Understanding The Types of Warehouse Management Systems
The warehouse is the beating heart of the organization. With goods moving in and out consistently, any mishap can create a domino effect that can impact the entire company’s performance. How do you ensure that your warehouse operations are shipshape? An efficient warehouse management system is the answer! However, identifying a suitable solution from the available types of warehouse management systems can be tricky.
A proper warehouse management system can help improve order fulfillment, enable your team to be more responsive in real-time, and strengthen your supply chain. Over 83% of warehousing and logistics providers already use WMS. Which warehouse management system is best for you, though? This article will explore the world of WMS and highlight the significance of each type of system so you can make an informed decision.
What is a Warehouse Management System?
A warehouse management system is software that improves warehouse operations. It automates and streamlines processes enhances productivity, eradicates error risks, and creates a well-planned layout. These system applications play a key role in supply chain management. They offer real-time analysis and tracking and provide data filtering for key performance indicator (KPI) analysis.
A subpart of warehouse management systems is inventory management systems. As the name suggests, these applications handle warehouse inventory. They contribute to optimizing supply chain management. They provide inventory control, thus mitigating risks of inventory overstocking, pilferage, and wastage. All these functions will improve customer service and boost profitability.
Let Us Help You Identify The Right Warehouse Management Solution For Your Business
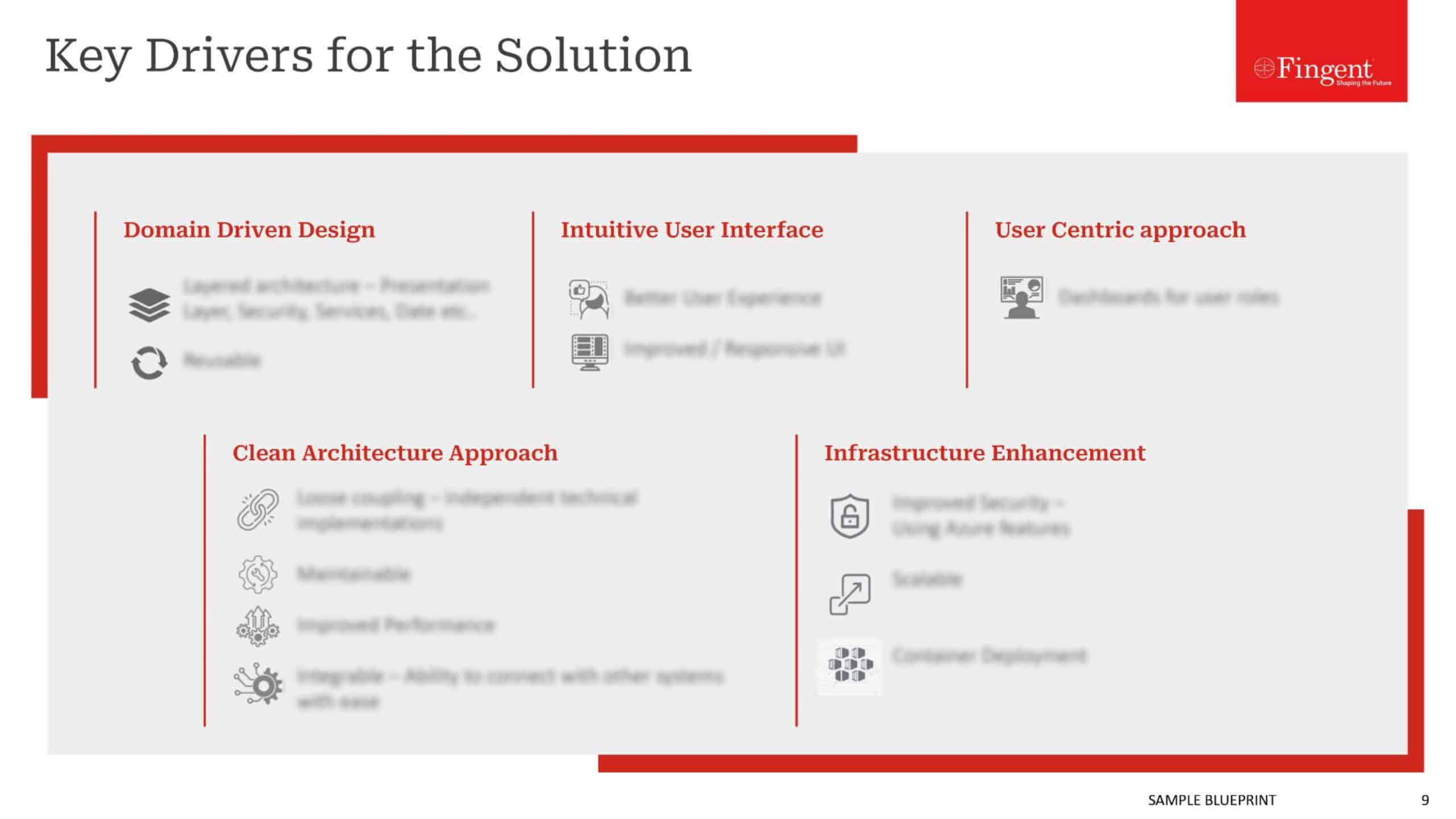
How Many Types of Warehouse Management Systems Are There in the Market?
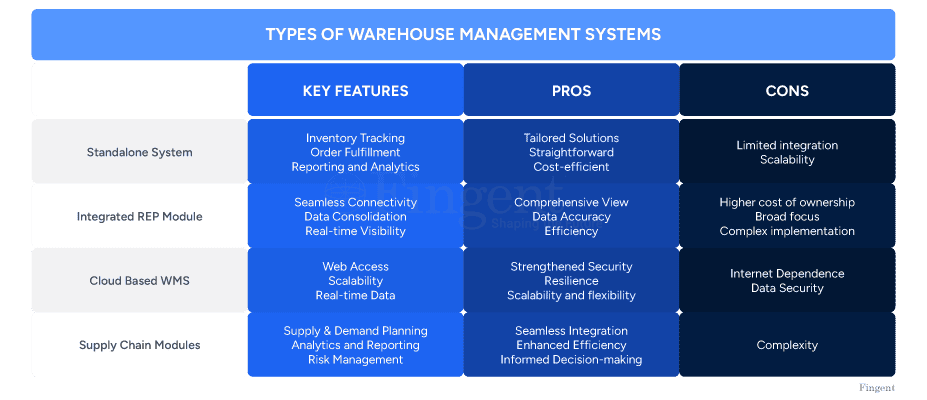
Different businesses require different functions from their warehouse management system. Four types of warehouse management systems cater to these businesses’ unique needs: Standalone, ERP Module, Cloud-Based, and Supply Chain Module. Each of these applications has its benefits. They differ in integration capabilities and suitability for various business sizes. Understanding the key differences between these systems is important before you choose.
What Are the Key Types of Warehouse Management Systems Available?
Let’s take a close look at the four primary types of WMS systems and their key features, benefits, and drawbacks.
1. Standalone System
Standalone WMS is a software solution designed for small and medium-sized businesses. It offers cost-effective management that organizations with a tight budget can benefit from. This system application provides a focused approach without extra integration with other systems.
Key features:
- Inventory tracking: Provides detailed visibility into warehouse stock levels, locations, and undertakings. Additionally, it also offers barcode scanning, RFID tracking, and real-time inventory updates
- Order fulfillment: It optimizes order processing, picking, packing, and shipping. Other features include automated pick lists, packing slip generation, and real-time shipment tracking.
- Reporting and analytics: It automatically generates reports on inventory movement, order accuracy, and warehouse performance. These reports undergo analytics that provide insight into improvement with visualization tools.
Benefits:
- Tailored solutions: These solutions are designed specifically for warehouse operations and provide advanced features customized to your organization’s unique needs.
- Straightforward: Since it is not linked to any other business software, it comes with fewer complications. The steps involved in setup and maintenance are simple and run in a shorter time frame.
- Cost-efficient: This solution focuses on a set approach without extensive integration with other systems, making it affordable for small—to medium-scale businesses.
Drawbacks:
- Limited integration: Since it doesn’t integrate into other business systems, it has restricted functionality.
- Scalability: This system doesn’t offer easy scalability due to its limited integration.
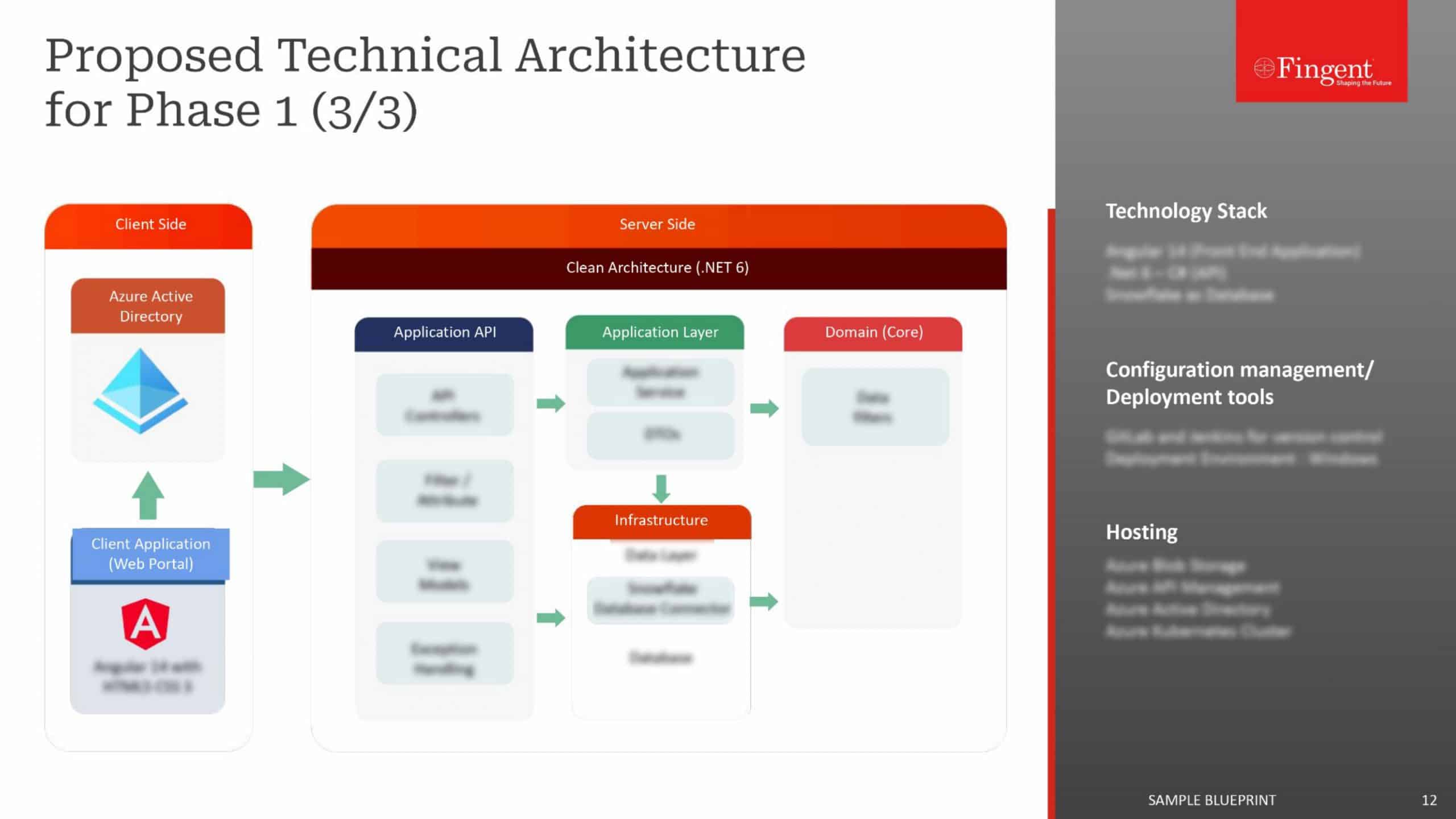
2. Integrated REP Module
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software tracks and organizes business resources. This ERP module is often integrated with HR software systems and CRM solutions. It is suitable for businesses of all sizes and fulfills many client requirements.
Key features:
- Associated with enterprise resource planning system: It provides seamless connectivity between warehouse management and other business functions. It efficiently bridges the accounting, procurement, and customer relationship management gap.
- Data consolidation: The module oversees and synchronizes the centralization of business data. Furthermore, it provides up-to-date insights into inventory activity and warehouse operation, enhancing decision-making, operational efficiency, and productivity.
- Real-time visibility: The ERP module offers comprehensive visibility into business operations, from procurement to order shipment and financial reporting.
Benefits:
- Comprehensive view: Since it centralizes business data, there is a single source of truth. It mitigates the risk of any misconceptions across various departments in an organization.
- Data accuracy: It streamlines integration with various business functions. This way, data inconsistencies are removed.
- Efficiency: Streamlining is its strongest feature. By automating data transfers and process handoffs, it simplifies workflow.
Drawbacks:
- Higher cost of ownership: Implementation will include installing software and integration services. The initial investment and ongoing maintenance cost can strain resources, so it is not very popular among smaller businesses with simpler warehouse operations.
- Broad focus: It may neglect some specific management features due to its broad approach.
- Complex implementation: The implementation process can often be complicated and time-consuming. It also requires a great deal of resources that most businesses lack. Another major drawback is its lack of flexibility since customizations cannot be fit within the broader ERP system.
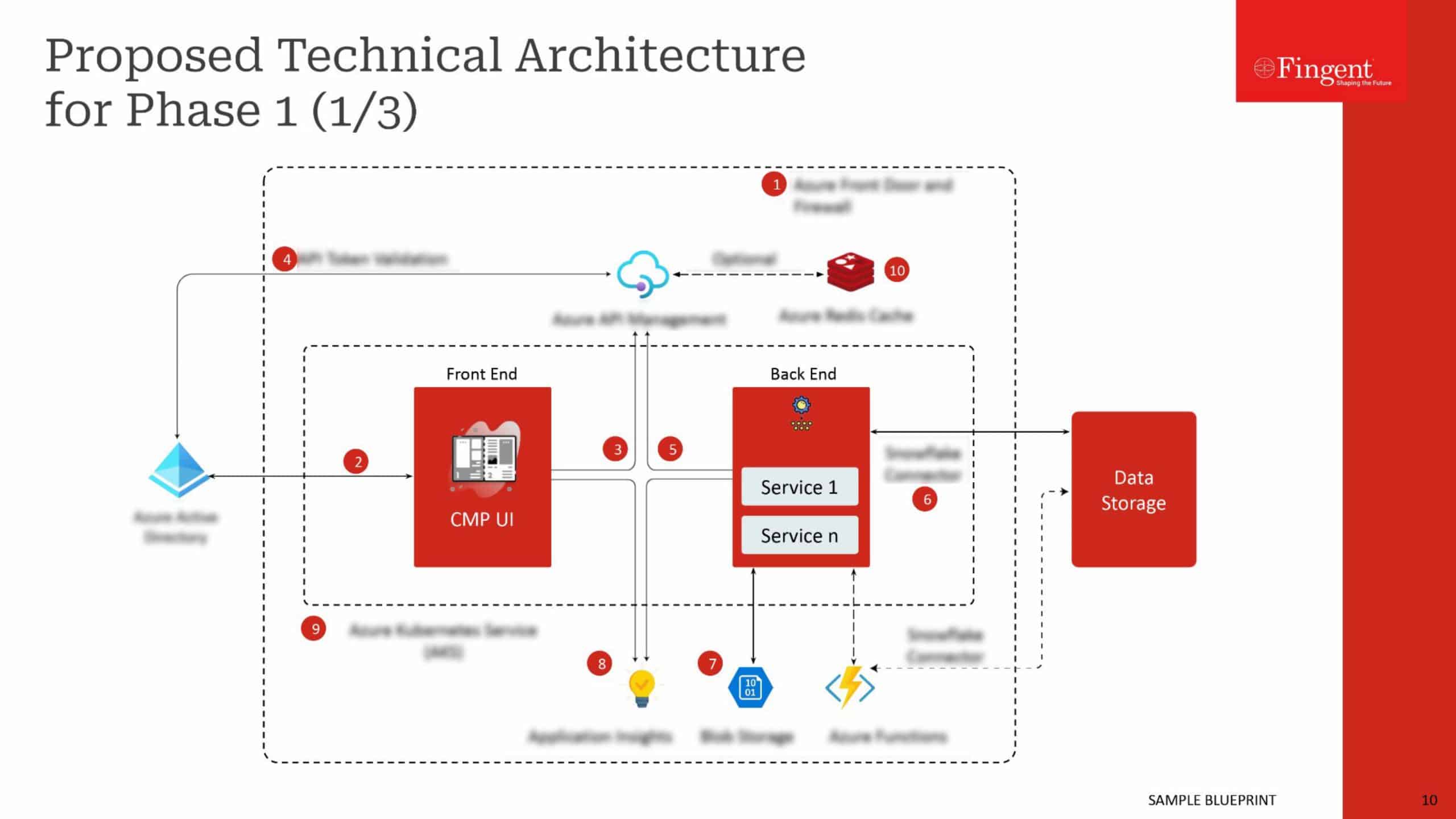
3. Cloud Based WMS
As the name suggests, this solution is web-based. It follows a centralized approach based on cloud technology. This type of WMS is popular for its scalability and deployment speed. It can provide speedy chain execution at cheap inventory expenses. The application does not need extensive installation or assimilation with legacy hardware or networks. It is the perfect pick for any business, big or small!
Key features:
- Web access: Since it is web-based, it can be accessed anywhere.
- Scalability: This solution is capable of scaling itself according to the business. It can also adjust resources based on demand and business needs.
- Real-time data: The cloud-based WMS provides real-time inventory and warehouse operations updates. Due to its web-based nature, it also provides mobile access.
Benefits:
- Strengthened security: Cloud-based WMS deploys many safety measures to keep data safe, including encryption, access controls, and security audits.
- Resilience: This solution is immensely resilient to connectivity issues. It is designed to maintain functionality even when the internet connection staggers. When the internet connection is restored, local caching and data synchronization are conducted automatically.
- Scalability and flexibility: The solution allows businesses to adjust their software usage based on business needs. Thus, users only pay for their services, saving extra costs.
Drawbacks:
- Internet dependence: Despite quickly recovering from internet connection cuts, they can disrupt access and operations.
- Data security: Privacy and security are unspoken risks with web-based systems. Businesses are at risk of security breaches, and confidential data stored on external servers is at the most risk.
Read more: Warehouse Management System:Business Applications & Case Studies
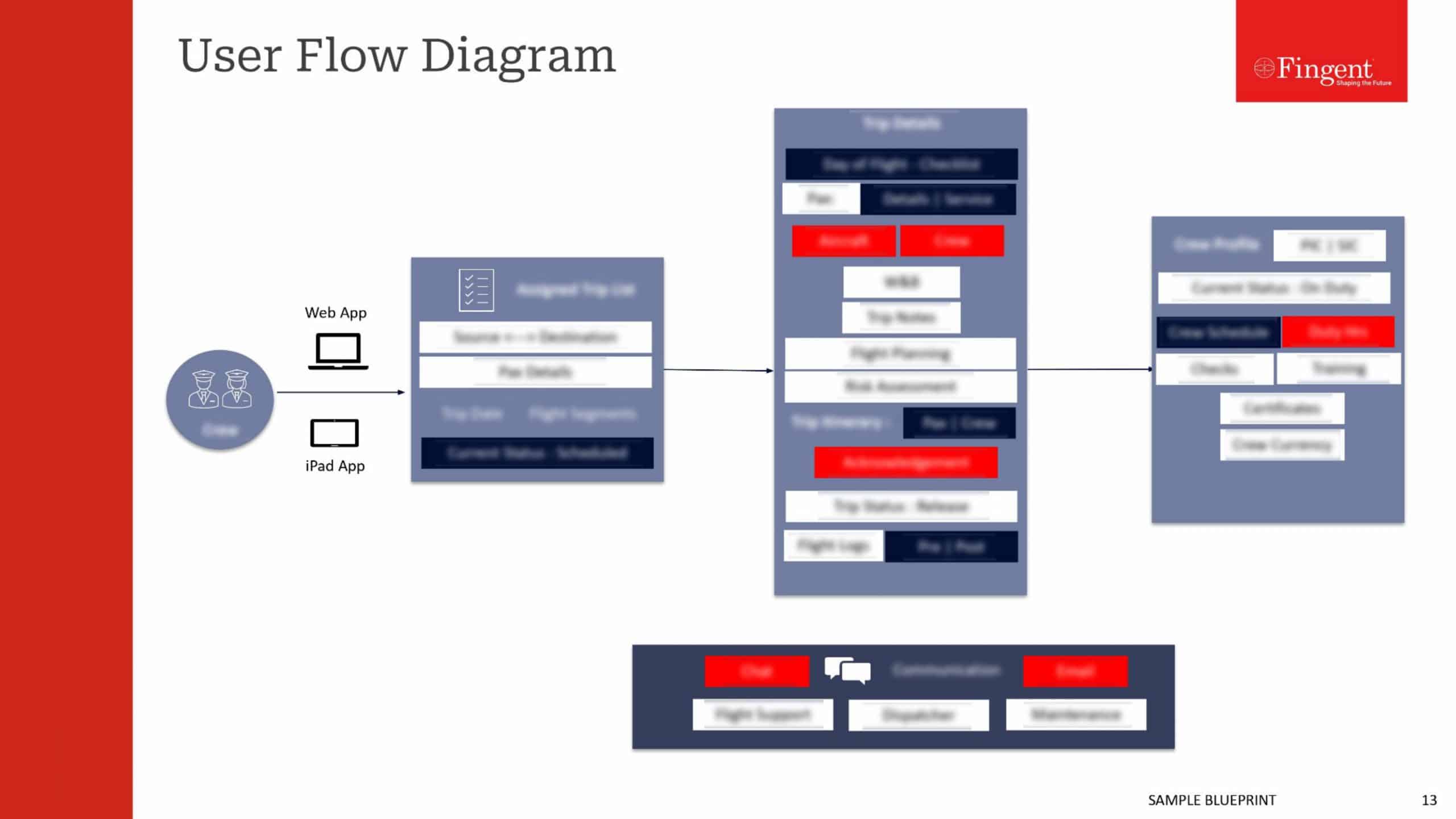
4. Supply Chain Modules
These modules focus solely on supply chain management. They automate the monitoring of inventory restocking, material procurement, and other mundane tasks. This technology helps customers manage various aspects of supply chain visibility.
Key features:
- Supply and demand planning: It can predict future demand based on historical data, trends, and market analysis. Hence, it ensures optimal stock levels in the warehouse. It also manages supplier relationships and purchase orders to coordinate for timely supply.
- Analytics and reporting: These modules can track key performance indicators (KPIs) and provide reports for insights into supply chain performance.
- Risk management: It can identify and perform regular risk analysis tests. It also develops contingency plans and strategies to mitigate the disruption.
Benefits:
- Seamless integration: It can easily assimilate with other supply chain software applications, allowing for smooth data sharing and real-time visibility within warehouse operations.
- Enhanced efficiency: It optimizes warehouse processes and reduces inefficiencies, leading to cost savings and a faster response time frame.
- Informed decision-making: This system analyzes data in real-time and helps make informed decisions and forecast demand.
Drawbacks:
- Complexity: One of the main disadvantages of this WMS is that it requires extreme customization and extensive integration with other systems. This leads to higher costs and can be complex for beginners to understand.
Why Does Your Business Need To Build A Modern Warehouse Management System?
Frequently Asked Questions about Warehouse Management Systems
1. Why is a Warehouse Management System important for businesses?
Implementing a WMS enhances organizational efficiency. It automates and streamlines warehouse processes, improving inventory accuracy, reducing operational costs, and enhancing customer service. It also provides real-time analysis of inventory and warehouse operations.
2. What are the key features of a WMS?
- Inventory Management: It tracks stock levels, locations, and warehouse movements.
- Order Fulfillment: It can handle product picking, packing, and shipping processes.
- Labor Management: It optimizes workforce productivity by automating mundane tasks.
- Reporting and Analytics: It can run analytics and provide insights into warehouse performance.
3. What are the costs associated with implementing a WMS?
The cost of investing in a warehouse management system depends on your business size. Factors such as operational complexity and on-premises or cloud-based solutions play a key role. The expenses often include software licenses, hardware, implementation services, and ongoing support.
4. What are the latest trends in WMS technology?
- AI and Machine Learning: AI enhances decision making and ML provides predictive analytics.
- Automation and Robotics: Automation increases efficiency, and robotics mitigate the risk of errors.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT improves real-time tracking and monitoring of assets.
- Mobile Solutions: It promotes remote access and offers flexibility for warehouse managers.
Read more: Elevate Your Business with IoT in Warehouse Management
5. What challenges might businesses face during WMS implementation?
The most common challenge is staff resistance to change. Other challenges include data migration issues and integration with existing systems. Appropriate planning, training, and change management strategies can help curb these challenges.
Why Choose to Build a Custom Warehouse Management System?
Irrespective of the types of warehouse management systems you choose, buying a custom one is the best decision for a company. It offers several advantages, such as a uniquely tailored solution, scalability, and flexibility. These systems sync your business’s processes, ensuring seamless integration with existing operations. The unique solution will allow for better alignment with specific workflows.
Custom WMS also provides flexibility and scalability. With these systems, you can opt to grow and evolve. This adaptability is valuable for companies with intricate or specialized needs. With a custom WMS, you have ultimate data security and compliance control. This becomes crucial when dealing with sensitive information. A custom solution can be more expensive than off-the-shelf software. Yet, it provides a better return on investment by enhancing operational efficiency.
How Can Fingent Help?
At Fingent, we understand your goal to ensure the right products are delivered on time. We specialize in helping leading logistics and supply chain companies leverage new-age technologies for effective warehouse management and operations. Our custom solutions are crafted to cater to warehouse management’s unique needs and challenges.
Tap into our expertise to develop the best custom WMS for our clients. Our in-depth experience in B2B e-commerce applications, product ordering systems, and self-service payment portals has helped clients worldwide gain a competitive edge.
Stay up to date on what's new

Recommended Posts

18 Oct 2024 Logistics
Why Opt For A Cloud Based Warehouse Management System?
Managing a warehouse need not be so hard! A Cloud based warehouse management system helps warehouses get their act together and focus on what’s most important. Overly packed workers, stockouts,……
Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new