Category: Enterprise Software
Infince to Exhibit at The Small Business Expo, New York and Boston
WHITE PLAINS –April 17, 2018– Infince will be exhibiting during The Small Business Expo ( America’s biggest event for entrepreneurs and business owners ), in New York on Thursday, May 3, 2018, and in Boston on Thursday, May 17, 2018. Infince will be located at Exhibitor Booth 521 in New York’s Javits Center and Booth 420 in Boston’s Hynes Convention Center.
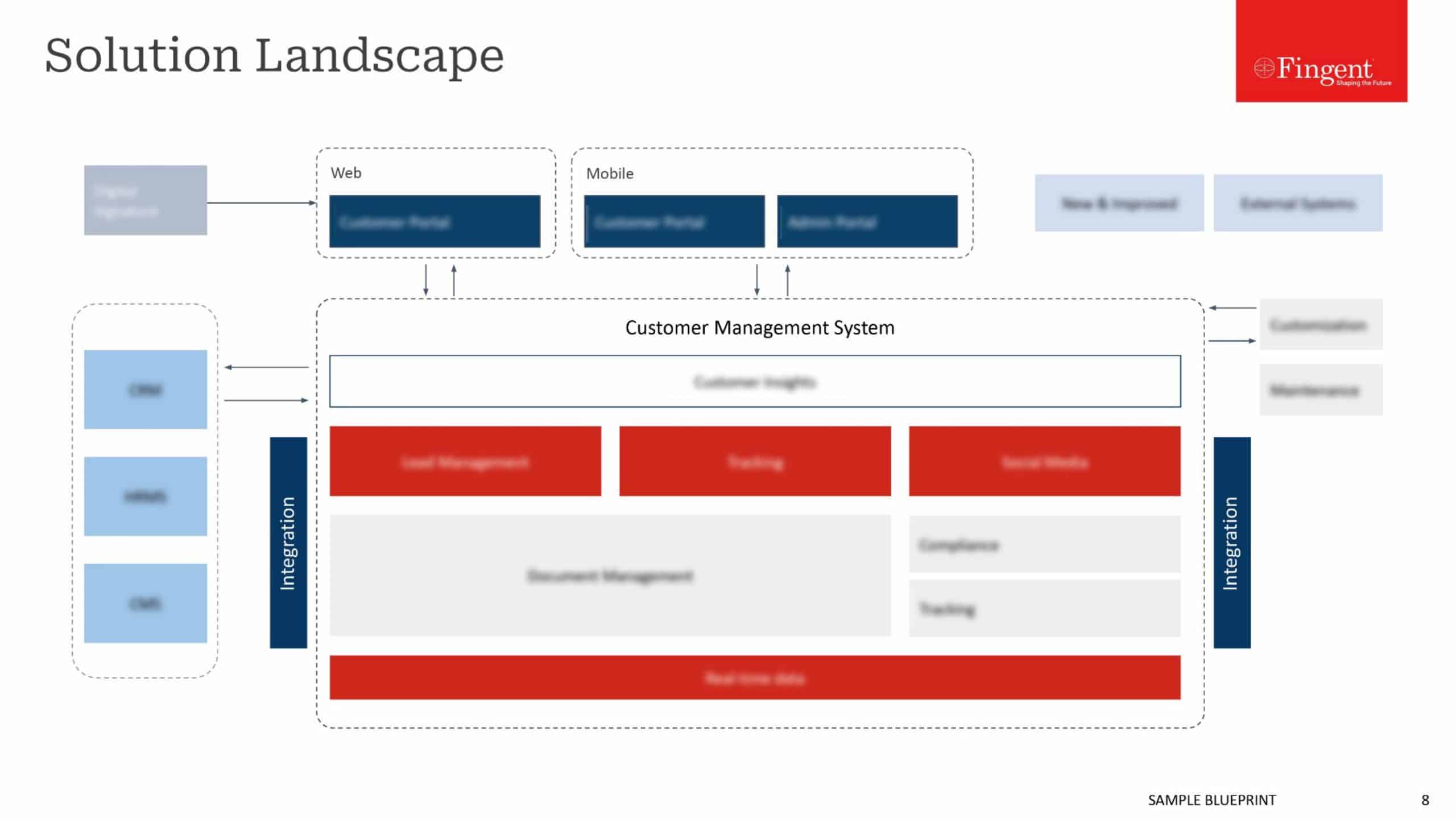
Infince delivers the three IT-essentials for business: run-your-business software, secure cloud hosting, and concierge IT services, on a single tightly integrated platform. Created by Fingent, a leading developer of cloud-based technologies, Infince gives a business instant access to a complete, reliable, fully supported, and secure IT infrastructure, even if they don’t have any in-house IT expertise. Perfect for today’s “deskless” worker and employees who BYOD.
Software: Infince offers a turnkey library of free, open source, enterprise software, including customizable CMS, ERP, CRM, and marketing automation software; and enables unified access to popular SaaS services, all of which can be activated or deactivated on demand. This integration greatly facilitates onboarding and offboarding of employees. A business’ internet domain, email server, and website can be set up with a few clicks. Out of the box, each user gets a suite of business office software, email, chat, secure file sharing, and productivity tools, including video meetings.
Cloud: Unlike other cloud providers who have complex configuration options primarily catering to software developers, provisioning cloud resources on Infince is easy-to-do and easy-to-understand. Infince lets a business owner grow and manage their IT infrastructure themselves, in economical bite-sized increments. All employee files and communications are secured and inaccessible to search engine companies.
Services: Infince offers a variety of service options including online help desk and expert application technical support, self-help support, configuration assistance, server management, and affordable custom programming services.
Cost and Pre-requisites: An introductory starter package supporting up to 10 users is offered at $50 per month, and it requires no annual commitment. As a “thin client,” virtual desktop, Infince can be run from anywhere there is available internet service and on any device with supported browsers: from Chromebooks, tablets, and smartphones, to PC’s and Macs.
“Infince is a complete and worry-free cloud offering that lets a business adopt technology quickly, with integrated support, and lets owners stay focused on achieving their core business goals.” said Stephen Cummings, SVP.
Easy to use and simple to deploy, Infince makes it economical for a small business to get big business technology. For more info, see infince.com.
About Fingent: Fingent, the creator of Infince, develops software that equips businesses to operate more effectively, more efficiently, and with more resiliency. Since 2003, Fingent has developed sophisticated web and mobile software solutions that have been key to our clients’ business success — rapidly, on schedule, and on budget. Fingent has offices in White Plains, NY, and Cambridge, MA. For us, it is not just about delivering software, but also about partnering in business efforts to shape a brighter and smarter future.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
The worldwide enterprise mobility market is growing by 24% GAGR, and its value will likely touch $140 billion by 2020. A key contributor to the growth is Android. However, enterprise seeking to leverage the gains of Android-powered mobility, however, needs to roll out intuitive Android apps, through which they can channel the ecosystem to the desired effect.
Here are the benefits enterprises stand to leverage by investing in Android apps
1. Android Cut Costs
Android is open-source. Its Software Development Kit (SDK) is available free of cost. Enterprises rolling out Android apps to power their systems and processes need to spend only on the development costs. They can minimize the software licensing costs, and get their software free of any royalties. The saving is considerable, considering CFOs in today’s highly competitive age are penny-pinchers, and reluctant to invest in anything not directly contributing to the bottom-line.
2. Android facilitates Easy Integration
Most enterprises have multiple entities, departments, and processes. Having separate and distinct systems or processes for each entity needlessly duplicates the efforts and costs needed to maintain such systems, and also creates disjoints and data silos. Many enterprises strive to run company processes through a single integrated system. Android is the perfect platform for such an approach, as is is resilient, and able to run on any device or form factor. An enterprise can easily develop a CRM on Android and seamlessly link it with an Android developed a marketing automation suite, a Human Resource Information System, and more, creating an integrated whole. Such an approach ends the menace of data silos and facilitates the smooth and seamless flow of information across the enterprise.
A comprehensive Android-based platform is a convenient way to manage all functions of enterprises. The enterprise can roll out several functional apps, each linking to the integrated system. Such apps, which sits over the traditional enterprise systems, and which updates the systems in real-time, may be tailored to suit the workflow and process of the employee or the department. It gives an unprecedented level of flexibility to the employees and makes the enterprise adapt to respond to changes faster. For instance, if a particular situation requires a new workflow or a new level of coordination, all the enterprise needs to do is roll out a new app and disseminate it to the concerned employees or stakeholders.
3. Android Delivers Flexibility
Many-a-times, enterprises are forced to adjust their business operations to cater to the demands of an inflexible system. The ease and low costs to develop Android apps, and the flexibility of the Android platform mean enterprises need not make such sacrifices and can pursue their objectives in the most efficient way possible. Android makes it very easy and viable to develop tailor-made, and even innovative apps to suit any processes or any requirement. Custom apps may also be localized to maximize productivity.
4. Ease of Installation and Use
Developers have it easy with Android, thanks to the availability of Android tools which offer easy ways to improve, fix, and update apps thanks to the facilities that Android tools provide them.
Android applications are flexible and resilient to be published and pushed in multiple ways. It may be hosted in an app store, or even distributed through APKs. Enterprises can easily ensure their employees, customers or other targeted stakeholders can access and download the app in a very simple way, without any hassle. Unlike other stacks, which require a lot of learning curve and even set-up assistance, Android’s simple and easy nature makes it a DIY proposition.
Android brings very few complications or compatibility issues. Custom built Android apps, designed with end-user requirements in mind offer very little complication and syncs seamlessly with any business software, including legacy systems. The open source nature also means the availability of several connectors to link enterprise applications with popular packages such as Salesforce, MailChimp, and more.
Bizness Apps – “Mobile Apps For Businesses Made Easy” [Source : Flikli]
5. A Fillip for BYOD
The Bring your own Device (BYOD) concept is a rage in enterprises. A big reason for its popularity is the win-win proposition it offers to both the enterprises and the employees alike. Enterprises save on hardware and training costs, whereas employees get the convenience of working in their own familiar devices, with the associated productivity benefits. However, the success of BYOD depends on the availability of highly functional apps, through which employees can access their work. Logging in to the corporate intranet through a mobile browser every time is highly cumbersome and in any case, an inefficient way to work, frittering away much of the gains of mobility.
Android apps allow the employee to work seamlessly. It allows the enterprise to set policies to ensure BYOD does not compromise the integrity of enterprise data and processes.
With BYOD, employees, especially those on the move, can access enterprise applications securely through the API, and from their usual device. This expedites the decision-making process, makes work seamless, and saves the executives’ effort.
6. Valuing the Stakeholders
Forward-looking enterprises of today share some common traits, and being responsive is one such trait. Enterprises which are responsive to its stakeholders, promote an open culture, and encourage feedback, gain a positive image, and reap rich indirect benefits out of it. A collaborative software development approach, with end users and other stakeholders having a major say syncs with such a culture and environment.
Android is the perfect medium for such a culture and approach. The large and vibrant Android community makes it the perfect option to receive customer feedback. Users of an Android app can easily share their feedback and even rate the app in the Play Store. Several freely available tools make collaboration easy.
7. Improved Customer Engagement
While mobile apps revolutionize the internal workings of an enterprise, its potential to boost customer engagement stands underrated.
Mobility is clearly the future, with more people already accessing the Internet through their smartphones than through traditional computing devices such as PCs and tablets. Among the various mobile platforms, Android is the dominant player, with 84% of the total mobile market share. Android’s dominance is unlikely to end anytime soon either. Enterprises investing in customer-facing Android apps, and promoting customers to download it to their smartphones, stand the chance of establishing a secured and reliable engagement channel with the maximum number of customers.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
The term “blockchain” is now commonly used as a synonym for cryptocurrencies, thanks to the tremendous popularity of Bitcoins. However, Blockchain is only the underlying technology behind Bitcoins. The potential of blockchain is open in many sectors, from banking to logistics, from healthcare to public administration, and more.
Blockchain transactions move data incrementally in peer-to-peer networks, with transaction records kept in transparent ledgers. The technology brings about a paradigm shift in the way enterprises approach data, and how developers write, market, and sell software.
Establishment of New Standards
Blockchain enables smart contracts, which allows any user to store, verify, and execute code on a blockchain. Several projects are now ongoing, holding the potential to replace the traditional processing, storage, and computing elements of the computing stack.
The Hyperledger Fabric, for instance, provides the foundations for identity, privacy, and processing. Developers may build robust components atop the fabric. Ethereum offers a similar blockchain, in either public or private mode. Both allow developers a choice of using enterprise-friendly programming languages to develop smart contracts. Ethereum has its own language which resembles JavaScript. Unlike what conventional languages offer, this Ethreum language allows users to define their own understanding of “consensus” and “currency.”
Blockchain standards are still fluid, with several new standards and protocols coming up by the day. A churn is imminent in the space, but the underlying reality of new standards and protocols is here to stay. The soaring popularity of the blockchain means these new blockchain standards, offering infinite greater possibilities compared to conventional programming, will soon become the norm in software development.
Understand the Blockchain in Two Minutes [Source: IFTF]
Transparent, Multi-Functional Databases
Blockchain adopts a distributed database where data records are accessible to everyone and is but protects against unauthorized access. These databases, built on peer-to-peer technology is more robust and secure and again eliminate the “middleman” provider.
A user having access to the application developed using the Blockchain development technology may view the data or add a record to the database, but cannot modify or delete any data record. Such robust databases improve the integrity of the entire process manifold. The benefits are especially huge in protecting the integrity of information in several sensitive industries, where even a minor change can have big implications.
Several major industries are already exploring the possibility of integrating blockchain databases into their core systems. For instance, GE’s Aviation Division plans to adopt these databases in aviation. The new blockchain-based software could manage GE’s aviation inventory, sales tracking, and record keeping, with a high level of transparency and integrity.
Innovations in this field even allow adding a blockchain layer to existing databases such as MongoDB and RethinkDB. Such interesting approaches allow enterprises to leverage the benefits of blockchain database without overhauling or uprooting their incumbent databases.
Usually, transparency runs counter to integrity. Greater the transparency, greater the risk of the information being tampered. Blockchain databases facilitate both and offer added advantages of cost-effectiveness and improved functionality. At the same time, there is improved accountability and better transaction support.
Empowerment of New Small sellers
In today’s business ecosystem, any transaction between two parties is done through a third-party middleman, whose primary role is to enforce reliability and trust. For instance, most online financial transactions are done through PayPal, Moneybookers or other intermediaries, who acts as the depository for people sending and receiving money. Likewise, freelance software development largely takes place either through software development firms or through third-party portals such as Upwork. Without such a third-party firm or portal, there is no reliable way for a buyer to contact and get work done from a seller, and for the seller to ensure he gets paid for the work done. The system is loaded against individual programmers, who rarely have the means or the time to market themselves and conduct the extensive administrative requirements vital to establish trust and integrity.
Blockchain offers a level playing field, offering a tremendous advantage to small players. Small sellers can now compete effectively with biggies, and eliminate the middleman firm or portal in the process. The peer-to-peer network of blockchain enables self-executing contracts, which facilitate payments between customers and developers, eliminating the middleman. The net result is an encouragement of small teams and individual developers, radically altering the hierarchy of the software industry.
The blockchain ecosystem is also throwing up various resources, which facilitate such decentralization and de-institutionalization of online transactions. A case in point is Game Protocol, a “decentralized gaming ecosystem” offering crowdfunding and other development tools to host games in the marketplace. The tool also accepts cryptocurrency transactions, allowing enterprise software developers to sell their products directly to the market without the help of an institutional or a virtual middleman who takes a cut of the proceeds.
New File storage Protocols
The Blockchain technology also offers a host of innovative file storage approaches.
The InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) project, which straddles storage and communication systems, offers a radical improvement to the incumbent HTTP communication protocol. The HTTP protocol downloads a single file from a single machine at a time, whereas the IPFS downloads pieces of a file from multiple decentralized machines simultaneously, similar to how torrents operate. The process also co-opts the concept of Git or shared depositories and comes with several handy considerations such as convenient file naming and solid use cases. The protocol offers client libraries for popular incumbent languages, such as C++, Swift, Phyton, and JavaScript.
Filecoin offers another innovative storage mechanism. The protocol rather than adopt the conventional blockchain method of tracking transactions between blocks of spare storage around data centers and the Internet builds on traditional storage mechanism and adds a blockchain layer to it. Users may bid for the space on offer, and track usage,
The bottom-line of all these innovations is a radical shift in the approach to programming. Many of these new innovations are sure to become the dominant norm in the near future. Top software developers would need to radically alter their approach and co-opt these new concepts.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
In today’s tech-neutral age, knowledge and skills are the key sources of competitive advantage. Smart enterprises institute Learning Management Systems (LMS) to harness and organize the corpus of knowledge available within its ecosystem.
However, the success of such initiatives depends not merely on setting up a Learning Management System. Success rather depends on ensuring that the system is compatible with the enterprise requirements and scalable to match the ever-changing requirements in an extremely fluid business environment.
Learning Management Systems traces its origin in delivering eLearning courses to the workforce through the internet and company intranets, in compliance with the established eLearning standards such as AICC and SCORM standards. However, the nature and scope of LMS have evolved considerably since then. While the exact nature of the LMS may vary, depending on enterprise requirements, successful LMS of today invariably facilitates seamless integration of the physical and virtual classrooms, promotes social learning, and fills in critical gaps in learning. The best LMS are scalable, portable, promotes gamification, and makes managing talent seamless across the enterprise.
Integrated Virtual Classrooms
An effective Learning management System co-opts virtual classrooms, including “live” classrooms, to deliver the power of training and education to anyone, at any time, and any place. Today’s LMS include multimedia-rich virtual classroom content or have ready-to-use APIs, to co-opt the most popular classrooms into its fold, with just a few simple clicks.
Any good LMS offers APIs to connect with the millions of courses and lectures available in popular online portals such as the eDX, and even YouTube.
Promotion of Social Learning
An effective LMS goes beyond formal training and promotes social learning. The conventional method of imparting learning is storing content in a repository and creating access rules around it. Social learning goes a step ahead, to offer users the power to create content, and thereby exchange anecdotes and real-world experiences. The learners collaborate with each other in real time, creating an interactive and participatory learning experience, replicating the feel and experience of a physical classroom. From the enterprise perspective, such an approach furthers the creation of a sustainable pool of knowledge and makes very effective training.
Truly successful Learning Management Systems also tap into gamification, or staring up a friendly competition among learners, to increase engagement. Some of the most common gamification options to make the course more engaging include badges, leaderboards, levels and more. Another option is a small token prize for the learners who do exceptionally well.
Filling in the Gaps
A robust Learning Content Management System automates the task of curriculum management. It scours the training material, syncs with the curriculum, and fills critical gaps in knowledge or information. It also updates the existing content, removing obsolete or outdated information, and updating the content to reflect real-time information, on the basis of latest research, statistics, and other findings. Of course, the caveat is that any LMS is only as effective and relevant as the content and rules fed into it in the first place.
A Flexible Learning Approach
A Learning Management System empowers learners to structure and assemble their own learning. An effective LMS is flexible and modular to allow learners full of the required learning materials and resources to form a curriculum customized to their learning needs and suited to their learning styles.
A key element of flexibility is portability. In today’s extremely fluid business environment, where enterprises have to go where business takes them rather than wait for business o come to their office, a portable cloud-based LMS, accessible through mobile front-end apps is the way forward. For instance, offering training sessions on a tablet with the option to follow us using a desktop computer, with seamless sync between the two, helps the learning progress whenever he is free, such as when commuting to the office.
The best LMS is flexible enough to offer training content at multiple levels, and in multiple formats. Smart LMS also offers the option to support training in multiple languages, a key requirement in today’s hyper-globalized world.
Effective Administration of Training Requirements
Today’s LMS bridges the gap between the classroom and eLearning environment. It offers an effective medium to sync between the two, enabling trainees to extract the best of both worlds. It facilitates easy management of complex and dynamic resources, including training inventory, trainer and external vendors, training rooms and venues. The LMS takes over and automates the vexatious tasks such as coordinating several training programmes, planning and administering training sessions, tracking pre-training and post-training feedback, and compiling training materials. The LMS also makes effective follow up through email and push notifications, logs attendance, and more. By these processes, the platform reduces the administrative drags characteristically associated with such processes.
Scalability
The best Learning Content Management System platforms are scalable, granular and flexible. A scalable platform enables starting off with a manageable base, fine-tuning the system, and growing it organically.
Starting small has its advantages, in being able to check if the implemented programmes actually benefit or meet the intended outcomes, and if the targeted recipients are indeed receptive to the initiative. Creating pilot programmes to validate the hypothesis and assumption is a fundamental time-tested practice to avoid failure. For instance, once this process is completed it would be ruinous to discover the selected platform crashes under the pressure of 10,000+ learners all over the world.
Starting small, however, should not become a limitation or a stumbling block for future growth. A good LMS platform should be capable of managing a large amount of data easily, accessibility for a large number of users to the system at the same time, and allow them to connect from all over the world without delays.
A sound and robust LMS is a key asset in today’s knowledge organizations. By facilitating the learning and training requirements, it equips the workforce to face the emerging challenges, and focus their energies on their core competence.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
The Prelude
Software Development has shaped the economic and social face of the world in the last three decades. What was once considered gibberish and confined to the elite minds that put humans on the Moon and cracked the German Enigma is now a popular profession that has created landmarks like the Silicon Valley and icons like Bill Gates and Steve Jobs. With the spurt in revolutionary product ideas in the late 90s, the need to put those ‘ideas’ into execution demanded the best development-skills, and this ‘demand’ has been only growing with time.
This brings us to an aspect of software development that has always been a vital business decision for companies – the most cost-effective engagement model. Business Software development has moved from being a mandatory in-house requirement by relaxing its rigidness and now accepting offshore and even freelance development. Choosing the right engagement model for software development is therefore essential to create state-of-the-art products without which it is impossible to survive in this cut-throat market.
Here is what we think about choosing the right engagement model:
1) The Package Tour aka the Fixed Price Model
Imagine this: You have decided that you want to visit a popular tourist destination, and it’s just to check an item off your bucket-list. The best bet you probably have is to take up a package that includes every attraction in the city; you may even fix the sightseeing spots which interest you before the tour starts!
This is a great option if you have done some meticulous research on the places you need to visit, the distances between them, the time spent in traveling from one location to another, the opening and closing hours of museums and galleries, and so on. The flip side is that you are in no position to experience flexibility. However, you can be satisfied that everything you’d asked for was provided and that you are not paying anything more or anything less than what you had agreed on initially.
Extend this to the realm of software development engagement; if you know your requirements, and your financial and temporal limits, this ‘Fixed Price’ model is the best choice for you. The Fixed Price model can also serve as a litmus test for hiring freelancers or development partners.
The Pros:
- It’s well-defined and well-negotiated. There’s no room for lapses.
- There is a push to get the complete picture of the software even before the development starts.
The Cons:
- There is no room for flexibility. Your eureka moment of a new feature should wait to materialize.
- Any gaps in communication would mean that the delivered product could be unsatisfactory.
The Fixed Price model works best for developing products on a short-term basis with features that are hot in the market, maybe with some additions and features that give it an extra garnish of appeal!
2) The Chauffeur-Driven Hired Car aka the Time & Material Model:
So, you’ve arrived at your destination, and you are feeling a bit adventurous and you are sure that you do not wish to confine your experience to a ‘package’. So, you decide to hire a car with a driver and pay that person for the time spent and distance covered (the experience and expertise of the driver would be an added variable).
In this manner, you are free to add items to your itinerary, and you are free to remove them at your will. You feel free to stop at any place and enjoy as much as you want, as long as cost and time are not concerns.
This is what the Time and Material model feels like for both companies and freelancers alike. Great products are not built because of a moment of realization, but by systematically accumulating and integrating ideas. For this to happen, flexibility is an essential attribute, which in this fast-paced market, in Sherlock’s words, is Elementary, Dear Watson!
This model also ensures continuous communication and a transparent and healthy vendor relationship.
The Pros:
- Super-Flexible
- You Only Pay For What You Get (If only there was an abbreviation like WYSIWYG!).
- There is a definite possibility for networking, not just on professional, but also on social lines.
- Granular Monitoring on a regular basis, especially in Agile Methods.
The Cons:
- You pay until you get what you want.
- In rare instances, in unethical companies, there could be a deliberate delay in development.
We’re yet to come across a situation or an industry where this might not work; who would not want to get into a development method that is so flexible, accommodative and modular.
3) The Self-Driven Car aka the Dedicated Developer Model:
You arrive at your destination, and instead of trusting a package, or instead of hiring a car by the hour, you decide to take a car all by yourself. It doesn’t matter whether you drive your car for an hour in a day or 23 hours and 59 minutes in a day, it’s all yours. Drive it on the road, and (if the car allows) offroad – there’s no stopping you!
However, this comes with a condition – you will need to know where you’re going, and everything about where you will go, maybe not the route map, but at least the time and distance. All this might sound difficult, but at least, the comfort-point you have is that the car you’ve hired is as good as yours, except that it’s not.
Hiring dedicated developers to work like that – you can take them in-house, and you need to pay them a fixed amount on a monthly basis. Once your product is done, you can, without the guilt of firing or the pain of attrition, ask them to leave. This also means that you have saved up on the recruitment costs, and you don’t have to keep paying for a resource you no longer need.
This model brings the best of both the above models – you have agreed for a fixed payment on a monthly basis (with no hard restrictions on the product-features) and you are free to alter the product or the features, or even shuffle the resources based on their skill-sets!
The Pros:
- You are in complete control. It’s almost like having an in-house team.
- You don’t have to go through the hassles of administration and hiring.
- There is a sense of ‘belonging’ for the dedicated developers in terms of both- the product and the organization.
The Cons:
- It needs management skills and a blue-hat vision of the product to get the best out of a dedicated team.
- If you have both in-house and dedicated developers, there is a chance of conflict.
- Or even worse, there can be possible siphoning of talents!
The Verdict:
You might have already sensed that we’re leaning towards the Time and Material model as it gives significant control, and with strategic planning, it could be cost-efficient as well!
Our recommendation is still strong towards the Fixed Price model for smaller products with limited functionalities, and for short-term projects like developing a module for an already robust tool. Conversely, if your project is long-term and extensive, it makes more sense to hire dedicated developers.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
In today’s age of hyper-competition, businesses need to focus their systems on the customer. A critical area of focus is business software. Much of business software hitherto focused on internal efficiency. However, competitive pressure mandate a realign, with the focus on the customer, and specifically customer support.
Businesses Need to Roll Out Mobile Solutions
Nowadays, the basic support for customer commerce is through customer-facing mobile apps. About 80% of shoppers use their mobile phones for product reviews, to compare prices, and find store locations. A good chunk of these customers completes the purchase process online as well. About 54% of Millennials and 49% of Non-Millennials prefer shopping online. Businesses need to roll out customer-facing mobile apps and responsive websites, to facilitate e-commerce and other customer interactions.
The Rise of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
E-commerce websites offer a world of convenience to the customer. It brings the shopping experience anywhere, from home to office, and from the boardroom to the bathroom. However, such convenience comes without the “touch-and-feel” experience of physical stores. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (VTR) technologies bridge the shortcoming and offer the best of both worlds.
Cases of retailers supporting customer commerce through VR and AR-based software abound.
- Swedish furniture giant IKEA’s VR app allows customers to view different kitchen decors. Customers can walk around IKEA kitchens virtually, using a VR headset and app.
- Sephora’s app allows users to take selfies and apply the brand’s cosmetic products to their images. Customers can get conclusive proof of whether a shade of lipstick will look good on them, rather than debate endlessly or speculate.
Artificial Intelligence Systems Facilitate Personalization
Personalization is the order of the day.
Most businesses already use Google Analytics tool to segment customers. They target segmented groups with different discounts and deals. Marketers also use various other predictive analytics tools to analyze historical data. Advanced solutions deliver accurate predictions about demand. Enterprises could focus their efforts on products having the greatest potential for profits.
However, such a superficial approach will undergo a sea change in the future. More-and-more shoppers now leverage Artificial Intelligence, to source products, bargain prices, and pick up products. As a case in point, connected smart fridges detect when the stock of milk becomes low, and trigger an automatic reorder with a linked e-commerce store. Enterprises who can roll out business software to align with such smart systems, and leverage “A-Commerce” or Artificial Intelligence-based commerce, stands to gain big.
Adaptive Design Comes Centrestage
Customers’ needs are never set in stone. Smart businesses keep track of changing customer preferences and the underlying influencers of such change. Business software which connects with potential clients on a personal level, in real-time, is central to such efforts.
Use-cases abound for businesses leveraging technology, to adapting its products and services to serve real-time customer needs.
- Curve, a credit card company allows customers to switch cards even after completing the purchase. An executive purchasing a computer for the company with his personal card, to take advantage of a bargain, could later change the billing to the company card, after getting authorization.
- KLM’s new clip, attached to the traveler’s bag, offers real-time directions, suggestions, and alternatives. For instance, when a user is stuck in a long line at the Eiffel Tower, the clip suggests the nearby hot-air balloon at Parc André Citroën. The clip also directs users to specific in-house services, stealing customers away from the competition.
- Tesla recently increased the range of its electric vehicles for customers struck in places affected by Hurricane Irma. Range limitations in Tesla’s vehicles meant owners couldn’t evacuate the area.
Virtual Companions Become Mainstream
Most smart businesses now empower their workforce, especially support agents with virtual assistants. Such virtual assistants automate daily tasks in ways CRM can never enable.
Virtual assistants offer agents deep real-time insights on information hidden inside the company databases and other systems. Locating such information manually is a time-consuming task, in the absence of clear-cut information on where such information resides. The obvious benefit is a speedier resolution of consumer issues, leading to improved customer satisfaction and accelerated sales cycles.
Virtual assistants also take the shape of chatbots, replacing the manual assistant altogether. Technology has evolved considerably on this front, and businesses are co-opting it in a big way. In the future, even the most basic bots will become more interactive than Siri and Alexia of today.
AI infused bots learn from users, to offer highly relevant insight and suggestions. It could open the database and pry a solution even before a manual agent has the chance to comprehend the question. Further, the technology to make bots understand emotional intelligence has arrived. Such Emotional Intelligence capable bots would know how exactly to respond to a frustrated customer. Going forward, bots would handle most normal queries, leaving human agents only with long-tail and complicated queries.
Social Media Rises in Importance
Social media caught on big-time, with estimates suggesting a 394% increase in social media use in recent years. The widespread popularity is mainly on account of the transparency, the social media delivers. The best businesses leverage such transparency to further their business model.
Traditionally, businesses had complete control over their products and services. The business model essentially boiled down to a “take-it-or-leave-it” approach. The transparency infused by social media has changed the power equations. Customers now have unprecedented choice and ability to gather real feedback from real users of any product or service. If something goes wrong, rest assured everyone will come to know about it.
Smart companies cope with such change by giving more power to its customers. They listen to the customer eagerly and align their business software to take feedback. This ensures that the business and the customer work together, for mutual benefit. Businesses roll out more collaborative systems and link it to their key product development and management channels.
Enterprises need not always go in search of new technologies. What is important is the way in which any technology, new or old is applied. Any business today needs to adapt and change its services and products to meet the changing needs of the customers. Customer focused business software is a major enabler in this direction.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Cognitive computing in a broad sense refers to software mimicking the functioning of the human brain, to make better decisions.
Computers have caught on ever since its inception, owing to its ability to undertake lightning-fast calculations, much beyond the range of human capabilities. However, computing devices face a serious limitation in not being able to accomplish tasks humans take for granted, such as understanding the natural language or recognizing unique objects in an image. While artificial intelligence offers a start in this direction, cognitive computing represents the coming of age in this front.
Cognitive computing, in a sense, represents the third era of computing, with computers that could tabulate sums the in-thing in the 1900s, to programmable systems in the 1950s, and now cognitive systems.
Personal digital assistants such as Siri, already present in smartphones come close to cognitive computing but are not true cognitive systems. Such systems can only respond to a preset number of requests, whereas true cognitive applications give a thoughtful response, without being restrained to a preprogrammed response set.
How Do Cognitive Applications Work?
Cognitive computing aims to simulate human thought processes in a computerized model. To this end, cognitive applications use deep learning algorithms and neural networks and leverage the latest technological solutions such as data mining, natural language processing, and pattern recognition.
Cognitive applications draw on multiple sources of information, including structured and unstructured digital information, sensory inputs such as visual, gestural, auditory, information, sensor-provided information, and more. It then processes the gathered information by comparing it to the set of data it already knows. As such, the more data the system encounters, the more it learns, and the more accurate the system becomes, over time.
Cognitive computing applications integrate data analysis with adaptive page displays (AUI) to tailor content for the specific audience and specific situations.
IBM Watson, one of the earliest approaches to cognitive computing, offered a path-breaking combination of natural language processing, machine learning, and knowledge representation. Watson ingests questions or inputs in natural language mode, search its repository for information, develops and analyze hypotheses on its own, and generates answers, also in natural language mode. What made Watson successful was not just the combination of the multiple capabilities, but the seamless and powerful integration of such different capabilities in a way it influences each other.
Basic Characteristics of Cognitive Applications
Cognitive applications are a cut above ordinary applications, as evident from the following basic features or characteristics.
Adaptive: Cognitive applications are adaptive, capable of integrating information around its ecosystem, as it changes. These systems feed on dynamic data in real time, or near real-time, to master ambiguity and unpredictability. It adapts to the changing goals and requirements of the enterprise, which is common in today’s highly fluid business environment.
Interactive: Cognitive applications interact easily with users, and also with other processors, devices, and cloud services. Such seamless interactions allow users to make explicit their requirements comfortably, and the network ascertains the requirements automatically to some extent.
Iterative: Cognitive applications are iterative and stateful. These apps ask questions or find additional sources by itself when a problem statement is ambiguous or incomplete. It also remembers previous interactions, and pulls in suitable information relevant to the current context, from such corpus.
Contextual: Cognitive computing applications understand and identify contextual elements such as location, time, meaning, syntax, processes, regulations, user’s profile, and more, connected to its ecosystem. The apps act on the basis of such information, automatically.
Dark Data Compatibility: Cognitive computing systems have the capability to deal with “dark data.” Traditional business intelligence and analytics solutions are mostly unable to comprehend social media postings, electronic medical record notes, electronic fitness device readings, unstructured images, and the bulk of general data generated by users in normal day to day settings today. Cognitive Computing apps process such multi-structured and unstructured dark data, to pull out non-obvious insights and subject it to analytics. Combining such dark data with the readily available structured information such as customer records unearth patterns, relationships, and other contextual associations not discernable otherwise.
Cognitive Applications in Action: Use cases
While cognitive computing has been around for quite some time, it is only recently, with the advancements in technology giving it a boost, that it has come to the mainstream. Several practical use cases have already emerged.
Many businesses now use cognitive computing applications to connect with their customers and other stakeholders at a more personal level and offer highly relevant recommendations. Such apps modify the recommendations automatically as they understand more about the stakeholder, and as the situation unfolds. Furthermore, such apps pick up subtleties that traditional analytics would miss.
IBM Watson, one of the earliest manifestations of a cognitive computing platform, already finds widespread use in healthcare. The cognitive computing platform collates the entire gamut of knowledge around a medical condition, such as patient history, journal articles, best practices, diagnostic tools, and more. It then analyzes the information, and offer a recommendation in sync with the changing condition of the patient. It is virtually impossible for any human to possess such vast range of information, leave alone analyze it. Doctors may leverage such insights to adopt evidence-based treatment options considering all factors, including the individual patient’s presentation and history. This is a big upgrade from the present scenario where the doctor makes educated guesswork, based on grossly incomplete information, with the decision based on the doctor’s limited range of knowledge. The insights available through cognitive computing enable even fresher doctors to perform as effectively as experienced specialists.
Cognitive computing applications are also making its mark in a big way to improve consumer behavior analysis, facilitate personal shopping bots, in education, diagnostics, and other areas. A good real-life example is Hilton Hotel’s Connie, the first concierge robot, which helps visitors with regards to hotel information, local attractions, and more, with questions posed in natural language rather than computing language.
Cognitive computing delivers positive ROI. Enterprises have already succeeded in applying it to convert even traditional cost centers such as customer care to profit centers. For instance, a packaged goods company applying cognitive computing to resolve customer problems automatically, pre-empting the usual practice of customers raising a ticket, could achieve a 30% reduction in tickets. Considering the cost of each ticket was $24 to $160, the savings are substantial.
Enterprises adopting cognitive computing, however, need to develop purpose-built applications to address specific use cases relevant to their stakeholders. Success depends on not just technical competence, but the extent to which the cognitive computing technology is interwoven with the business or customer needs.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
So your company has recently purchased an Enterprise Software that will help the organization run. But did you check whether the technology solution provider has provided a maintenance plan along with it? Or, have you researched whether the software builders are competent when it comes to after-sales support? Like a vehicle that requires maintenance, software is no different. It is imperative to include a maintenance plan when you buy a software solution because:
Corrections and bug fixing
A fully-functional software might not display errors and bugs in the beta stage until it is put actively in the environment. A maintenance contract will ensure that these bugs and bad codes are fixed. It also covers the systems for major repairs and advanced problem solving that otherwise would cost more money and time.
Flexibility
A software solution is adaptive since it evolves with use every single day. With changes on a daily basis, your software might need an upgrade, update, and even change in modules. Plug in these changes can along with the maintenance team that knows the ins and outs of the software. It also keeps the software up-to-date and increases its lifespan in the company.
Compatibility
Since technology is growing each day, the addition of new hardware to the systems is inevitable. A maintenance contract from your software provider can help in addressing compatibility issues with this newer hardware. It would help one tackle with ease, any modification of the existing system.
Improve performance
Some vendors provide one or two free upgrades and patches in their maintenance contract that help in keeping your software on par with the latest trends. These upgrades might include some major overhaul or issues raised by other users.
Saving IT expenditure
A smart move in any business is to save money before earning the profits. Having a maintenance contract does cost a little extra but covers important bug fixes, routine upgrades, and critical problem-solving. In a way, it fixes an annual price on the IT expenditure and removes the chance of any unforeseeable expense that might occur due to the software.
Re-engineering the software
As a part of preventive maintenance, the software can be re-engineered and restructured to adapt to the changing conditions. This type of maintenance is mostly used as a preventive measure to avoid problems that might occur instead of fixing existing problems.
Staying ahead in the race
As you evolve and grow, so does your competition. Your enterprise software plays an important role when it comes to staying in forefront of the competitors or fulfilling the requirements of tech-savvy customers. A regular maintenance can help with adapting to time. Also, changes in business patterns and legal government rules can be done easily under a contract.
Remember each technology solution provider will offer various types of maintenance. You will have to first identify what are the requirements of your business and what type of maintenance will suit them. Secondly, check if the contract is worth the price with respect to the coverage and the background of the provider. See what are the different maintenance features provided. These may include the number of updates provided in a year, availability of support team in need of emergency, and turnaround time for problem-solving.
Robert Glass has a very well-written fact about maintenance that goes like this – ‘60% of software’s cost is maintenance, and about 60% of the maintenance cost is an improvement.’ Established and genuine software providers not only offer complete software solutions but also maintenance services that encompass all the said points that help run a smooth business.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Cloud computing refers to the method of computing in which an interconnected network of remote servers is utilized for the execution of the operations such as storage, management, and processing of information. The business units in the current era are making use of multiple cloud computing services and techniques in an integrated architecture. There are various deployment and delivery models of the cloud which are amalgamated as one unit for the execution of business processes and activities. However, with the expansion of such practices, there are some security issues that have been observed.
The security issues and occurrences are primarily associated with network-based security risks, availability, confidentiality threats and integrity risks. Events such as Denial of Service (DoS) attacks, malware attacks, message/media alteration attacks, spoofing and phishing attacks, man-in-the-middle attacks, and eavesdropping attacks are common in the multi-cloud environment.
Organizations are required to follow certain steps towards security to make sure that the security risks and occurrences are prevented, detected and controlled. The following security measures and steps shall be included in for achieving a secure multi-cloud environment.
- Prioritization of Visibility: The business organizations in the multi-cloud environment must ensure that they have complete visibility across all the cloud instances. Behavior-based monitoring shall be adopted for enhancing the visibility. Objectionable modifications and malevolent activities will also be highlighted with this process.
- Adherence to the Best Practices: In the case of the multi-cloud environment, there are various systems, devices, and networks that are involved. Each of these entities has a set of guiding principles and standards. The cloud security team must analyze and understand the best practices that are associated with each entity. For instance, in case of NoSQL databases present in the multi-cloud environment, it would be best to meet the compliance requirements, install advanced access control and authentication measures and promote database security for the overall security of the cloud.
- Flexible and Secure Governance: Governance is a critical element in any of the organizations. It is possible to establish trust and security across the organization only with the aid of well-governed systems. In association with the multi-cloud environment, the processes such as identity management, scheduling activities and resource allocation must be securely governed.
- Encryption of the Data at Rest: It is often witnessed that the business organizations enforce and implement the encryption of the information that is in-transit. However, the encryption of the information at rest is often not paid due attention. Such loopholes in security provide the attackers with an opportunity to get hold of the information at rest and misuse the same. It is, therefore, extremely necessary to encrypt the information at rest using advanced encryption algorithms.
- Advanced Shared Responsibility Model: Sharing of resources is one of the prime features of cloud computing, which gets enhanced in the multi-cloud environment. There are overlapping responsibilities and ideas that are often observed which may lead to the occurrences of loopholes in the security. Every entity that is present in a multi-cloud environment must make sure that complete justice is done to the shared responsibility model of the cloud. The allocation of roles and responsibilities shall be done in such a manner that there are complete transparency and ease of execution that is involved.
- Network-based Security Controls: Most of the security issues that occur in the multi-cloud environment have networks as the prime agents of the threats. It adds to the requirement of implementing automated and advanced network security tools and controls to ensure that such risks are avoided and controlled. Some of these tools include network monitoring tools, intrusion detection systems, intrusion prevention systems, anti-malware tools, and anti-denial tools.
Cloud strategy and planning has provided the organizations with the ability to enhance the performance, speed, and quality of their respective business operations and activities. With the occurrence of the security risks and threats, there is a poor impact on the business continuity and customer engagement. It is, therefore, required to include the basic and advanced steps to security to deal with the security issues and problems. These steps shall combine administrative, physical, logical and technical controls.
The use of security solutions that are available in the market will allow the organizations to achieve and maintain security in the multi-cloud environment. These solutions will provide an integrated security mechanism and will eliminate the need to deploy security measures for each of the cloud model and elements. Security concepts and requirements, such as information security, network security, and database security are now provided in a single package by the leading software solution providers while entrusting them for your digital transformations.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new