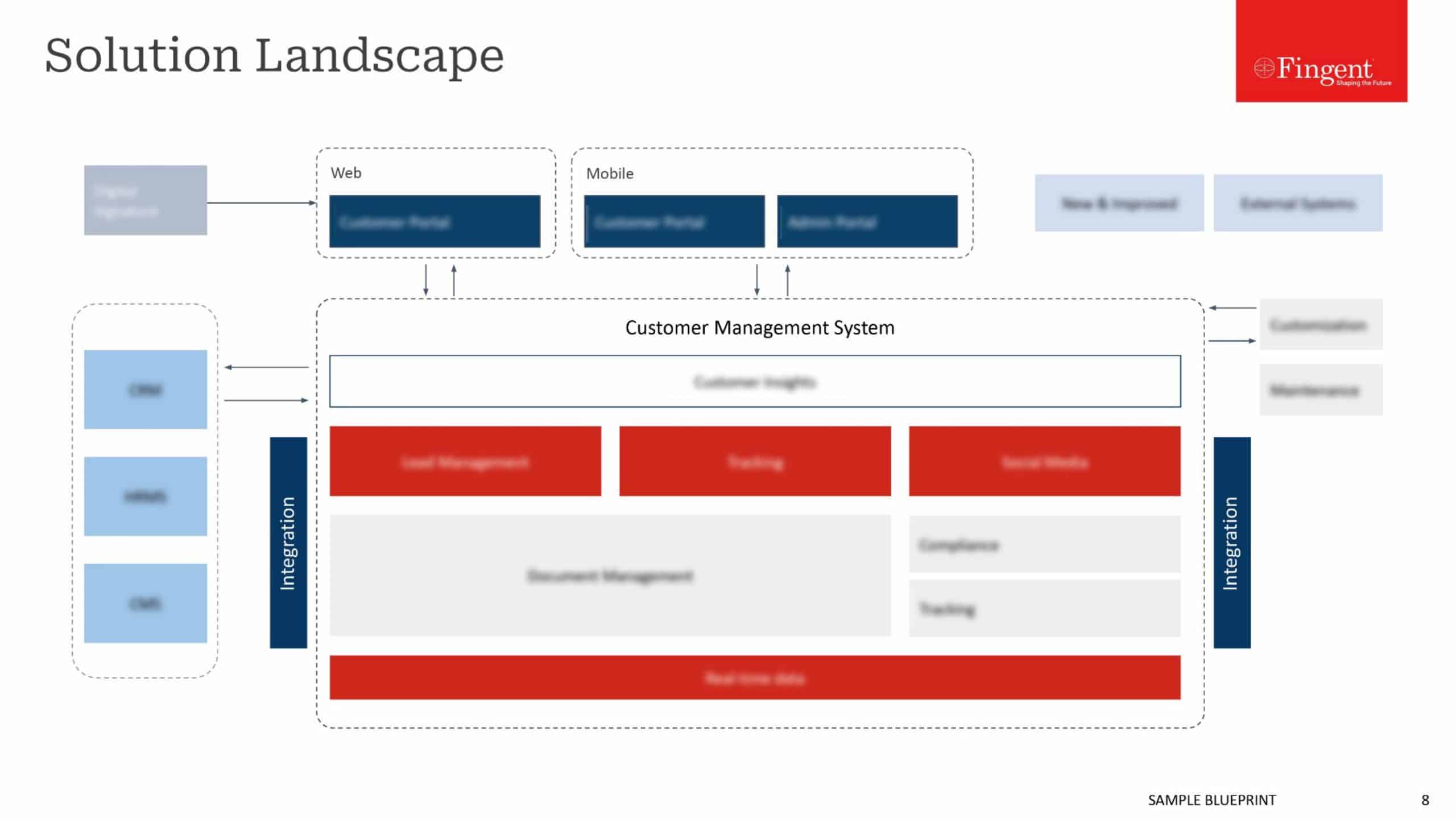
Type of Application: There are primarily three categories of mobile applications as native apps, web apps, and hybrid apps. Native apps are platform-dependent apps that require significant effort, cost and time to be developed. These apps score high in terms of user experience but also come with higher costs. Web apps are the applications that are cheaper and can run on multiple platforms. However, these are less powerful in comparison with the native apps. Hybrid apps are the amalgamation of native and web apps that combine the web code with the native language. The type of the app shall be decided as per the business specifications and the target users.
Mobile User-Interface (UI) Design Parameters: The design of the mobile app plays a key role in its success or failure. It is necessary to have a responsive and visually appealing design to provide the best user experience. Consistency is one of the primary design principles that shall be reflected in the mobile application. The layout, styling, and navigation shall not vary from one screen to another. Users shall feel connected with the application and therefore, it is necessary to have a match between the mobile app and the real-world scenarios. Also, the users shall be provided with considerable control and freedom in terms of the application usage. Visibility is also one of the prime principles that must be included in terms of system feedback to the users. Use of error messages will boost the application design and will also lead to the avoidance of the problems. Application designers must avoid the use of excessive scrolling or overload of content on any of the application screens. Users shall be able to easily recognize the application flow and they shall also be provided with the flexibility and ease of usage. Help and support documentation must be included in the application to gain customer trust.
Offline Access: Users do not wish to spend a lot of data on any application and like to access certain features of the application in the absence of network connectivity. The application that is developed for a business must grant users access to app features in offline mode too. It will enhance the application availability leading to higher customer satisfaction.
Marketing Strategy: Development of an accurate marketing strategy for any mobile app is very important for the success of the application. It is required for the business to make the customer familiar with the features of the app so as to enhance the number of app users. There are various marketing mediums that are available such as tele-media, social media, and print media and so on. Identification of the marketing channels along with marketing strategy shall be developed for the required marketing of the app.
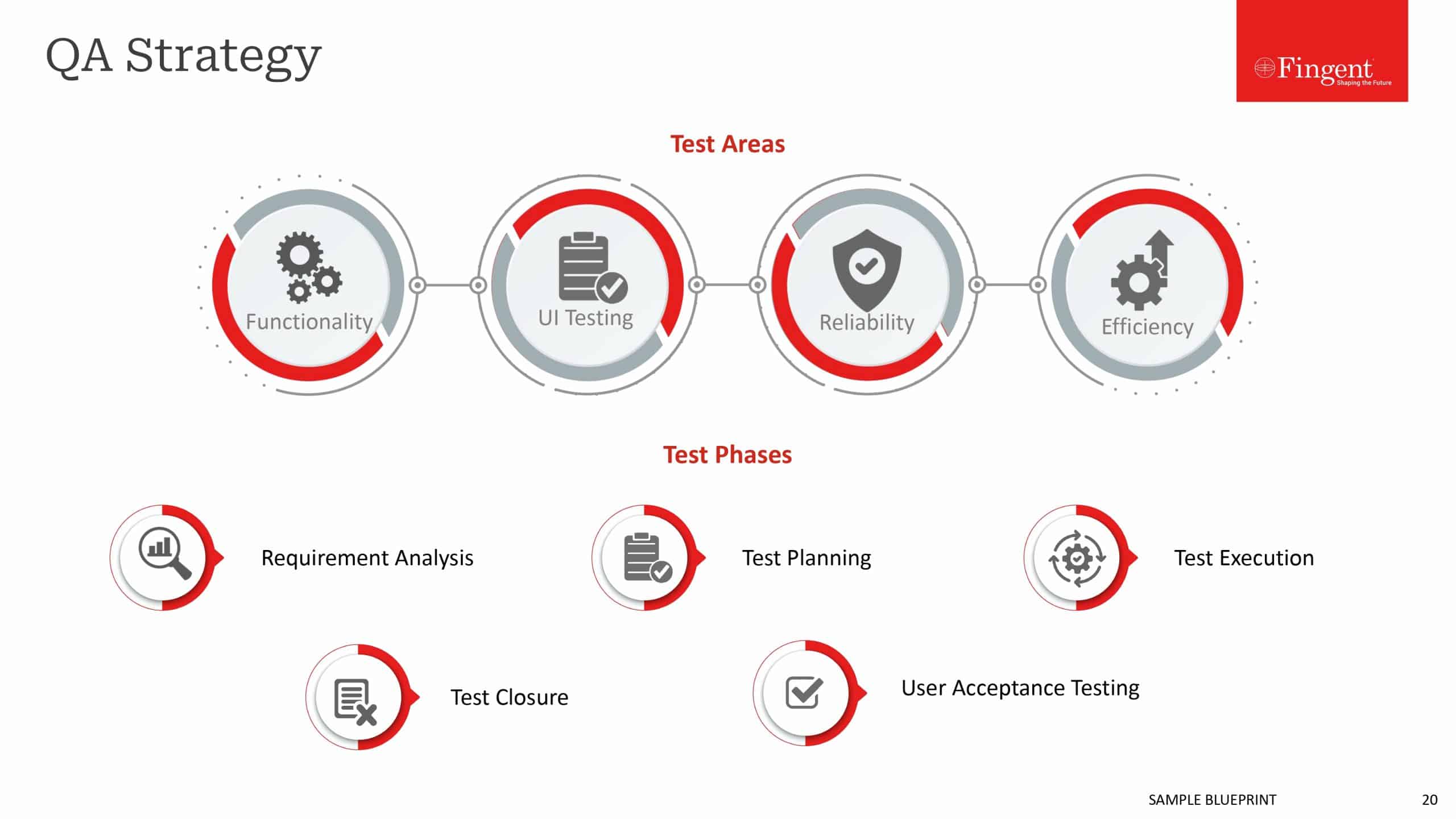
Mobile Application Testing: Testing of the mobile application shall be carried out before its deployment. The application developers shall not restrict to system and integration testing in case of the mobile app. Other forms of testing such as load and performance testing, security testing and UI testing shall also be carried out to avoid any defects in the functional specifications along with the system qualities and UI parameters. Customers shall also be included in the testing processes to gain their valuable feedback. The final release shall not include any of the bugs identified in the testing procedures.
Data Analytics Tools: There are various automated tools that have been developed for data analysis. Such tools shall be integrated with the mobile app developed for business so as to analyze the customer data and identify the customer preferences, choices, patterns, and trends. These results will allow the business to improve their strategies and practices. Also, the app shall be developed as per the customer requirements and preferences.
Mobile applications have become an integral part of the modern-day businesses. It is, therefore, a prime concern for businesses to develop mobile apps to be omnichannel and to offer amazing user experience with all necessary features and functionalities. Responsive web design shall be used during the development of the mobile apps to achieve higher customer satisfaction. A phased approach shall be used by the mobile application development team which shall include planning & analysis, designing, development, testing and deployment as the primary phases.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
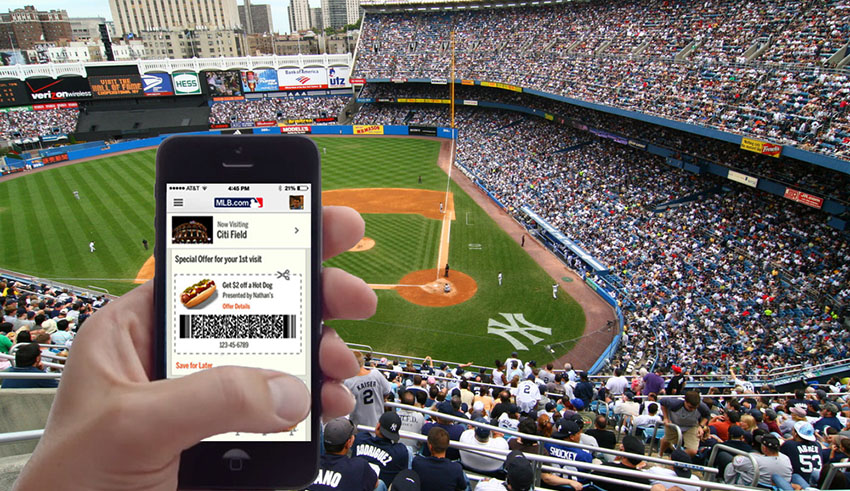
Ever since the introduction of iBeacons in mid-2013, it has increasingly gained popularity and has literally changed the way consumers search for stores and purchase products from stores, in the retail industry. That is just one industry iBeacons have influenced greatly. There are a number of other industries which make use of this technology nowadays. Before we get into the different industry uses of iBeacons, it would be worthwhile to discuss what exactly iBeacon technology is.
What is iBeacon
iBeacon is a kind of wireless technology that uses the Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) protocol to provide location-based information and services to devices. It was introduced by Apple and is now being used by Android as well. iBeacon makes use of a small Bluetooth transmitter known as a ‘beacon’. It basically generates content or even actions through interaction with a beacon in close proximity of an app installed on your device. This works with mobile apps running on both iOS and Android devices.
For example, in a grocery store, beacons could be placed in specific places around the store and if a consumer, having an iOS or Android device walks in, the device would detect close proximity to the beacons. Retailers could use this technology to send out special offers and promotions to the consumers’ devices and even make contactless payments. It Would require the use of consumer’s shopping history to understand preferences and interests in order to make it more effective. This is how iBeacons can be used to enhance consumer experience.
That said, here are some other industries where iBeacon technology is being used widely:
Sports
Manufacturers have tie-ups with sports associations to provide fans in sports stadiums with personalized and interactive experiences with iBeacons. For example, the Major League Basketball Association is working with Apple to serve this purpose with its Ballpark App. It welcomes fans as they enter the stadium with interactive maps that show them to their seats, gives player updates and videos about the stadium, the game etc. That way, fans feel as though they are a part of the game.
Airlines
Airports have started to enhance their services to consumers by improving on consumer experience while they are at airports. For example, Virgin Atlantic, one of the leading airline companies in the world, started an iBeacon trial at the London Heathrow Airport. The premium passengers of Virgin would receive personalized offers and alerts through their phones. Initially, they used beacons to alert consumers about keeping their electronic boarding passes ready before travel and also to send out offers regarding currency exchange. They were also able to inform consumers about entertainment facilities inside the flight before travel.
Events
One of the most popular music and film festivals in the world ‘The South by South West’ (SXSW) started using iBeacons since 2014. Through their official mobile app, and with the help of beacons, of course, they were able to provide enriched customer experiences. All the attendees received their registration quick codes on their phones, as soon as they were in the vicinity of the event’s registration counters. They also made use of a number of beacons placed at a number of event venues, whereby they could welcome the attendees to different sessions and also invite them to join sessions along with information about various sessions.
Electronics
In the case of home electronics, there are Apps that make your living a whole lot simpler. As a matter of fact, you don’t even have to pull off your couch if using the new Launch Here app. With the help of beacons, it changes your phone into a smart personal assistant that lets you launch other apps of your choice. For example, a beacon placed in the living room sofa or anywhere else in the living room, could send you signals to launch the remote app on your phone so that you can use it as a remote or maybe even launch the TV app on your phone. You could also use beacons in other appliances like the refrigerator, to help you create a shopping list or so.
These were just some industries that use this increasingly popular technology to provide improved customer experiences. There are many other industries as well that are yet to use this, although they are well on their way. The education industry is one such example, where they are slowly coming up with new innovations that improve the interaction between teachers and students. Beacons can help a great deal in this regard.
Soon ibeacons will lead to disruptions in most industries and it will be a matter of time before they become mainstream entities in every industry. Have you seen these little beacons or better, have they made life easier for you somehow? Let us know in the comments below!
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
How often have you come across a situation where you needed a mobile application and had to choose between a native or hybrid application?
We as developers, have come across a number of business heads and managers, who have had a tough time deciding on the approach they had to take for the mobile application they required. More often than not, business officials are seldom aware of the technical specifications of native as well as hybrid apps. Hence, they are often confused and unable to decide between the two.
For example, one of our clients from the mining industry specialized in providing cut and fill earthworks for residential, commercial and industrial development projects, faced a similar problem. They needed a software that enabled them to move from their paper-based project management system to an online one. They also required a mobile application that enabled their field agents to gather information from their sites and also access project information contained in the main application as well. The client was confused as to what approach to use for their mobile application. After detailed analysis of their requirements, we churned out the best possible approach for their business. Similar issues persist among most entrepreneurs today.
Hence, in this article, we take you through the significant aspects of native and hybrid applications that have helped us advice our clients in deciding between the same.
Native apps
A native application is basically one that has been developed for use on a particular platform or device. And for the same reason, they are able to make use of the specific features of the operating system as well as other software installed on the device. This also implies that native apps can make use of specific hardware features as well, that are part of the device and the latest technology available with the device like the Camera, the GPS, the contacts, the accelerometer etc. Some of the general features of native apps are as follows:
They are coded in a specific programming language such as Objective-C for iOS, Java for Android and C# for Windows operating systems.
They are easily available on an app store or a market place specific to the device and they can be installed from there.
Each native app requires its own development process depending on the platform it is being developed for.
Hybrid apps
A hybrid application is one that has combined features or elements of native and web apps. Unlike native apps, they are not built for use on a particular platform, but they are made available over multiple platforms just like a web app. The major difference between a hybrid app and a web app is that hybrid apps are hosted within a native application that makes use of the mobile device’s Web View. It is more like a browser that runs full screen. Hence, they are able to utilize most of the device capabilities just like native apps. Some of the general features of hybrid apps are as follows:
- They are coded using a combination of technologies like HTML5, CSS and Javascript.
- They are easily available on the app store to be installed.
- It uses hybrid technologies like PhoneGap (or Apache Cordova), which provides APIs to gain access to native platform features like the camera and contacts.
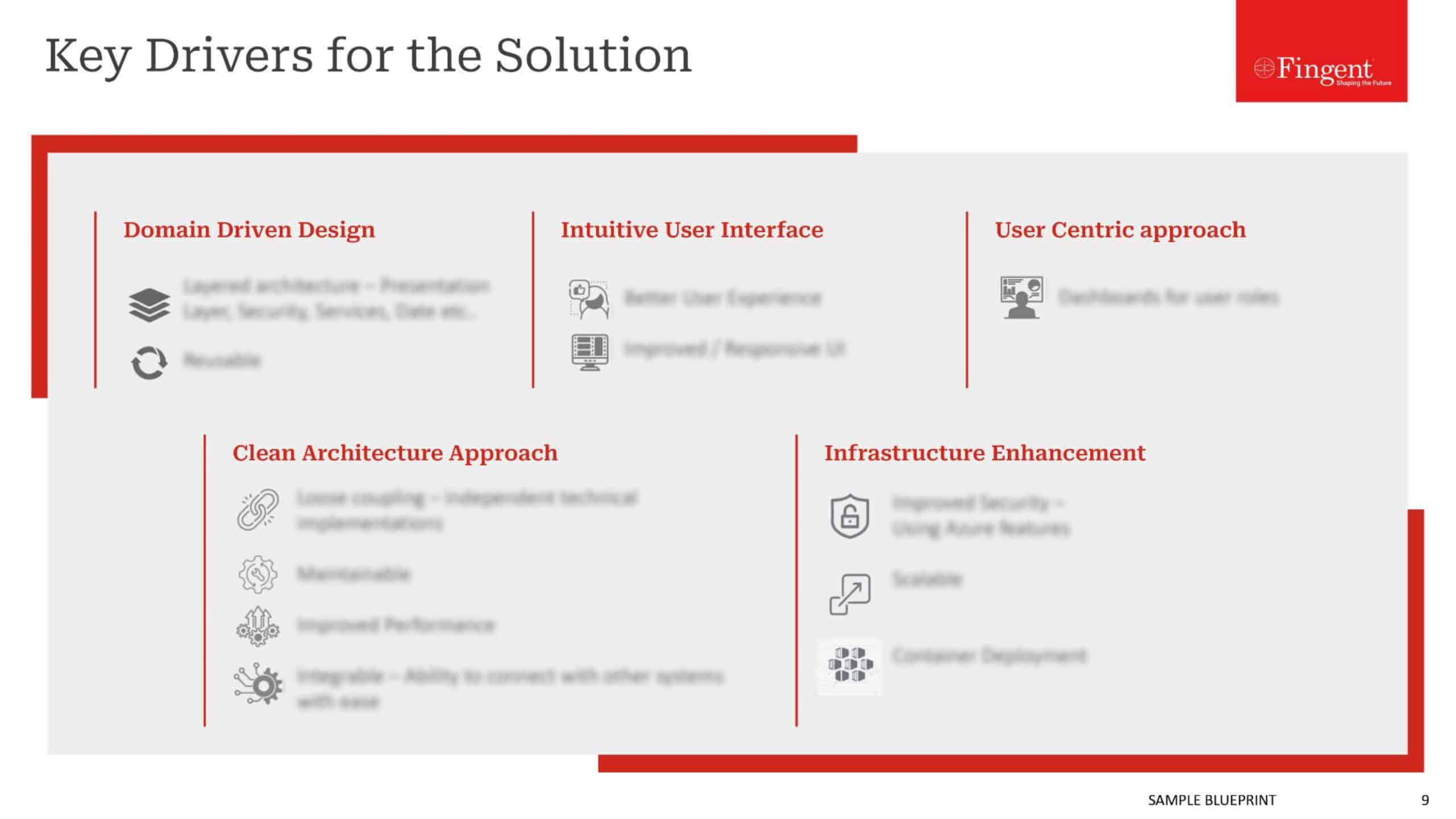
COMPARISON OF NATIVE AND HYBRID APPS
Now that we have a basic understanding of both kinds of apps, here we have a comparative study of the features and elements of the two.
User Interface
In terms of user interface, there is not much of a difference. There may be minor differences in the looks and the like, to enable a consistent user experience depending on the platform. Apart from that, both native and hybrid apps are designed to look and work the same way in terms of user interface and experience.
Development
Native apps, as mentioned before are developed using specific programming languages for specific platforms, such as Objective C for iOS, Java for Android and Visual C++ for Windows operating systems. They make use of standardized Software Development Kits (SDKs), user interface elements like buttons and text boxes, and other development tools provided by the manufacturer of the respective platforms in the process of development. They are developed using code specifically written for the app. It basically means that native applications are harder to develop and take more time.
Hybrid apps on the other hand, are developed using HTML or CSS or Javascript or a combination of these. As mentioned before, they are made to work inside a native app container so that they can have access to the hardware capabilities of the device. More importantly, most of the functionalities of hybrid apps are taken care of from the back end or server side, unlike native apps.
One of the most popular platforms that is being used for hybrid applications these days is Apache Cordova, which was earlier known as PhoneGap. It helps to provide a consistent and reliable set of Javascript APIs in the form of plug-ins which are built using native code, so that the app has sufficient access to hardware capabilities on the device. They take lesser time and effort to develop, as they make use of already existing code segments across multiple platforms.
Delivery method
Native apps as well as hybrid apps can be downloaded from an app store and installed on the device. Since hybrid apps make use of plug-ins to enable the hardware functionality as a native app does, even hybrid apps are available on the store, unlike web apps. For the same reason, the users need to manually download and install updates as and when they are ready.
Accessibility
Native apps, as they are developed for a specific platform, have access to all hardware and software functionalities of the device or platform on which it is installed. Hybrid apps on the other hand need plug-ins to have access to device specific features.
While choosing between native and mobile apps, some of the factors that you need to consider are as follows:
- Time – Native mobile applications require a longer duration of time to be developed because we need to start it from scratch. There is a lot of effort involved in building a native app as the entire code needs to be written to program the whole app. Hybrid apps on the other hand require much lesser time as they can use already written HTML code components across various devices. If you are looking to develop a mobile application and you want it done within a short period of time, then, a hybrid app would be a better option. This is one of the reasons that make hybrid apps popular.
- Budget – Native mobile applications are more expensive to build for the same reason why they require more time to develop. The effort that has to be put into making a native app is a lot more when compared to hybrid apps. Hence, the costs involved in developing native apps are more than that for hybrid apps. If you have cost concerns regarding your mobile application, then it is always better to go for hybrid applications. They are usable across multiple platforms and are available at a lesser cost.
- Requirements – If you need an application that uses features like video editing and trimming, or if your application needs access to in-device features like contacts, then you need to go for a native application. Hybrid apps do not have that capability.
- Scalability – This is an extension of the requirements factor. Native applications are more scalable than hybrid applications. If you plan future expansions to your application with more native features or features that require more communication with the Operating System of the device, it is always better to go for a native application. Hybrid apps can be made to have native features to some extent, but if you are planning to integrate many more features and add more functionalities to your app in the future, then you need a native app.
- Speed – Native applications perform faster and are easier to work with as they use the device’s built-in features. Hybrid apps, on the other hand, may not be as fast.
The basic advantages of a hybrid application over a native application are in terms of cost and time. Although, you get more efficiency and accuracy through native applications. These points will definitely help you choose better between native and hybrid apps..
Nevertheless, what matters the most is your requirement. And your final decision is entirely dependent on the kind of requirement you have.
Need more help? Talk to us! We can create powerful custom mobile applications or help you decide what works best inline with your business goals.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new