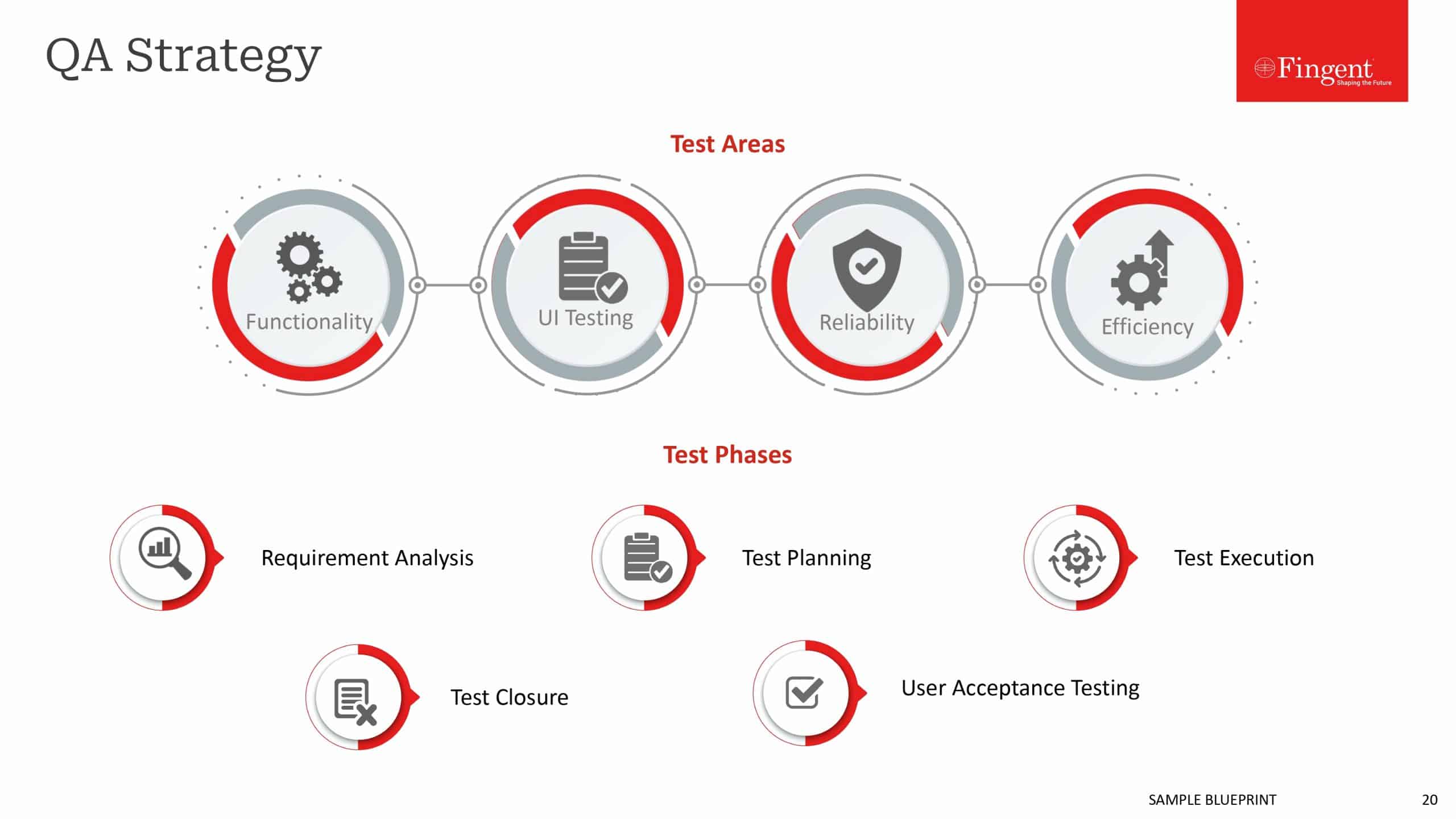
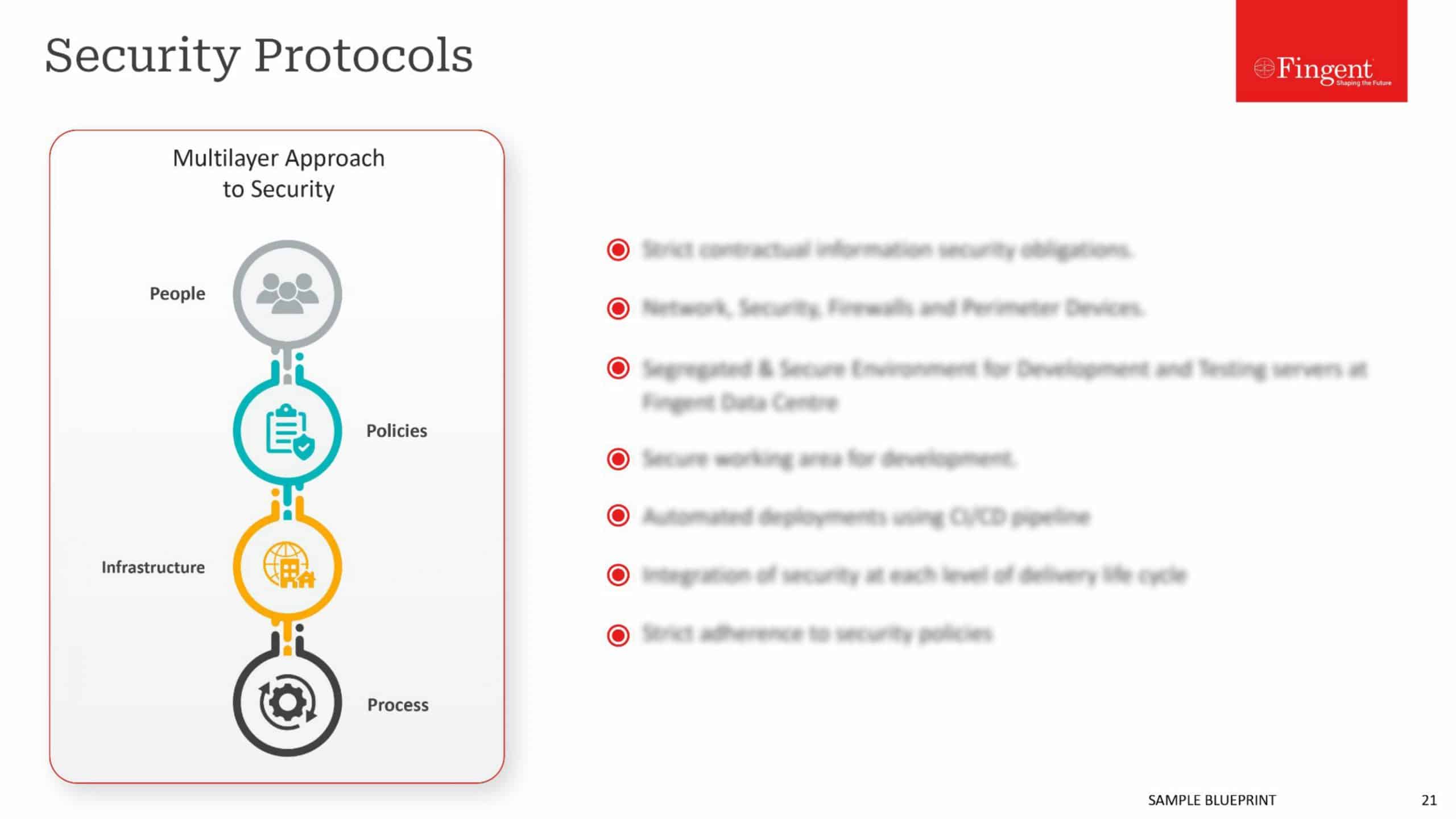
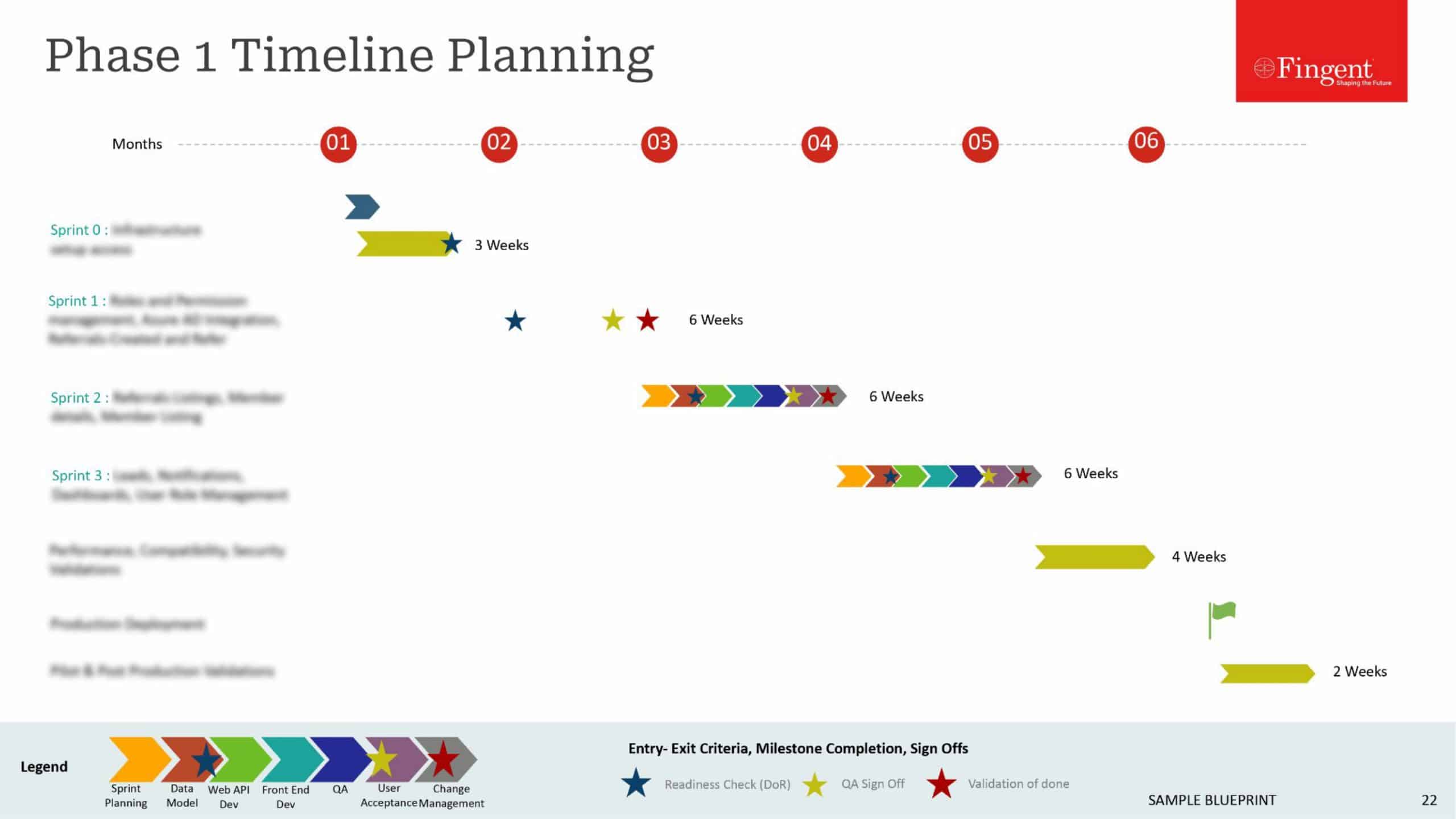
Tag: Manufacturing Industry
In the competitive manufacturing world, being average won’t secure a win. Businesses need technology to outperform competitors, reduce costs, and build a stellar reputation that echoes through the manufacturing jungle. Let’s delve into the heart of the matter and see how a Custom Inventory Management System can help manufacturers navigate the twists and turns of the manufacturing maze. We’ll explore the inventory management challenges and examine how a tailored approach can help manufacturers not only stay afloat but thrive in this demanding landscape.
Why Manufacturers Need a Custom Inventory Management System
The manufacturing landscape is a dense, competitive jungle where businesses grapple for survival. According to recent statistics, the manufacturing sector is expected to experience nearly 13% annual growth during CAGR 2023-2028, intensifying the competition among industry players. It’s a wild terrain where those with the most efficient processes and strategic tools emerge as the victors.
Unfortunately, off-the-shelf inventory management systems are like one-size-fits-all shoes—they might work for a few but for the majority. They’re uncomfortable, restrictive, and prone to blisters. Off-the-shelf IMS solutions lack the tailored fit that manufacturers need to address their unique challenges. On the other hand, having a custom inventory management system is a perfect fit that enhances your strengths and minimizes your industry weaknesses.
So, before we consider the benefits of custom IMS, let us understand what we are up against.
Watch: How Custom Software Solutions makes complex business processes simple and efficient!
Inventory Management Challenges
In the fast-paced world of business, where every second counts, there’s a labyrinth of challenges that manufacturers face. Let’s explore the hurdles that many businesses encounter.
1. The E-commerce Explosion: Fulfillment Challenges
With the exponential growth of e-commerce, the pressure on warehouses and fulfillment centers has reached unprecedented levels. Quick shipping expectations, order customization, and the demand for eco-friendly packaging add layers of complexity to the fulfillment process.
According to a recent survey, 43% of retailers cite inventory management as one of their top challenges.
2. The Pitfalls of Prediction
In the realm of inventory management, crystal-clear foresight is as elusive as it gets. According to a survey, a staggering 34% of businesses struggle with erroneous inventory planning. The challenge lies in predicting the unpredictable as market trends shift and consumer preferences meander.
3. Overstocking Woes: Balancing Act
Picture a warehouse bursting at the seams with excess inventory – a scenario that many businesses are all too familiar with. The consequences of overstocking are far-reaching, from increased carrying costs to the risk of product obsolescence. The typical retail store in the United States functions with a mere 63% accuracy in its inventory tracking.
4. When Supply Fails to Meet Demand
Out-of-stock situations can swiftly turn customer satisfaction into frustration. In a study by Harvard Business Review, 72% of stock-outs resulted from flawed in-store ordering and replenishing practices, such as retailers ordering insufficiently or belatedly, creating inaccurate demand forecasts, or mishandling inventory. Only 28% of stock-outs were linked to replenishment and planning issues in the supply chain. These instances not only lead to missed sales opportunities but also dent a company’s reputation.
5. Disparate Data Dilemmas
In an era where data is king, disparate data sources can wreak havoc on inventory management efficiency. While a substantial 82% recognize data as an asset, nearly half of respondents (47%) use data sporadically due to the challenge of data silos. The challenge is integrating information from various touchpoints, from sales channels to supplier databases, into a cohesive and actionable dataset. Seamless connectivity is the linchpin for informed decision-making.
6. The Tightrope Walk of Supply and Demand
Timing is everything, they say, and in the world of inventory management, this couldn’t be truer. Picture this: you bulk produce a trendy product just in time for what you thought would be the peak season, only to find yourself drowning in unsold items as the market takes an unexpected turn. The challenge here lies in the delicate balance of predicting consumer behavior and adjusting manufacturing quantities accordingly.
Businesses often grapple with the dilemma of when to pull the trigger on orders and how much inventory to procure. It’s a tightrope walk between meeting customer demand and avoiding the financial strain of excess stock. A misstep in either direction can lead to financial woes and surplus goods gathering dust on shelves.
7. Inaccurate Inventory Counts
Imagine this scenario: you conduct a routine inventory count, only to discover a significant discrepancy between the numbers on paper and the actual stock on the shelves. The repercussions are far-reaching, leading to stockouts, overstock situations, and, worst of all, dissatisfied customers. Addressing this challenge requires implementing robust inventory tracking systems and conducting regular audits to catch discrepancies before they snowball into major headaches.
8. Disorganized Warehouse: Where Lost Items Find a Home
Step into a disorganized warehouse, and you might feel like you’ve entered a labyrinth with no exit. The chaotic arrangement of goods not only slows down order fulfillment but can also result in misplaced items and increased operational costs. Navigating through the clutter becomes a time-consuming and frustrating ordeal for warehouse staff.
The challenges of inventory management are an integral part of the business landscape. Custom Inventory Management System, tailored to the unique needs of your business, holds the key to overcoming these challenges. Let’s explore how.
Decoding the Inventory Management System
At its core, an inventory management system is a digital brain that tracks, organizes, and optimizes all things inventory-related. From the moment raw materials arrive at the doorstep to the triumphant exit of a finished product, this system works tirelessly in the background, leaving manufacturers with the peace of mind to focus on what they do best – creating exceptional products.
Now, you might wonder, “Why should my manufacturing company invest in an inventory management system?” Well, the benefits are abundant, and they extend far beyond mere organization. Let’s dive into the advantages:
- Precision Planning: By analyzing historical data and market trends, IMS helps manufacturers predict demand, ensuring that the right amount of raw materials is ordered at the right time. This not only prevents overstocking but also eliminates the nightmare of stockouts.
- Cost Savings: In the world of manufacturing, time is money. An efficient inventory management system streamlines processes, reduces manual errors, and minimizes the need for excess safety stock. This translates into significant cost savings. Manufacturers can bid farewell to unnecessary storage costs and capitalize on discounts through bulk ordering without the fear of overstocking.
- Enhanced Productivity: A well-organized inventory is synonymous with increased productivity. Employees spend less time searching for misplaced items, and the entire manufacturing process becomes a well-oiled machine. With the guesswork taken out of inventory control, workers can focus on what they excel at – producing high-quality goods.
- Customer Satisfaction: Timely deliveries are the heartbeat of customer satisfaction. An inventory management system ensures that products are manufactured and shipped promptly, meeting customer expectations and fostering loyalty. Happy customers are repeat customers, and an efficient inventory system is your ticket to building lasting relationships.
- Real-time Visibility: Picture this scenario – a manager sitting in the office, with a few clicks, monitors the movement of every item in the inventory in real time. An IMS provides this level of transparency. From tracking shipments to monitoring stock levels, real-time visibility empowers decision-makers to make informed choices, thereby steering the company toward success.
An inventory management system is a strategic ally that empowers manufacturers. So, whether you’re a seasoned manufacturer or a budding entrepreneur venturing into the world of production, consider the investment in an inventory management system as the crescendo that elevates your operations to new heights. But why custom inventory management?
Tailored Excellence: The Advantages of a Custom Inventory System
When it comes to managing inventory, a custom-built solution can be a game-changer for your business. Here’s why:
- Precision Tailoring: Customize every feature to meet your unique business needs, ensuring a perfect fit for your workflows, products, and processes.
- Efficiency Redefined: Eliminate unnecessary features and focus on what matters most to your business, streamlining operations and avoiding confusion.
- Scalability on Your Terms: Grow seamlessly with a system designed for scalability, adapting to your business’s expansion without disruptive transitions.
- Integration Harmony: Ensure a smooth fit with your existing technology stack, leading to fewer disruptions and a cohesive tech ecosystem.
- Cost-Effective Long-Term: While the initial investment may be higher, a custom solution can be cost-effective in the long run by preventing payments for unused functionalities and increasing overall efficiency.
- Dedicated Support: Enjoy personalized support from developers who understand your system inside out, ensuring faster and more effective assistance.
In the realm of inventory management, a custom-built solution isn’t just software; it’s a strategic asset crafted to elevate your business operations.
Read more: Understanding The Types Of Warehouse Management Systems
Elevate Your Business with Fingent’s Custom Inventory Solutions
Embark on a transformative journey with Fingent’s custom inventory solutions. Collaboratively tailored to match the unique intricacies of your business, our systems prioritize user-friendly functionality, scalability for growth, seamless integration with your existing tech stack, and long-term cost-effectiveness.
Beyond development, our dedicated support team ensures smooth operations. With a proven track record across diverse industries, Fingent stands ready to elevate your business through a personalized and efficient inventory management experience. Ready to unlock your business’s full potential? Let Fingent guide you through this transformative journey. Let’s talk.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Manufacturing has long been a driver of global prosperity and economic growth. We all see astounding growth as the manufacturing industry evolves and keeps up with changing consumer needs.
This has led industry leaders to shift their focus from traditional to smart factory technology. A smart factory offers many benefits to operators, managers, and executives of companies in this industry. And yet, a few companies hesitate to start their journey the ‘smart way.’ If you are one of those companies, this article will help you with details and show you how a smart factory can bring its business operations and customer satisfaction to a new level.
Let us begin by understanding what a smart factory is.
What Is a Smart Factory?
Take a manufacturing facility and completely digitize it – that is what a smart factory is. The smart factory is a digitized manufacturing facility that uses digitized manufacturing methods, devices, and systems to continuously collect and share data. This data is used to make informed decisions that improve processes and address manufacturing challenges. The smart factory is a new industrial revolution phase focusing on real-time data, connectivity, automation, and Machine Language.
A smart factory uses the best digital and physical worlds to monitor the entire production line, from supply chain management to manufacturing tools. It can even monitor the work of an individual operator on the factory floor.
Why Is It Smart to Embrace the Smart Factory Movement?
According to a press release by Marketsandmarket, the smart manufacturing market was projected to reach USD 228.2 billion by 2027. It is expected to grow at a CAGR of 18.5% from 2022 to 2027. Then, most businesses consider smart factories highly beneficial and crucial across industries and sectors. Here are some of those significant benefits:
- Measure key performance indicators: A smart factory provides managers with automated data that is accurate. This data gives them the ability to measure key performance indicators more efficiently.
- Think ahead better and faster: Smarter predictive maintenance allows managers to predict and resolve maintenance issues better and faster.
- Efficient demand management: It can forecast more accurately and thus reduce waste enabling efficient demand management.
- Boosted productivity: Managers boost productivity as it can provide seamless data on machine maintenance and potential bottlenecks.
Key Elements of a Smart Factory
There are a few elements that make the smart factory what it is. Understanding these elements will help you see how it fits into your business.
1. Robotics
Robotics is a crucial element of a smart factory. Robotics enables smart material handling and adaptive operations. Besides, robots come with flexible infrastructure that can scale depending on business needs.
2. Big data and IoT
The Smart factory provides augmented access to large amounts of data obtained through the cloud and connected devices. This can empower manufacturers to identify patterns and insights, thus enabling them to make more informed decisions to optimize operations and improve productivity in the long run.
3. Cloud-based management
Cloud-based management includes a suite of professional software architecture that can be developed to empower highly efficient business operations. This can offer market reactivity and scalability. It can also provide real-time visibility into a business’s inventory and manage supply chain operations from the manufacturing to the end customer.
4. Virtual reality
Manufacturers have been using virtual reality for some time now. It uses computer-generated visuals that help improve the experience of the user. It trains engineers to handle complex virtual processes, maintenance systems, and troubleshooting.
5. Cybersecurity
Smart factories tend to increase cyber security threats. Thankfully, smart factory technologies are equipped to streamline cyber threats. For example, AI-powered bots act as guards 24/7, ensuring data security.
6. Additive manufacturing
Additive manufacturing is used for rapid prototyping, on-site manufacturing, and more. It saves time and costs spent on production and tool replacements. Quick reproduction, reconfiguration, and validation can also enable reverse engineering.
Read more: ERP Systems for Manufacturing: How it Improves Business Process
A Look into The Future of Smart Factories
Manufacturers that leverage smart factory technologies will unlock game-changing flexibility and agility. Emerging imperatives for the manufacturing industry include supply chain resilience, enhanced productivity, flexibility, and sustainability. In simple terms, only those manufacturing systems that enable a demand-driven and dynamically optimized value chain will survive and thrive.
1. Increasing demands
In the coming years, factories will face more stringent regulatory and compliance requirements ever. Such demands also merge with global trends toward adopting digitization. Given their ability to drive exponential productivity and sustainability benefits, digital technologies are at the heart of these changes.
2. Automation and beyond
Across the world, manufacturers began their digital transformation with automation to minimize manual operations and maximize output. But technological advances are enabling manufacturers to empower operators to understand operational data. Furthermore, newer platforms and integration technologies are driving down the cost of digital transformation.
3. Transformational gains
By implementing an integrated automation system, manufacturers can accelerate their sustainable manufacturing vision. Driven by the unrelenting need for agility and resilience, manufacturers can empower their workforce by adopting smart factories. By building future smart factories, they can unlock value benefits for all stakeholders along the way.
Creating a Smarter Future for Manufacturing with Fingent!
A smart factory is a direct way for manufacturers to excel in a competitive and dynamic marketplace. Partnering with the right app development company could mean make or break for you. Manufacturers need the right partner to help them implement solutions correctly. Fingent has been a consulting partner to several manufacturing companies and proved its mettle. Have a look at our Case Studies:
With the right partner, upgrading a traditional factory to a smart factory is much simpler than most imagine. Fingent builds custom solutions to integrate factories with smart solutions. Through our experience, we have already helped many businesses transform their traditional factories into smart factories.
Our experts at Fingent can help retrofit most existing manufacturing equipment and set up a centralized hub that can receive data from all the sensors. A cloud service could be set up to monitor and analyze from offsite. What is more, these solutions are upgradeable.
This allows established factories to upgrade at their own pace while keeping the upgrade cost low. Do you have a traditional factory that needs to become smart? Contact Fingent today!
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
The COVID-19 pandemic has accentuated the need for resilient supply chains and human-machine collaboration at work. Full or partial shutdowns, as well as social distancing regulations, impose factories and workspaces to operate with the minimal onsite crew. Despite labor shortages, supply chain disruptions, and other production challenges, manufacturers are under constant pressure to respond to the evolving market needs. The demands for mass customization, quality expectations, faster product cycles, and product variability are at an all-time high. Tackling these persistent challenges requires combining human skill and ingenuity with the strength and speed of robots. To bring the best of both worlds – human creativity and robotic precision – manufacturers should adopt cobots (collaborative robots) that can reduce human interaction in feasible situations and accelerate production cycles.
Cobots allow manufacturers to maximize production and address the changing demands while ensuring the safety of their employees, clients, and partners. Why are cobots the future of manufacturing? How do they help build manufacturing resilience? Let’s explore further in this blog.
Read more: What are cobots and how can they benefit industries
Cobots Enhance Manufacturing Efficiency
Collaborative robots or cobots are designed to safely work alongside humans in tedious, dull, and hazardous environments. Unlike the traditional industrial robots that work in fenced premises to avoid close proximity with people, cobots operate in a shared workspace alongside human labor. For instance, a robot that helps humans sort foam chips in a lab is a cobot, while a robot welding a sharp cutting tool in a restricted factory area is a typical industrial robot.
Conventional industrial robots have long enabled manufacturers to leverage automation and compensate for labor shortages, but they are typically designed to execute one specific task. Moreover, they lack the cognitive capabilities possessed by humans to reprogram their operations based on new circumstances. In contrast, cobots don’t require heavy, pre-programmed actuators to drive them. Cobot motions are steered by computer-controlled manipulators, such as robotic arms, which are supervised by humans. Thus, cobots facilitate effective human-machine collaboration at work.
Cobots can be programmed to perform a wide range of tasks in a factory setting such as handling materials, assembling items, palletizing, packaging, and labeling, inspecting product quality, welding, press-fitting, driving screws and nuts, and tending machines. While cobots attend these mind-numbing jobs, human workers can focus on tasks that require immense resourcefulness and reasoning.
Read more: Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
Benefits of Cobots in Manufacturing
Modern manufacturing requires effective human-machine collaboration to cut expenses, reduce time-to-market, and address growing customer demands. Here’s how cobots empower manufacturing enterprises.
1. Easy to Deploy and Program
It takes days and weeks to install and program a traditional industrial robot. A cobot, on the other hand, can be set up in less than an hour. They are lighter than conventional robots. With user-friendly mobile applications and customized software, you can swiftly program the cobot to get started. Right software configurations enable cobots to learn new actions, without any specialized training. Using intuitive 3D visualizations or simple graphical representations, you can move the robot arm to preferred waypoints. Your employees can focus on more critical tasks while the cobot takes care of mundane jobs.
2. Flexible to Perform Different Tasks
Cobots can be easily shifted from one workstation to another due to their flexible hardware. With minimal software customizations, cobots can be re-deployed or repurposed to perform different functions across various departments. For example, a cobot that performs picking and packing can be re-programmed as a filler by replacing its robotic arm with a tube and nozzle.
Read more: Challenges, Opportunities, and Technologies That Will Revolutionize Manufacturing
3. Save Production Cost and Time
A study conducted by the World Economic Forum in association with Advanced Robotics for Manufacturing found that collaborative robots can cut nearly two-thirds of the cycle time required to pack boxes onto pallets. Because cobots are designed to work without any breaks, they reduce the idle time between cycles. The International Society of Automation reports that cobots can save production costs by reducing 75% of manual labor. Traditional robots increase the installation costs for manufacturers as they need to set up additional safety measures around the deployment area. Cobots don’t incur such extra expenses as they can be set up in close proximity to humans.
4. Improve Employee Engagement and Productivity
Cobots work in collaboration with people to refine and process the tasks better. They can never replace the human touch in production. When cobots take care of repetitive tasks such as screwing a bottle or packing medical equipment, employees can focus on more important functions such as running quality checks or inspecting a worksite. It allows manufacturers to optimize their productivity and boost employee morale. Businesses can also prepare their workforces to learn new skills.
5. Maintain Consistency and Accuracy
From the first to the hundredth task, cobots maintain the same level of accuracy and consistency. Humans can get drained easily, whereas a cobot never deviates from the actions for which it is set up. This helps ensure high product quality and uniformity. With the right software and hardware configurations, cobots can produce more finished goods at an incredible pace, faster than handcrafting.
Cobots and The Future of Manufacturing
Industry 4.0 paved the way for automation and smart manufacturing powered by data-driven technologies such as IoT, cyber-physical systems, wearables, AR, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, cognitive computing, and so on. Though the sole focus of Industry 4.0 is to improve process efficiency through physical and digital integration, it accidentally ignores the significance of human value in process optimization. Industry 5.0 re-shifts its focus on human value by fusing the roles of mechanical components and human workers in production. This makes cobots the very foundation of the next wave of the industrial revolution, that is, Industry 5.0.
Denmark-based Universal Robots reports that cobots are at the heart of Industry 5.0. Cobots democratize robotic capabilities, thereby serving as a personal tool that can be leveraged by any member of the workforce to apply creative skills and generate more value. Cobots can be used as a plug-and-play solution across a variety of manufacturing and industrial operations such as automotive production, food processing, chemical plants, medical devices, and kits, among others.
Since they collaborate well with humans in a safe environment, cobots will:
- augment intelligent decision-making,
- drive high-quality products to the market,
- enable mass customization and personalization,
- optimize manufacturing costs,
- generate new job roles (eg: Chief Robotics Officer), and
- boost virtual education to make the most of collaborative robotics.
Read more: How Custom Software Development Helps Manufacturing Industry
How We Help Manufacturers Leverage Cobots and Other Emerging Technologies
As technology matures, manufacturing enterprises need to build use cases that prove the inevitability of human-robot collaboration. We help develop POCs and use cases that demonstrate how your business can benefit from cobots. Our experts can develop your cobot management software or mobile app from scratch or customize your existing software to address the evolving market demands. Fingent custom software development company can work along with your cobot hardware manufacturers to develop a robust software orchestration layer that can control the movement of your cobots. We also simplify the training process to help you get started in no time.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
As the world deals with the short and long-term effects of Coronavirus, the manufacturing industry has suffered significant challenges during 2021. This knock-on effect is likely to be felt into 2022 as consumer demand and spending habits have transformed during the pandemic.
The pandemic demonstrated that major events can have a profound impact on manufacturing operations. Fluctuations between local and national lockdowns have directly impacted the manufacturing industry. Among various other things, it has led to delaying tax bills, postponed mortgage payments.
Knowing what challenges await manufacturing industries will help you and your team come up with the best strategy to achieve success in 2022. So, this article will cover some of the biggest challenges manufacturing industries will face in 2022. We will also look into how these industries can approach the challenges with the help of technologies.
Top challenges prevailing in the manufacturing industry-2022
1. Need to increase sales and revenue
The pandemic made businesses lose several thousands of dollars pushing manufacturing industries to put extra effort into recouping financial losses. Some companies chose to double up on their marketing efforts.
However, the right step would be to create a strategy to start building the business’s pricing power. Building a price power is the surest way to enjoy sustainable earnings.
2. Labor retention
The pandemic era has made it challenging to tackle labor retention issues among the workforce. As the pandemic continues, it is become increasingly hard to find experienced and motivated workers.
To complicate matters, with a fair portion of workers are nearing retirement manufacturing industries are facing a looming shortage of skilled labor. The newer technologies require a workforce with top-tech skills.
3. Customer self-service capabilities
Manufacturers are ever concerned about delivering their products to customers on time. Though the technology makes it possible for customer self-service capabilities, it is not commonly used.
Customers find it frustrating to constantly contact manufacturers for updates on their orders, requests for new proposals, and so on. Customers prefer immediate access to information.
You can address this issue by simply keeping the needed data for customers in a self-service portal. This will allow your customers to retrieve a solution. Plus it can enable the sub-contractor to track and accept tasks assigned to him without bothering anyone.
4. Maximizing work with minimum staff
The social distancing protocol due to the pandemic has forced manufacturing companies to run the factories with lesser staff. This is the time to explore the implementation of more automation technologies.
Read more: Top 10 Technologies That Will Transform Manufacturing!
Most-followed technologies that enable manufacturers to stay on top of the challenges
As Industry 4.0 is still in progress, most manufacturing industries are shifting gears in an effort to automate their manual processes. And the challenges are accelerating this shift now more than ever. Take a look at the top opportunities new technologies bring to the manufacturing industry.
1. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence capabilities
The biggest asset of any company is its data. It is vital to use algorithms to use this enormous amount of data effectively. Humans cannot do this task as efficiently, quickly, and accurately as by AI-led technologies. This ensures your manufacturing is more productive and less wasteful.
According to a global survey conducted by McKinsey & Company, 44% of respondents report cost saving from AI adoption.
2. 3D printing
Manufacturing companies can greatly benefit from 3D printing technology as it can enable manufacturers to make faster and cheaper prototypes.
It can double the performance while lowering the cost by half. It is a cost-effective way to troubleshoot or test the products. It also enables manufacturers to produce products that are in high demand.
3. Smart factories with 5G
The fourth industrial revolution is ushering in an era of smart manufacturing that is enabled with connected devices over 5G networking.
These can make decentralized decisions as the 5G mobile network is faster and more powerful. It is capable of handling full integration of all the devices in a smart factory making it a default choice of manufacturers.
4. Internet of Things
Industrial IoT makes it possible to interconnect sensors and electronic devices that collect and exchange data. It drives AI and performs predictive analytics. IoT is changing the way products are made and delivered.
A study conducted by MPI Group revealed that roughly 63% of manufacturers believe that applying the IoT to products will increase profitability over the next five years.
5. Predictive maintenance
The manufacturing industry depends heavily on predictive maintenance technology. In the past, routine maintenance checks were scheduled to detect unnoticed malfunctions. But that would halt the production and cost money.
Today’s digital technology has enabled machines to send messages to notify workers if or when maintenance is required. These real-time alerts equip the maintenance team to identify and correct mechanical failures without downtime.
6. Shift in the scope of the job
As technology takes over repetitive tasks, employees will need new skills. These skills would include data analysis, software engineering, programming, customer service. R&D and product development, and so on.
7. Agility and responsiveness
Changing customer demands and market conditions require manufacturers to focus on improving responsiveness and agility. Responsiveness and agility are achieved when the time to create, receive, schedule, and process a customers’ order is reduced.
This will enable manufactures to match production cycles and product demand levels. Matching these two aspects can help manufactures pump their operations with greater agility.
Read more: ERP Systems for Manufacturing: How it Improves Business Process!

Fingent can help revolutionize your manufacturing company
Identifying improvement opportunities can help your manufacturing industry enjoy significant benefits. Fingent can help you improve your business process and facilitate growth toward building an incredibly smart manufacturing plant.
Fingent is a custom software development company with vast experience in crafting remarkable digital success stories for diverse manufacturing companies across continents.
We will help you to stay abreast with what may affect your business and provide you with potential solutions available. To help plan for 2023 contact Fingent!
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Why Should Manufacturing Companies Leverage Odoo ERP?
As the manufacturing industry flourish, the need for a centralized control mechanism to ensure streamlined and effective operations is turning imperative. Processes like material sourcing, inventory, invoicing, purchase, order, accounts, and human resource management needs to be automated to make room for high-level practices and decisions. In such a scenario, how do you think Odoo ERP can help manufacturing companies accelerate efficiency and business success?
Odoo ERP can empower businesses with centralized management! From inventories to work orders, to customers and accounts, Odoo ERP enables streamlined management of the entire business processes, seamlessly. Leveraging Odoo ERP and using its open-source methodologies can enable manufacturing companies to derive the required speed, flexibility, and transparency to drive business growth and success.
Here at Fingent, we provide ERP solutions for various industries challenges including those of the manufacturing industry. But before we dive deeper into how Oddo ERP can simplify management for manufacturing companies, let’s take a look into the prevailing challenges of the industry.
Read more: Drive digital transformation in manufacturing
Challenges Faced By The Manufacturing Industry
From inventory to sales to the customer, the manufacturing industry deals with a huge amount of data, on a daily basis. As digitization is taking precedence, enterprises are looking for business models that are supported by intelligent systems. Therefore, companies must use an ERP system to manage their operations. Here are few challenges that organizations face without an ERP system in place.
- Forecasting demand – To avoid waste, spoilage or over/under production, businesses must gauge customer behavior and demands. As markets are becoming more volatile and unpredictable, it is becoming increasingly difficult to predict trends and plan production and distribution.
- Planning inventory – Inventory, if managed manually is bound to have errors that can cause inaccuracy of data, stock issues, and bad decisions, all of which can hinder returns. For the smooth functioning of a manufacturing company, data accuracy and consistency are important.
- Lack of skilled labor – To preserve the quality of services and reputation, manufacturing companies must hire and retain skilled workers. With fairly large applications and without a quick processing tool, HR may find it difficult to select suitable candidates.
- Minimizing costs and improving efficiency – One of the best ways to increase returns is to lower production costs while maintaining an efficient supply chain. However, this must not compromise quality. So, manufacturing plants need to automate their operations and management.
- Client Relationship Management(CRM) – Customer loyalty, though important does not come easy in today’s competitive business landscape. Businesses must invest in resources that help prioritize client data for current and potential customers and manage sales lead. A CRM will take into account the customer preferences and demands along with market trends.
Read more: Odoo Migration: Why Is It Crucial and How to Do It Seamlessly!
Top Features of Odoo ERP System
Manufacturing firms must implement customized software solutions with multiple functionalities that are tailored to the industry. Odoo is an open-source ERP software that acts as an effective business management tool with its robust functions. Here are a few highlighted features of Odoo ERP for manufacturing:
- Inventory Management
- Material Management
- Purchase Management
- Production Management
- Sales Management
- Quality Assurance
- Customer Relationship Management
- Accounting and Invoicing
- HR and Payroll Management
All these features can be customized based on your business needs.
In addition to the above features, Odoo ERP helps in automating the maintenance order for repairs and other preventive maintenance. It includes a scheduler functionality that uses statistical calculations to alert you in case of any failure.
Read more: 5 Salient Features of Odoo that Make it a Reliable ERP for Enterprises
6 Ways Manufacturing Industry Can Benefit From Odoo ERP
1. Automation
As digitization is gaining a lot of importance, companies must optimize workflows in the supply chain through automation. Processes such as inventory updates, payments and invoicing, tracking, distribution, and sales across different channels, even making decisions on high volume orders can be automated using Odoo.
Automation drives efficiency, productivity, accuracy, lowers operational costs, and ensures employee safety. All this helps in meeting the changing supply demands of a changing market.
2. Master Data Management
Odoo ERP comes with master data management capabilities that allow companies to incorporate business processes without duplication of data. The master data management ensures there is a consistent exchange of organizational data, eliminates redundancy, and simplifies business operations.
3.Quality Control
With Odoo ERP, companies can set quality checks for certain triggers. It can help schedule operations and even send maintenance requests automatically whenever needed.
The tool also allows enterprises to track different versions of a product(Product Lifecycle Management) and manage its routing accordingly.
4. Forecasting
Odoo ERP is equipped with analytical tools that locate patterns, observe huge datasets and forecast future trends, and enable manufacturing companies to create business strategies accordingly. These predictive capabilities allow companies to focus on production to meet customer demands and earn their loyalty.
Read more: How Odoo ERP Helps Leverage Business Intelligence and Data Analytics
5. Managing the workforce
Odoo’s HRM module automates the basic segregation process based on the required attributes for the post and enables better recruitment. It also includes training and development, capabilities and skills management, compensation records, and employee data.
Additionally, Odoo ERP comes with an employee scheduling feature that helps schedule and track tasks.
6. Returns
Odoo ERP helps businesses to maximize returns by improving operational efficiency, boost productivity and enhance customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
At Fingent, we maximize the potential of manufacturing companies with future-proof technologies. We develop ERP systems that integrate WFM, CRM, HRM, and accounting services for businesses of every size. For custom Odoo ERP development, talk to our experts.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
How Cloud ERP and ERP Systems Support The Manufacturing Industry?
The manufacturing industry has always been highly dynamic and competitive. However, the COVID-19 pandemic and the extension of lockdown restrictions weigh down on manufacturing companies across the globe, causing many to lose momentum. At the same time, customers who are always on-marketplace are expecting high-quality, individualized products delivered within shorter timeframes. To meet these requirements, manufacturers must synchronize their demand chain with the supply chain. The appeal of ERP systems (enterprise resource planning systems) for manufacturing in this scenario is evident. Here’s everything you need to know about ERP systems for manufacturing.
What is the importance of ERP systems for manufacturing?
ERP systems for manufacturing enable manufacturers to compile and maintain their business in an easy-to-scale model. According to G2 (a leading tech marketplace), 47% of ERP users belong to the manufacturing sector, and nearly 50% of companies are keen on acquiring or upgrading their ERP systems.
Fortune Business Insights reports that the global ERP software market size is estimated to reach USD 71.63 billion by 2026, at a CAGR of 8.5% during the forecast period (2019-2026). ERP systems for manufacturing encompass every function and streamline every business operation.
Though automation is not a new concept, the convergence of the digital world with the physical world has transformed the supply chain. In manufacturing, AI can be used to increase uptime and ensure consistent quality. AI and analytics aid in better forecasting, which in turn means better business and better returns.
Read more: Top 10 Technologies That Will Transform Manufacturing in 2021
Here are six reasons that emphasize the importance of ERP systems for manufacturing.
1. Reduces forecast anxiety
Most businesses worry about the next quarter. ERP systems for manufacturing help generate forecasts and sales reports based on historical transactions. This increases the accuracy and dependability of production and keeps stock levels in line with the increase and decrease in demand.
ERP systems can combine data, statistical algorithms, and predictive analytics to help businesses identify future outcomes based on the past. Predictive analytics can help you determine customer responses, forecast inventory, and even detect fraud. Improved supply chain visibility will help you set the level of preparedness required on the supply side to match demand. It can help you anticipate customer demand and stock goods to fulfill the orders.
Read more: 5 Reasons to Integrate Your E-commerce Application with Odoo ERP
2. Increased mobility and employee efficiency
With the lockdown measures tightening, working from home can be challenging for businesses. When the pandemic threw a curveball at companies, ERP systems for manufacturing have handed them a new strategy by enabling employees to work remotely and access all the relevant information they need from a single portal. They can access data through their laptops and computers and even from their phones and tablets, no matter where they are.
3. Flexibility
As each wave of the pandemic takes the world by surprise, manufacturing industries must ensure they are flexible to respond quickly to changing market trends. Such flexibility enables a business to be collaborative in meeting demands and promoting increased revenue and efficiency.
4. Increased profitability
Are you focusing on increased revenue in the next few months? As you are already aware, getting more work done at a lower cost automatically improves profits and encourages growth. ERP enables manufacturers to be alert to changes and react quickly to variations in raw material costs and delivery timeframes.
Cloud-based databases enable business leaders to process information quickly and equip them to make high-quality decisions rapidly. ERP systems for manufacturing increase organizational efficiency, eliminate unprofitable areas and cut down on waste. Moreover, ERP software dramatically reduces control and inventory management expenses.
Read more: How Organizations can Gain a Competitive Edge by Implementing Digital Core ERP
5. Enhanced security
Advancement in technology has made data available at our fingertips. Unfortunately, it has also made it readily available for hackers and criminals. The significance of data privacy and confidentiality has prompted most countries to have data protection laws in place, and compliance with those laws is non-negotiable. ERP systems for manufacturing have various features that enable your business to protect personal information. ERP system allows you to code your data and secure it by restricting the data through identity and access management.
6. Customer service
Every business must be concerned about customer acquisition and retention. ERP systems for manufacturing allow you to centralize and streamline your client information. This will help your sales team focus on building and maintaining customer relationships. End-to-end tracking and insights offered by ERP will help you provide better customer interaction. Since ERP supports e-commerce integration, businesses can handle web-based order processing and client interactions.
Read more: How Odoo ERP Simplifies Sales Management in Your Organization
Cloud ERP for manufacturing
Fear of misstep may prevent businesses from moving to the cloud, but outcomes prove that cloud-driven ERP is far more beneficial when compared to manual methods. Here are some benefits of cloud ERP:
- As each department has its own requirement, a customized ERP solution caters to operational and departmental needs.
- Cloud ERP allows your employees to access their data on the go. This aspect has been very crucial given the unprecedented circumstances brought in by the pandemic.
- Real-time data and reporting help in determining the future of your business and accelerates your decision-making process.
Read more: Top 6 Reasons Why You Should Move to a Cloud-Hosted ERP
Tried and tested ERP systems for manufacturing in 2021
Functionalities of ERP systems for manufacturing help organizations minimize production lead times and increase automation. Here are three tried and tested top ERP systems for 2021:
1. Odoo ERP system
Odoo manufacturing ERP software allows you to handle complex production workflows, product planning, order and inventory management, schedule management, warehouse management, bills of materials, purchase, PLM, maintenance, and quality.
Odoo ERP for manufacturing allows you to:
- Create a manufacturing order
- Configure work center
- Configure routing
- Configure bill of material
- Create scrap
- Product life cycle management
- Preventive and corrective maintenance management
As an Official Partner of Odoo, Fingent is primed to provide the best Odoo ERP consulting, implementation, and maintenance services for your business.
Read more: Why Choose Fingent as Your Odoo ERP Partner
2. SAP ERP system
SAP manufacturing software and Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) solutions enable manufacturing companies to accelerate time to market, gain new production efficiencies and lower costs.
SAP offers a wide range of software solutions for manufacturing companies, such as SAP S/4HANA Manufacturing solutions, SAP Manufacturing Execution, SAP Manufacturing Integration and Intelligence, SAP Digital Manufacturing Cloud, SAP Environment, Health and Safety Management, and so on.
SAP ERP system helps in two specific categories:
Manage inventory and bills of material:
- Handle bills of material and multi-level bills of materials
- Record, track and produce serial numbers for incoming and outgoing products
- Manage multiple units of measure
Manage the production process:
- Generate both assembly and disassembly work order
- Maintain records
- Generate finished goods.
Read more: https://testingweb.fingent.net/sap-erp-central-component-sap-ecc/
SAP ERP software offers digital manufacturing solutions to meet the demands in a challenging market. SAP’s solutions for the manufacturing industry include Digital Manufacturing Cloud solutions, Manufacturing Execution System (MES), Production planning & scheduling, and IIoT. Being an SAP Silver Partner, we help businesses leverage the full potential of their SAP ERP software.
Read more: SAP Business One vs. SAP Business ByDesign: Helping Businesses Pick the Best
3. MS Dynamics ERP system
Microsoft Dynamics 365 ERP system offers a holistic package of solutions for manufacturing companies that include ERP, CRM, BI, Analytics, and a horde of top-notch applications. You can easily manage your assets, supply chain operations, production and purchase orders, supply chain planning, bills of materials, and a wide variety of applications that enhance your business performance from the shop floor to the last-mile delivery.
Tools of MS dynamics can help you:
- Control financial management
- Deliver better customer service
- Collaborate across your virtual organization
Read more: ERP Software Selection: 5 Step Checklist for CFOs
Over to you
Manufacturing is the economy’s backbone. ERP is an excellent tool that gathers all information from every corner of the business and translates it into financial data and other valuable insights that help companies make strategic decisions in 2021. The potential of totally streamlined business functions makes the benefits of implementing ERP systems for manufacturing a worthwhile investment.
Over the past 17 years, we have been helping businesses solve challenges through technology. Unlock your business value with custom ERP solutions or ERP implementation, migration, upgrade and support. Give us a call!
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Manufacturing technologies set to hold the reins
From big data analytics to advanced robotics to computer vision in warehouses, manufacturing technologies bring unprecedented transformation. Many manufacturers are already leveraging sophisticated technologies for manufacturing such as the internet of things(IoT), 3D printing, Artificial Intelligence, etc., to improve operations’ speed, reduce human intervention, and minimize errors.
As 2024 rapidly approaches, manufacturers will have to move away from Industry 4.0 and embrace Industry 5.0. The latter is all about connecting humans and machines (smart systems). Interestingly, Industry 5.0 may already be here. The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic only accelerates its arrival.
Read more: Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
Here are the top 10 technologies that positively impact the manufacturing industry.
1. Robotics
With advances in robotics technology, robots are more likely to become cheaper, smarter, and more efficient. Robots can be used for numerous manufacturing roles and can help automate repetitive tasks, enhance accuracy, reduce errors, and help manufacturers focus on more productive areas.
Benefits of Using Robotics in Manufacturing:
- They improve efficiency right from handling raw material to finished product packing
- You can program robots to work 24/7, which is excellent for continuous production
- Robots and their equipment are highly flexible and can be customized to perform complex jobs
- They are highly cost-effective even for small manufacturing units
Collaborative assembly, painting, and sealing, inspection, welding, drilling, and fastening are a few examples of the jobs done by robots. Today, robots work in several industries, including rubber and plastic processing, semiconductor manufacturing, and research. While they are mainly used in high-volume production, robots make their presence felt in small to medium-sized organizations.
Read more: What Are Cobots and How Can They Benefit Industries?
2. Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology has grown to a great extent in the last few years. It involves the manipulation of nanoscopic materials and technology. Though its widespread use is relatively new, it will be indispensable to every manufacturing industry soon. Further research and experimental designs suggest that nanotechnology can be highly effective in the manufacturing industry.
Applications of Nanotechnology in Manufacturing:
- Create stable and effective lubricants that are useful in many industrial applications
- Car manufacturing
- Tire manufacturers are using polymer nanocomposites in high-end tires to improve their durability and make them wear resistance
- Nanomachines, though not used widely in manufacturing now, are, for the most part, future-tech
3. 3D Printing
Post its tremendous success in the product design field, 3D printing is set to take the manufacturing world by storm. The 3D printing industry was worth USD 13.7 billion in 2019 and is projected to reach USD 63.46 billion by 2025. Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D Printing is a production technology that is innovative, faster, and agile.
Benefits of Using 3D Printing in Manufacturing:
- Reduces design to production times significantly
- Offers greater flexibility in production
- Reduces manufacturing lead times drastically
- Simplifies production of individual and small-lot products from machine parts to prototypes
- Minimizes waste
- Highly cost-effective
Major car manufacturers use 3D printing to produce gear sticks and safety gloves.
Read more: 3D Printing: Fueling the Next Industrial Revolution
4. The Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT in manufacturing employs a network of sensors to collect essential production data and turn it into valuable insights that throw light into manufacturing operational efficiency using cloud software. This connectivity had brought machines and humans closer together than ever before and led to better communication, faster response times, and greater efficiency.
Benefits of Using IoT in Manufacturing
- Internet of Things (IoT) reduces operational costs and creates new sources of revenue
- Faster and more efficient manufacturing and supply chain operations ensure a shorter time-to-market. For instance, Harley- Davidson leveraged IoT in its manufacturing facility and managed to reduce the time taken to produce a motorbike from 21 hours to six hours.
- IoT facilitates mass customization by providing real-time data essential for forecasting, shop floor scheduling, and routing.
- When paired with wearable devices, IoT allows monitoring workers’ health and risky activities and making workplaces safer.
The ongoing pandemic has expanded the focus on IoT due to its predictive maintenance and remote monitoring capabilities. Social distancing makes it difficult for field service technicians to show up on short notices. IoT-enabled devices allow manufacturers to monitor equipment’s performance from a distance and identify any potential risks even before a malfunction occurs. Additionally, IoT has enabled technicians to understand a problem at hand and come up with solutions even before arriving at the job site so that they can get in and get out faster.
Read more: Upcoming IoT trends that can shape the business landscape
5. Cloud Computing
After making its presence felt in other industries, cloud computing is now causing ripples in manufacturing. From how a plant operates, integrating to supply chains, designing and making products to how your customers use the products, cloud computing is transforming virtually every facet of manufacturing. It is helping manufacturers reduce costs, innovate, and increase competitiveness.
IoT helps improve connectivity within a single plant, while cloud computing improves connectivity across various plants. It allows organizations across the globe to share data within seconds and reduce both costs and production times. The shared data also helps improve the product quality and reliability between plants.
Read more: Why It’s Time to Embrace Cloud and Mobility Trends To Recession-Proof Your Business?
6. Big Data
The manufacturing industry is complicated in terms of the variety and depth of the product. As far as opening new factories in new locations and transferring production to other countries is concerned, companies can leverage big data to tackle it.
As the process of capturing and storing data is changing, new standards in sharing, updating, transferring, searching, querying, visualizing, and information privacy are arising. Think of manufacturing software like MES, ERP, CMMS, manufacturing analytics, etc. When integrated with big data, these can help find patterns and solve any problems.
Benefits of Using Big Data:
- Improve manufacturing
- Ensure better quality assurance
- Customize product design
- Manage supply chain
- Identify any potential risk
Explore our use case: Adding New Dimensions to Equipment Maintenance with IIoT, AR, and Big Data
7. Augmented Reality
In manufacturing, we can use AR to identify unsafe working conditions, measure various changes, and even envision a finished product. Augmented Reality can help a worker view a piece of equipment and see its running temperature, revealing that it is hot and unsafe to touch with bare hands. An employee can know what’s happening around them, like what machinery is breaking down, a co-worker’s location, or even a factory’s restricted sites. Simply put, AR applications can help inexperienced employees to be informed, trained, and protected at all times without wasting significant resources.
AR has made it possible for technicians to provide remote assistance by sending customers AR and VR enabled devices and helping them with basic troubleshooting and repairs during the COVID-19 crisis. Also, more and more customers are open to allowing manufacturers to implement AR with the long-term goal of creating permanent solutions. After all, it helps both the customers and field technicians by reducing the risk of exposure.
Read more: How Augmented Reality Can Simplify Equipment Maintenance
8. 5G
5G will have a tremendous impact on the manufacturing industry. It will be more transformational for devices that drive automated industrial processes.
The amazing low-latency and connectivity of 5G will power sensors on industrial machines. It will help generate a lot of data that will open new avenues of cost savings and efficiency when combined with machine learning. Currently, China and South Korea are leveraging 5G this way. Soon the US and the UK are expected to compete with them.
Read more: From Remote Work to Virtual Work, 5G is Reinventing the Way We Work
9. Artificial Intelligence(AI)
Manufacturers are already employing automation on the plant floor and in the front office. In the future, AI-powered demand planning and forecasting will continue to develop that will help manufacturers align their supply chain with demand projections to get data that were not possible previously.
A study from IFS shows that 40% of manufacturers plan to implement AI for inventory planning and logistics and 36% for production scheduling and customer relationship management. 60% of the respondents are said to focus on productivity improvements with these investments.
Read more: The Future of Artificial Intelligence – A Game Changer for Industries
10. Cybersecurity
Moving manufacturing operations to the cloud and building and integrating systems using IoT will equally create opportunities and challenges. In an increasingly insecure digital era, there is a pressing need for heightened security.
Manufacturing experts are investing in secure cloud-based ERP like SAP and Odoo to resolve the security challenges. Enterprises-big or small- will soon increase their dependence on cloud-based ERP systems to address security glitches and save costs by paying for usage.
Read more: Top 6 Reasons Why You Should Move to a Cloud-Hosted ERP
White Paper: What difference does RPA bring to your business? How can you embrace this disruptive technology to remain competitive? Download to learn more!
Conclusion
Technologies for manufacturing will decrease labor costs, improve efficiency, and reduce waste, making future factories cheaper and more environment-friendly. Additionally, improved quality control will ensure superior products that will benefit both the consumers and the manufacturers.
COVID-19 has changed the way the manufacturing industry operates. If your business wants to remain competitive, you will have to embrace manufacturing technologies to shape your company’s future. To know more about the forward-thinking strategies that integrate the latest trends and technologies, please connect with us today.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
How is AI Transforming Various Industry Sectors?
From Siri to self-driving cars, Artificial Intelligence has been breaking into new realms, including industries that are late to adopt technology or that heavily rely on manual labor. Gartner predicts that by 2020, AI will produce more jobs than it displaces. By 2022, one in five workers engaged in mostly non-routine tasks will rely on AI to do a job.
The future of AI only looks bright!
According to experts, AI and the future of work will amplify human efficiency and productivity. AI may match or even surpass human intelligence and capabilities on tasks related to pattern recognition, complex decision making, sophisticated analytics, language translation, reasoning and learning, and speech recognition.
This article discusses how five major industries are benefiting from AI and its innovations.
1. Healthcare
No surprises here. AI in healthcare always comes first on the list. From doctors, surgeons, nurses to desk receptionists at clinics, Artificial Intelligence is enabling process automation across the healthcare community and ecosystem.
AI tools enable medical professionals to diagnose symptoms, identify trends, analyze data or information that would predispose a person to a particular disease.
AI-powered bots assist surgeons with heart, thoracic, and colorectal surgeries. Using bots for surgeries helps lower the risk of infection and blood loss, reduce pain, ensure higher accuracy, shorten hospital stays, and expedite recovery. Digitized health records (EHRs) help patients access their information on a shared online health portal.
Along with other technologies, Artificial Intelligence is being widely used in the ongoing fight against the COVID-19 pandemic. Remote patient monitoring using AI-powered medical equipment or devices help doctors maintain a safe distance from the patients, while offering treatment. The massive amounts of data generated every second in the field of medicine can be utilized effectively to continuously train AI systems through which these systems acquire the capabilities to generate insights that can aid medical researchers.
Read more: How Emerging Technology is Transforming the Healthcare Industry?
The future of AI in healthcare could include everything from answering the phone to interpreting radiology images, and designing therapeutic drugs.
2. Manufacturing
AI plays a key role in helping achieve better productivity, efficiency, and visibility across manufacturing operations. AI systems can transform the way organizations run their production lines, enhance human capabilities, garner real-time insights, and facilitate the design and product innovation.
Read more: Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
Following are some of the ways by which AI impacts the manufacturing sector:
- AI systems help monitor every stage of the production cycle and machine learning algorithms can be used to predict the fill rate, thereby optimizing the manufacturing processes and production planning.
- Small, lightweight “cobots” help create safer working environments. Manufacturers can adopt robotics to perform dangerous jobs, thus sparing their employees for crucial tasks, thereby avoiding occupational health hazards. Cobots are considerably less expensive and easy to program than the usual industrial robots. Soon, machine learning algorithms can improve their capabilities and help the cobots take instructions from humans and interact with them in a better way.
Read more: What Are Cobots and How Can They Benefit Industries?
- Predictive maintenance helps companies understand when machines need to be attended and serviced. Using machine learning, predictive maintenance can generate valuable data that helps prevent unplanned downtime. Sensors and advanced analytics in manufacturing equipment allow manufacturers to respond to alerts and resolve machine issues on time.
- Engineers or designers can input design goals and other parameters into generative design software (a program that generates several outputs to meet specific criteria) to explore better designs. Using machine learning, designers can learn from each iteration and understand what works and what does not.
3. Finance
According to a report by Business Insider Intelligence, about 75% of bank respondents with assets worth over $100 billion said that they are using AI technologies compared to the 46% of banks with assets less than $100 billion.
As much as $199 bn is saved for the front office and $217 bn for the middle office. AI technologies in banking can help generate over $250 billion in value. Considering the significant savings opportunities, more and more companies are implementing AI. Simply put, AI helps financial services companies mitigate risk, reduce overheads, and generate more revenue.
4. Education
Thanks to the numerous AI applications, the academic world is becoming more personalized. Today, a student can access study materials easily through computers and smart devices. AI helps automate administrative chores and minimizes the time required to complete complex tasks thereby allowing teachers to spend more time with each student.
Teachers can assess both multiple choice tests as well as written responses easily. Robots are helping create smart content such as video lectures and simulations as well as digitized textbooks that can be customized to the learning requirements. Along with the learning aids, these digitized interfaces help students of all academic ages and grades.
There is also a rising interest towards smart campus initiatives. A smart campus is a physical or digital set-up in which humans and technology- based systems come together to create and deliver automated experiences across higher education institutions.
AI is eliminating the boundaries of learning regardless of the physical locations. Today, students can learn any course from anywhere across the globe, at any time. AI-powered education helps nurture the fundamental IT skills of students and soon, there will be a wide range of highly interactive and personalized courses available online.
5. Retail
The retail and e-commerce industry has huge volumes of customer information, sales forecasting, stock and inventory to be tracked. Artificial Intelligence helps simplify data management to a large extent. For example, while searching for a product on an e-commerce application, AI recommends similar items according to your budget, color preference, purchase history, browsing data, online behavior, etc.
Cart abandonment is a common issue in the e-commerce industry which occurs when a customer adds items to their shopping cart but does not purchase them. With the help of chatbots and predictive analysts, the likelihood of cart abandonment can be reduced. Chatbots can remind your customer of the items left in their cart before they choose to navigate away.
Previously, people had to rely on the FAQ section of the website to get their questions answered. However, this included unchangeable questions and static answers and most customers were not satisfied with the answers. Today, however, it is changing. A chatbot agent can respond to questions using Natural Language Processing or NLP in a much better way and ensure that potential customers don’t abandon your website. Integrating voice search features into e-commerce applications helps offer a seamless digital customer experience.
Read more: How Will Artificial Intelligence Transform The World By 2030
Final Thoughts
Artificial Intelligence and machine learning together are promising to help transform every industry by guiding, organizing, and automating work. AI is definitely here to stay! At Fingent top custom software development company, we have the expertise to help businesses of all sizes including startups as well as established enterprises to gain an edge over competitors.
From suggesting products or providing basic customer service or running software tests, developing apps, and completing extensive problem-solving procedures for industries, we use AI technologies such as machine learning, natural language processing, and business rules that will provide you with optimal results. Get in touch with us to learn more.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
Evolution Of The Digital Twin Technology
What is a digital twin? Digital Twins can be best defined as digital copies or virtual replicas of physical assets. Data scientists can make use of digital twins to try and run simulations before they build and deploy actual devices. Digital Twin technology transforms the way in which the Internet of Things, Artificial Intelligence, as well as, Data Analytics is optimized.
The concept of ‘digital twin’ rewinds back to the year 1970 with the launch of Apollo 13. NASA’s digital twin model of Apollo 13 was a famous rescue mission to assess space monitoring conditions. The concept of Digital Twins later gained recognition in 2002 at the onset of a presentation by Challenge Advisory at the University of Michigan. According to Gartner, the digital twin is one of the top 10 strategic technology trends since 2017. Gartner estimates 21 billion connected sensors and endpoints by the end of the year 2020!
Related Reading: Checkout in detail, where and why should you invest in IoT.
Digital Twins: Enhancing IoT Enabled Industries
Data scientists build digital twins that can receive input from sensors that collect data from its real-world counterpart. The twin is then allowed to simulate in real-time. This process provides critical insights and feedback that helps in analyzing the actual system’s performance. For instance, a twin car can be built digitally by validating various inputs to check on factors such as safety, mileage, etc.
Digital Twins impact various IoT-enabled environments such as manufacturing, automotive, healthcare, financial services, urban planning and many more. The major IoT-enabled industries that can leverage the benefits of digital twin technology and how they benefit from it are as follows:
- Manufacturing Industry: The Digital Twin concept with the IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) is implemented in the manufacturing domain. It can be designed and deployed in numerous ways such as in tracking and monitoring systems, evaluating production, troubleshooting equipment used, etc. As digital twins can predict failure chances, it helps in saving costs, time and in improving customer loyalty.
- Automotive Industry: The future of autonomous vehicles lies on well-connected road systems and vehicles. Critical data gathered from this network. The digital twins then act as simulated models that help engineers analyze the behavior of vehicles before they are used on roads.
- Healthcare: Medical monitoring technology is used to gather critical data such as heart rate, oxygen levels, etc. This data is used in the creation of digital simulations. Digital twins help the healthcare ecosystem in disease diagnosis, remote monitoring of patients, etc.
- Urban Planning Sectors: Vital data such as maps, blueprints of buildings, real-time data from sensors, etc are used to create digital twin models to improve urban planning services. These services include waste disposal, mobility services, providing resources like electricity and water, etc.
- Asset Management: Both worksite and remote industrial operations can be managed via digital twins with the help of remote asset monitoring services. Predictive maintenance of assets like machinery improves operational efficiencies and decreases disruption of business operations. Digital twins can also be converged with augmented and virtual reality techniques for better visualization of industrial workflows.
- Financial Services: Customer behavior can be easily monitored with digital twin technology. It helps in creating personalized profiles for individuals via data analysis of their previous behavior in buying decisions etc. It can also simulate cash flows and balance sheets. Client needs can be analyzed better by insurance firms and asset managers and can thus provide personalized experiences for their customers.
Digital Twin Technology: Fostering Innovation In IoT-Enabled Environments
According to Gartner digital twin will be used by 50 percent of the industries in 2021. This will result in a 10% improvement in operational efficiency in these IoT-enabled organizations. The digital twin technology is the most important Industry 4.0 technology that is available today.
It helps in automating decision-making processes, providing critical insights into dynamic recalibration of products and other equipment in the industries, monitoring the manufacturing processes and production lines, etc.
The digital twin technology helps in monitoring manufacturing components, assets, and critical processes in real-time. Also, it helps in improving OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness), increasing product quality, enhancing traceability, reducing wastage and boosting overall efficiency.
Main Data Elements in Digital Twin Technology: Key Benefits For Improved Innovation
There are three main elements in digital twins such as Past, Present and Future Data that improve efficiency in IoT-enabled industries. The past data is the data from the previous performance of individual machines etc. Present data is the real-time data from sensors, whereas the future data is the data received from machine learning algorithms and various inputs from engineers.
The key benefits of Digital Twin IoT enabled industries are as follows:
-
Automated Insights
It is important for an IoT-enabled environment to understand the relationship between different types of data within its network. This IoT data can be extracted and enhanced in the form of knowledge graphs. This helps in automating processes and improving decision-making.
-
Increased ROI Generation
A decline in revenue is mainly due to the downtime of machines. The digital twin technology can reduce downtimes, prevent failures, and increase the life-span of machines. This not only improves productivity but also brings down the operational costs significantly and improves revenue generation.
-
Predicting Failures
Digital twins provide a platform that enables IoT-enabled industries to be prompted constantly about production, operation and management activities. The virtual testing platform that it provides, simulate the real-world data into critical and meaningful insights. In addition to being a scalable solution, it also self-diagnoses problems. This makes it easy for industries to make human-machine interaction efficient and productive.
-
Digitizing The Whole Industry Ecosystem
There is a rapid adoption rate of digitizing operations by industries day-to-day in order to achieve positive business outcomes. This is made possible with the steady data flow from the environmental and operational sectors of the IoT-enabled industries.
This up-to-date and personalized data maximize profitability and productivity. In addition to being a high revenue opportunity, the digital twin technology also digitizes the working assets and processes in its entirety.
In a nutshell, the benefits that can be leveraged from digital twin technology for IoT-enabled industries are as follows:
- Reliable operations and management of equipment and production lines
- Increased Overall Equipment Effectiveness or OEE achieved via reduced downtime.
- Increased ability of customers to remotely configure products.
- Significantly reduced maintenance costs due to preventive measures taken that aid in finding out chances of failures or machine breakdown, etc.
- Improved production cycles leading to reduced downtimes.
- Better productivity
- Considerably reduced risks in areas of product availability, product failures, services, maintenance, etc.
- Provides critical insights of past, present and future data in real-time environments.
The globe is yet to witness over 50 billion connected devices by the time period of 2020-2030 and over 7 billion customers using the web worldwide.
For an immersive experience on how to transform your IoT-enabled industry or business with the Digital Twin technology, call us right away. We will help you gather brilliant strategies on fostering innovation with specific digital twin models!
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new



Talk To Our Experts
With the Industrial Internet, Industry 4.0, industrial robots and more, the manufacturing sector is seeing sweeping reforms in their processes and core functions. These reforms are making them faster, bigger and better and all of this has been possible because of digital transformation.
Digital transformation has changed the face of the manufacturing industry. From behemoth machinery and an army of workers, manufacturers have transformed themselves to a sleek, modern and more efficient entity. This blog will explore how digital transformation has made that possible. We will also see the most important digital trends in the manufacturing industry.
The Importance of Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
Change has been constant in the manufacturing industry. Right from the Industrial Revolution of the 1700s to today’s Industry 4.0, the manufacturing sector has had to adapt to the changes in political climates, economic upheavals, and technology. As technology fast forwards in our times, it is imperative that manufacturers keep up. The only way they can prepare their businesses for the digital revolution of our day is through digital transformation. Here are a few ways in which digital transformation is benefitting the manufacturing industry.
1. Keeping up with Customer Demands
A recent Harvard Business Review study of 75,000 people, showed that the most important factor in building customer loyalty towards an organization is the reduction of effort. Be it in collecting information on products, customer service or getting their needs met faster and more effectively, customers value the path of least effort. This is where the speed of innovation comes in. Manufacturers need to create products that are software-enabled and connected, and they must do this before anybody else!
A digital factory design where development, production, and other cycles aren’t siloed is imperative to this. Digitalization makes it possible for all these cycles to work in tandem and innovate much faster. The vision of a “smart factory” is that it can make critical product decisions about customer demand, design, material selection, scheduling and pricing, all in one process. This would speed up innovation, create personalized products and enhance the overall customer experience exponentially.
2. Refining Processes
Manufacturing is largely a process-driven industry, so there is an incredible amount of focus on process refinement. Digital transformation makes this possible in many ways. Automation of processes is a major step in that direction. This reduces manual errors, helps automatically detect production inefficiencies, allows for the pre-testing of new ideas more economically and helps optimize the performance of workers.
Predictive disruption analytics, KPI monitoring, and other digitally enabled tools help in refining processes as they are happening. This allows manufacturers to identify weaknesses and make improvements quickly. Machine Learning enables instructions and intelligence to be built into the machines as they are developed and deployed. As these machines are intuitive, they learn from the environment and aid in the continuous process refinement.
3. Revenue Gains and Cost Reduction
A PwC survey of over 2,000 participants from companies in nine major industrial sectors and 26 countries, predicts that Industry 4.0 will drive $493B in revenue gains and $ 421B in cost reductions globally by 2020.
These numbers are realized by the many opportunities brought in by digital transformation. The digitization and integration of vertical and horizontal value chains help bring a cohesive focus to the organization’s processes and production. The creation of new digitized products with analytical capabilities and integrating new methods of data collection and analysis helps manufacturers understand and cater to the needs of customers more effectively. Disruptive digital business models allow for a more agile approach throughout the organization and thus optimizes performance and cost. All this and more contribute to significant cost reductions and an increase in revenue.
Digital Transformation Trends in Manufacturing
Different technologies have opened up a wide area of possibilities in the manufacturing industry. Here are 3 Trends that are doing wonders in the manufacturing space.
1. IoT And Industry 4.0
61% of enterprises say that the “Internet of Things (IoT) plays a role in their digital business strategies with manufacturing and high-tech leading all other industries.” The manufacturing industry is evidently recognizing the critical impact of IoT in gaining a competitive edge. In 2016 alone, IoT, accounting for more than $178 billion in revenue. There are many avenues where IoT has helped streamline and simplify manufacturing processes. It is also a key component of Industry 4.0 and enables connected devices. This allows for the streamlining of internal operations and the optimization of products and operations through insights from the cloud.
Industry 4.0 has also made possible the trend of mass customization, which is characterized by a better and more effective response to the demands of customers. Connectedness and mobility have led to faster innovation and response. Logistics and supply chains have also benefited greatly from this connectedness.
Related Reading: Find how IoT is reshaping industries.
2. Machine Learning
Machine Learning has elevated the processes and operations of the manufacturing industry in many ways. A PwC study entitled Digital Factories 2020: Shaping the future of manufacturing showed that the adoption of machine learning and analytics by manufacturers to improve predictive maintenance is predicted to increase in the next five years by 38%. Advanced machine learning algorithms are able to identify and implement improvements in processes and operations, thus leading to reduced costs and increased revenue.
A study by The World Economic Forum (WEF) discussed how manufacturers are recognizing the ability to combine emerging technologies including IoT, AI, and machine learning to improve asset tracking accuracy, supply chain visibility, and inventory optimization. Thus, in various ways, Machine Learning is greatly contributing to lowering the cost of production, improving the speed of innovation and operations and enhancing the customer experience by accurately identifying and meeting customer demands.
Related Reading: Check out this infographic to learn more on the disruptive innovation: Machine Learning.
3. Advanced Robotics
Robotics is no more confined to the realms of accomplishing repetitive assembly line tasks. Robots are now intuitive, trainable and have the ability to mimic human attributes of dexterity and critical thinking. This makes them a formidable force in manufacturing.
Robots with advanced sensors and collaborative ability are now being deployed in hazardous environments to collect information and data pertinent to the manufacturing industry’s needs. This contributes greatly to providing safe working environments for humans. Apart from the physical robotic machines, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has also grown in importance. RPA goes a step above and beyond physical tasks and replicates human thinking ability and transforms processes and operations to the next level. Recently, the term ‘cobot’ was coined by professors at Northwestern University in America. This underlines the significant progress in Robotic Process Automation (RPA) where robots are now able to collaborate with humans in the workspace.
Related Reading: Read on to know how robotic process can help accelerate business growth.
Owning Digital Transformation
There can be no doubt that digital transformation is the way to go if manufacturers want to keep up with competition and stay relevant. Capitalizing on these digital trends for your business need not be a daunting task. At Fingent, we help manufacturers make sense of digital transformation and adopt it successfully. We can help you make a success of your digital transformation. Get in touch with us and see how.
Stay up to date on what's new

Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new